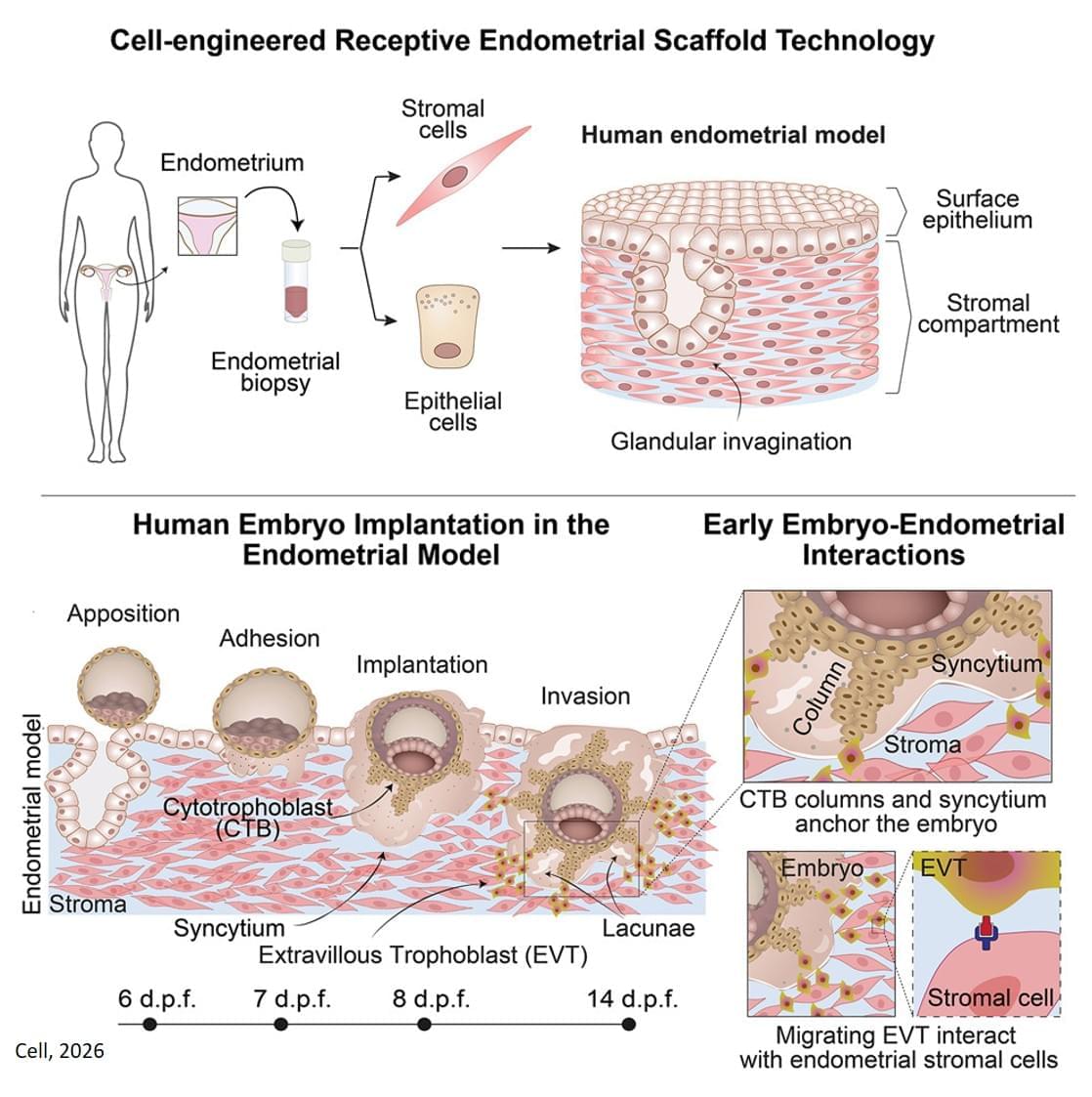
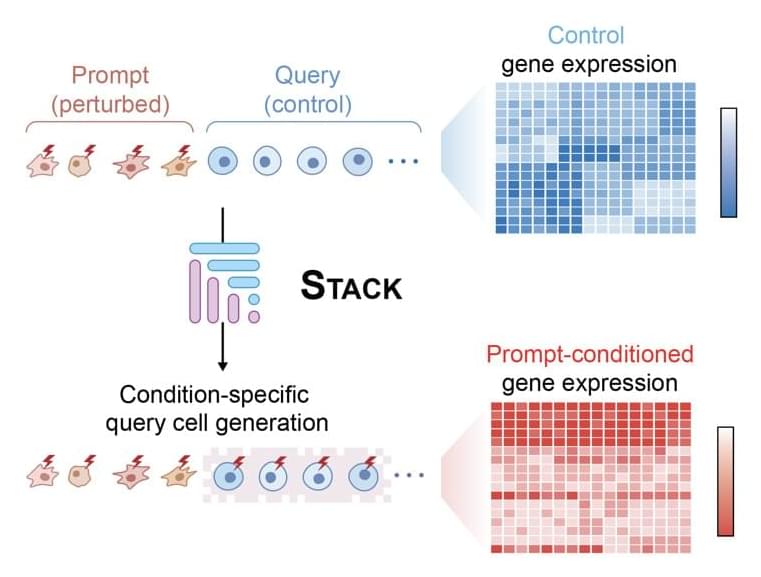
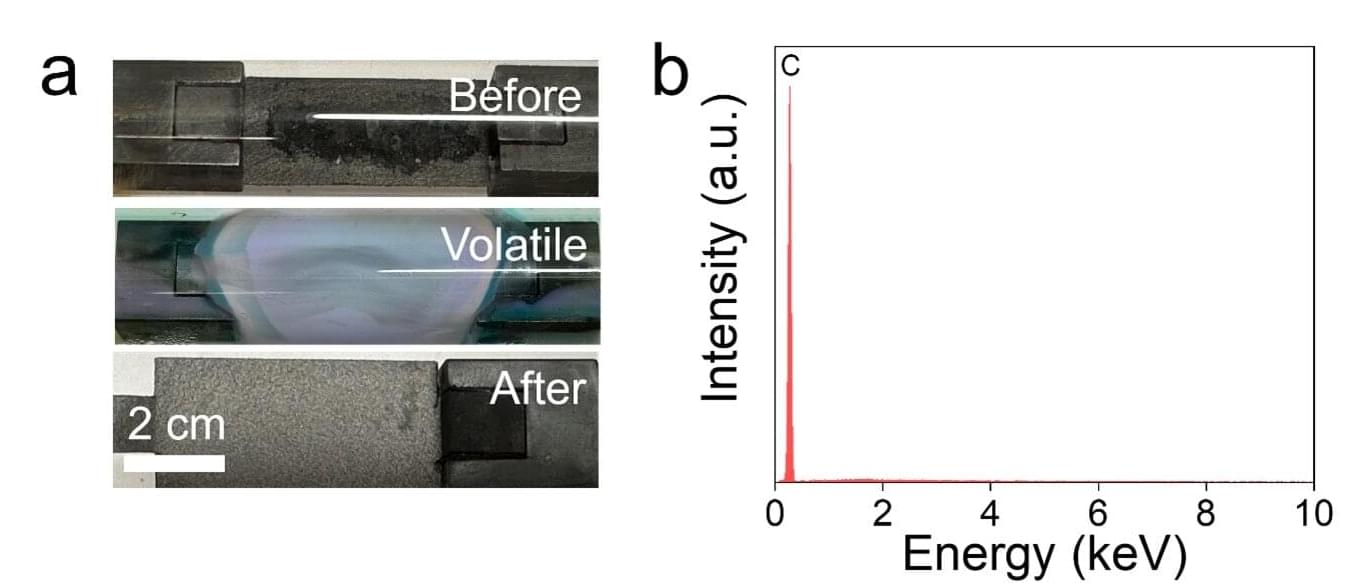
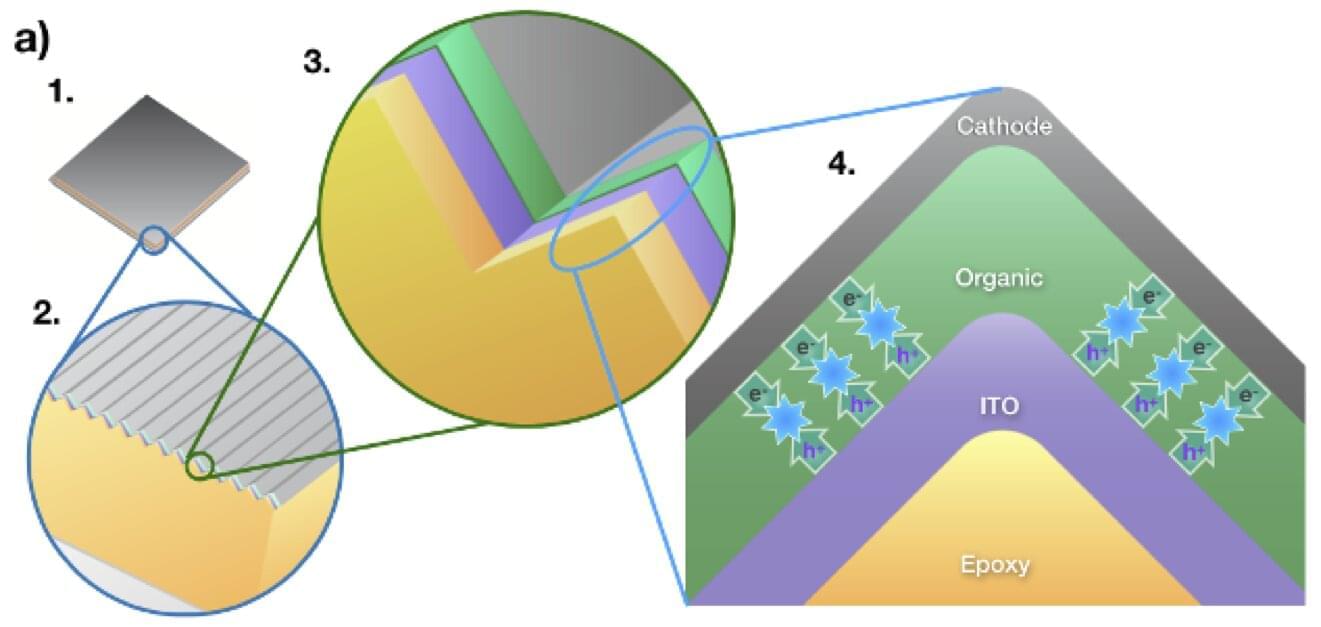
How Plasma Control Will Make Fusion Power Possible — Dr. Marco De Baar Ph.D. — Dutch Institute for Fundamental Energy Research (DIFFER) / TU Eindhoven.
Dr. Marco de Baar, Ph.D. is a full professor and Chair of Plasma Fusion Operation and Control at the Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e — https://www.tue.nl/en/research/resear…
In addition to his work at TU/e, Dr. de Baar is also head of fusion research at the Dutch Institute for Fundamental Energy Research (DIFFER — https://www.differ.nl/) located on the TU/e campus. As member of DIFFER’s management team, he has also served as the Dutch representative in the European fusion research consortium EUROfusion (https://euro-fusion.org/).
From 2004 to 2007, Dr. de Baar headed the operations department at JET (Joint European Torus), Europe’s largest fusion experiment to date, where he was responsible for the successful operation and development of the reactor. From 2007, he was deputy project leader in the international consortium that develops the upper port launcher. He is program-leader for the Magnetohydrodynamics stabilization work package in ITER-NL (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor — https://www.iter.org/).
Dr. de Baar’s main scientific interest is the control of nuclear fusion plasmas, with a focus on control of Magnetohydrodynamics modes (for plasma stability) and current density profile (for performance optimization). In his research program, all elements of the control loops are considered, including actuator and sensor design, and advanced control oriented modelling. He also has a keen interest in the operations and the remote maintainability of nuclear fusion reactors.