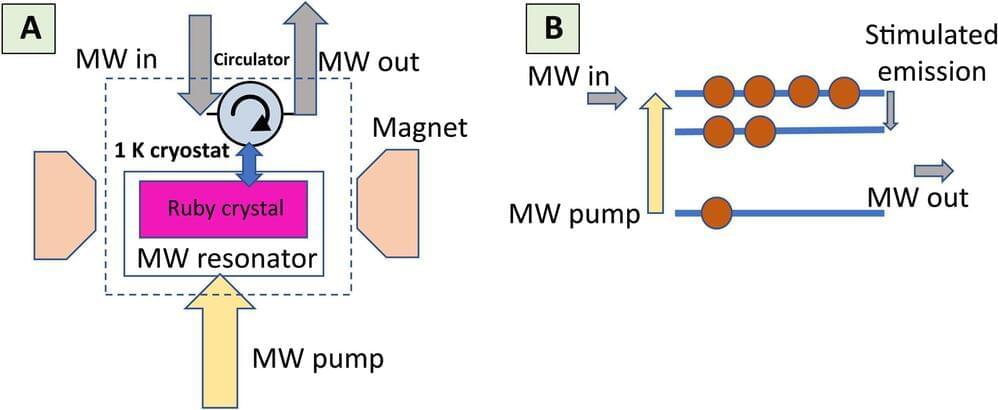
In physics, weak microwave signals can be amplified with minimal added noise. For instance, artificial quantum systems based on superconducting circuits can amplify and detect single microwave patterns, although at millikelvin temperatures. Researchers can use natural quantum systems for low-noise microwave amplification via stimulated emission effects; however, they generate a higher noise at functionalities greater than 1 Kelvin.
In this new work, published in the journal Science Advances, Alexander Sherman and a team of scientists in chemistry at the Technical-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, used electron spins in diamond as a quantum microwave amplifier to function with quantum-limited internal noise above liquid nitrogen temperatures. The team reported details of the amplifier’s design, gain, bandwidth, saturation power and noise to facilitate hitherto unavailable applications in quantum science, engineering and physics.