Mars has to have its own internet because no one’s going to wait 20 minutes for a download.


Elon Musk’s multibillion-dollar Mars rocket explained.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging field of computer programming that is already changing the way we interact online and in real life, but the term ‘intelligence’ has been poorly defined. Rather than focusing on smarts, researchers should be looking at the implications and viability of artificial consciousness as that’s the real driver behind intelligent decisions.
Consciousness rather than intelligence should be the true measure of AI. At the moment, despite all our efforts, there’s none.
Significant advances have been made in the field of AI over the past decade, in particular with machine learning, but artificial intelligence itself remains elusive. Instead, what we have is artificial serfs—computers with the ability to trawl through billions of interactions and arrive at conclusions, exposing trends and providing recommendations, but they’re blind to any real intelligence. What’s needed is artificial awareness.





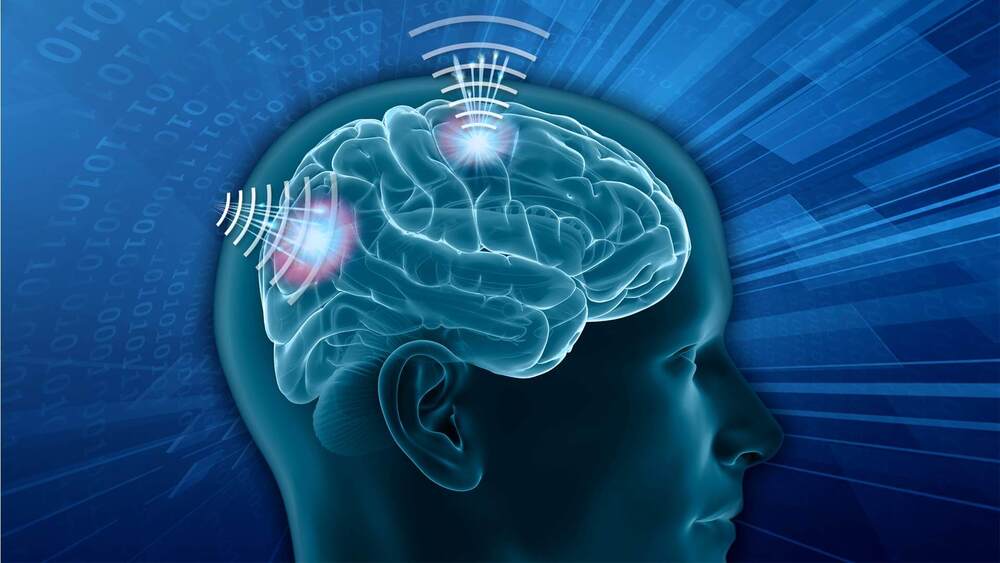
When Elon Musk and DARPA both hop aboard the cyborg hypetrain, you know brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) are about to achieve the impossible.
BMIs, already the stuff of science fiction, facilitate crosstalk between biological wetware with external computers, turning human users into literal cyborgs. Yet mind-controlled robotic arms, microelectrode “nerve patches”, or “memory Band-AIDS” are still purely experimental medical treatments for those with nervous system impairments.
With the Next-Generation Nonsurgical Neurotechnology (N3) program, DARPA is looking to expand BMIs to the military. This month, the project tapped six academic teams to engineer radically different BMIs to hook up machines to the brains of able-bodied soldiers. The goal is to ditch surgery altogether—while minimizing any biological interventions—to link up brain and machine.

Elon Musk’s appearance at Tesla owner-enthusiast Ryan McCaffrey’s Ride the Lightning podcast revealed a number of new details about the electric car maker’s upcoming halo vehicle, the next-generation Roadster. While addressing the all-electric supercar, Musk discussed the vehicle’s estimated yearly production numbers, its purpose, and some details about its “SpaceX package.”
Ever the candid interviewee, Musk admitted that the next-generation Roadster is really more like a dessert to the Model S, 3, X, and Y’s main course, in the way that its existence will probably not provide much of an impact to Tesla’s overall mission of accelerating the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Nevertheless, the Roadster still has a lot of merits, in the way that it could establish the superiority of pure electric propulsion compared to the internal combustion engine, bar none.
Musk noted that the Roadster is intended to outperform the best “Ferraris, Lamborghinis, and McLarens” on every dimension, on every level, including the track, thereby erasing the halo effect of gas cars. “We’re going to do things with the new Roadster that are kind of unfair to other cars. (It’s) crushingly good relative to the next best gasoline sports car,” Musk said.