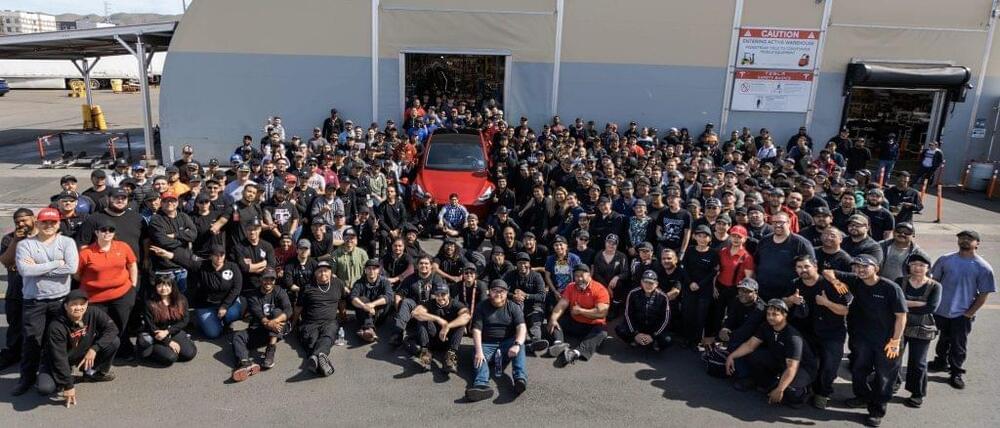
Elon Musk recently shared a rather interesting update on Twitter — his companies now employ about 110,000 people worldwide. This is quite impressive considering that in the grand scheme of things, Tesla, SpaceX, and Musk’s other ventures are still just getting started.
Musk’s update came as a response to a TSLA bull on Twitter who inquired if his companies had already reached the 100,000-employee milestone. Musk’s response revealed that his companies had not only met their 100,000 employee mark — they had already passed it.
Elon Musk did not share further details about his companies’ worldwide employee headcount, though there is a good chance that the lion’s share of his workers today are in the United States and China. These are the two countries where Tesla, one of Musk’s largest companies, has operational vehicle production plants, after all.