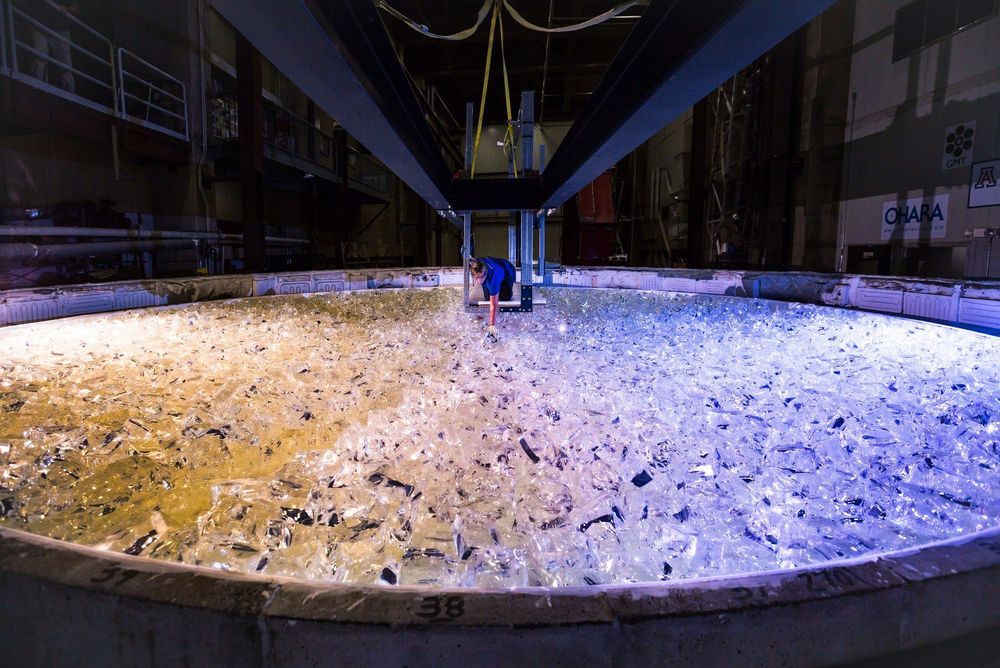
It’s easy to miss the mirror forge at the University of Arizona. While sizable, the Richard F. Caris Mirror Laboratory sits in the shadow of the university’s much larger 56,000-seat football stadium. Even its most distinctive feature—an octagonal concrete prominence emblazoned with the school’s logo—looks like an architectural feature for the arena next door. But it’s that tower that houses some of the facility’s most critical equipment.
Inside the lab, a narrow, fluorescent-green staircase spirals up five floors to the tower’s entrance. I’m a few steps from the top when lab manager Stuart Weinberger asks, for the third time, whether I have removed everything from my pockets.
“Glasses, keys, pens. Anything that could fall and damage the mirror,” he says. Weinberger has agreed to escort me to the top of the tower and onto a catwalk some 80 feet above a mirror 27.5 feet in diameter. A mirror that has already taken nearly six years—and $20 million—to make. “Most people in the lab aren’t even allowed up here,” he says. That explains Weinberger’s nervousness about the contents of my pockets (which are really, truly empty), and why he has tethered my camera to my wrist with a short line of paracord.