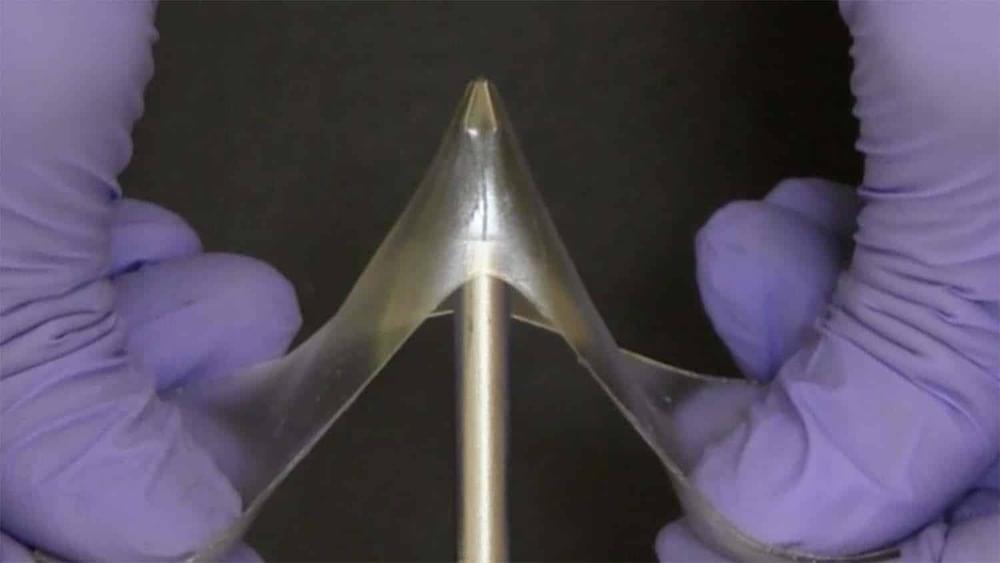
Researchers have created a new class of materials called “glassy gels” that are very hard and difficult to break despite containing more than 50% liquid. Coupled with the fact that glassy gels are simple to produce, the material holds promise for a variety of applications.
Gels and glassy polymers are classes of materials that have historically been viewed as distinct from one another. Glassy polymers are hard, stiff and often brittle. They’re used to make things like water bottles or airplane windows. Gels – such as contact lenses – contain liquid and are soft and stretchy.
“We’ve created a class of materials that we’ve termed glassy gels, which are as hard as glassy polymers, but – if you apply enough force – can stretch up to five times their original length, rather than breaking,” says Michael Dickey, corresponding author of a paper on the work and the Camille and Henry Dreyfus Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at North Carolina State University. “What’s more, once the material has been stretched, you can get it to return to its original shape by applying heat. In addition, the surface of the glassy gels is highly adhesive, which is unusual for hard materials.”