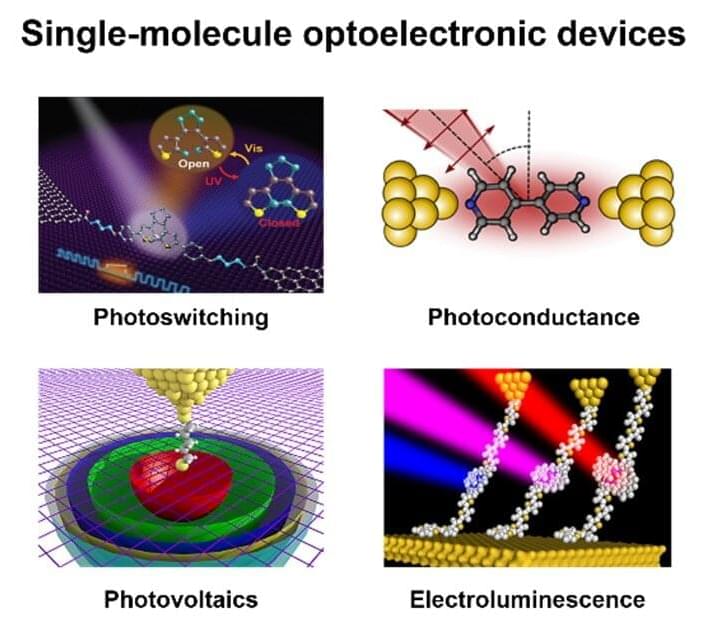
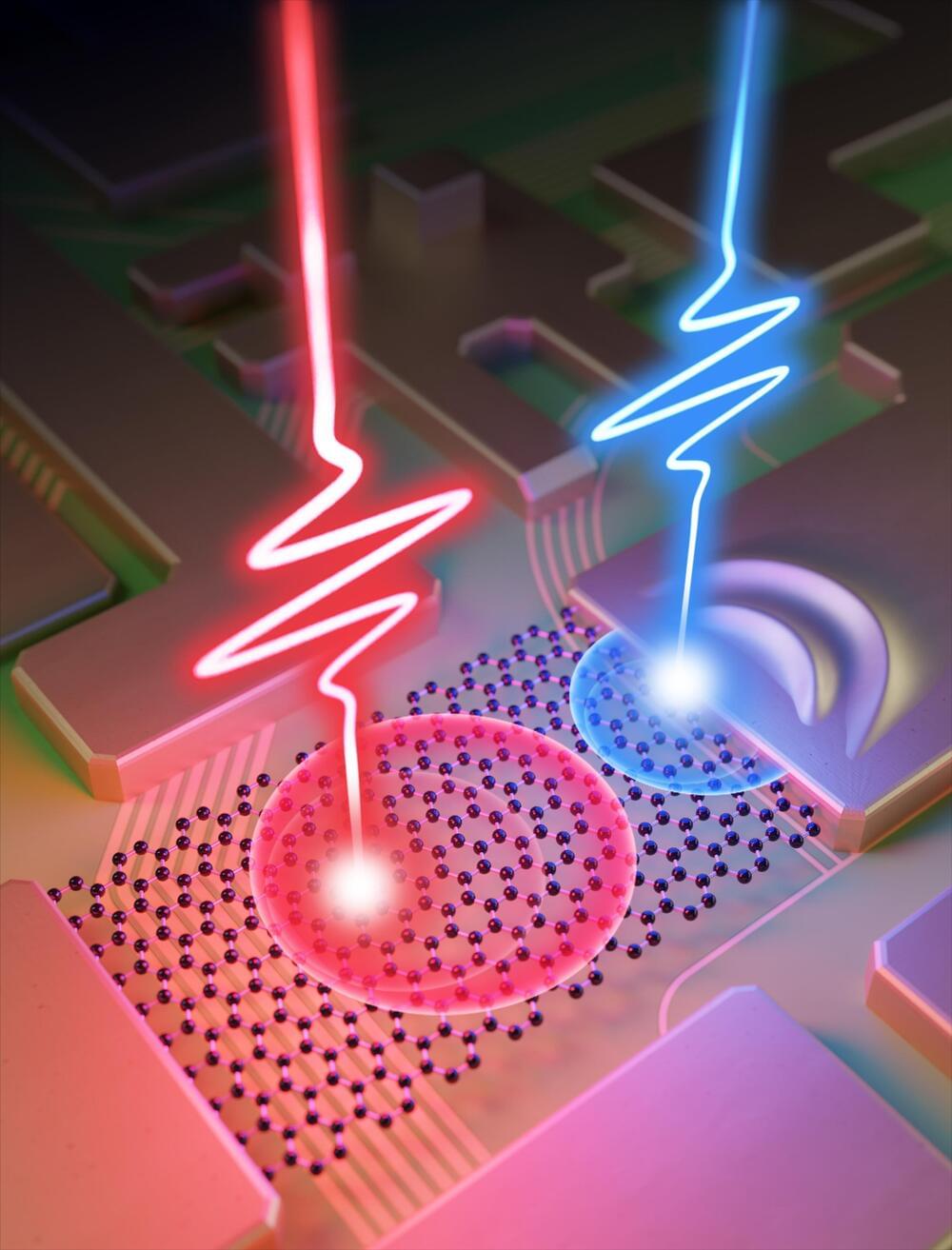
Single-molecule electronic devices, which use single molecules or molecular monolayers as their conductive channels, offer a new strategy to resolve the miniaturization and functionalization bottlenecks encountered by traditional semiconductor electronic devices. These devices have many inherent advantages, including adjustable electronic characteristics, ease of availability, functional diversity and so on.
To date, single-molecule devices with a variety of functions have been realized, including diodes, field-effect devices and optoelectronic devices. In addition to their important applications in the field of functional devices, single-molecule devices also provide a unique platform to explore the intrinsic properties of matters at the single-molecule level.
Regulating the electrical properties of single-molecule devices is still a key step to further advance the development of molecular electronics. To effectively adjust the molecular properties of the device, it is necessary to clarify the interactions between electron transport in single-molecule devices and external fields, such as external temperature, magnetic field, electric field, and light field. Among these fields, the use of light to adjust the electronic properties of single-molecule devices is one of the most important fields, known as “single-molecule optoelectronics.”