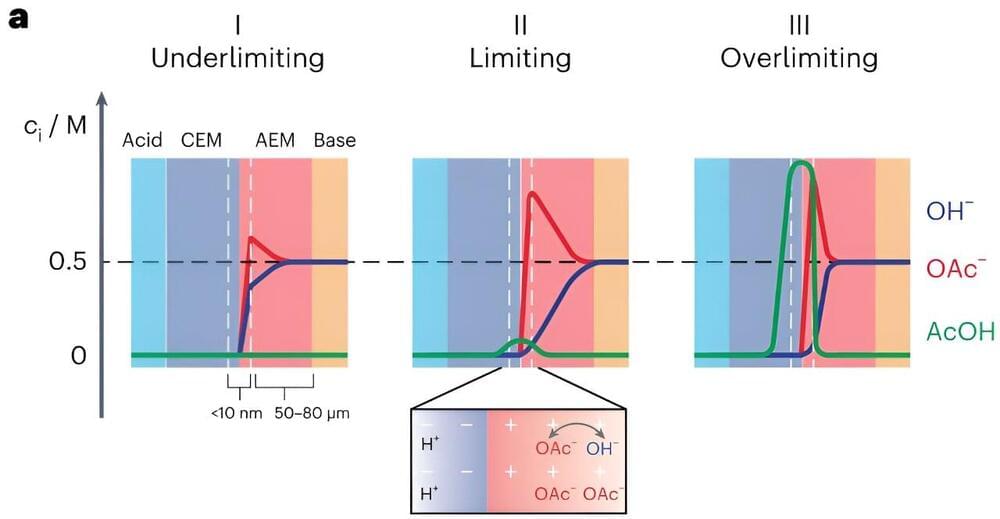
Bipolar membranes (BPMs) are a class of ion-exchange membranes typically comprising a cation-and an anion-exchange layer. While these membranes have recently been integrated in various electrochemical devices for a wide range of application, the processes underlying their operation are not yet fully understood.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently developed a new mechanistic model that explains the forward bias polarization mechanisms of BPMs in mixed electrolytes with varying acidities and basicities. Their model, introduced in Nature Energy, could guide the development of strategies to overcome the issue of ionic blockades, which can adversely impact the performance of forward bias BPM devices.
“We were initially trying to design an electrolyzer that converts carbon dioxide CO2 into useful feedstocks or fuels using bipolar membranes (BPMs),” Yogesh Surendranath, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore. “To provide a little context, CO2 electrolyzers are most efficient when operating with alkaline electrolyte solutions such as potassium hydroxide, but because CO2 is an acid gas, it reacts with alkaline solutions to produce carbonate solutions over time.”