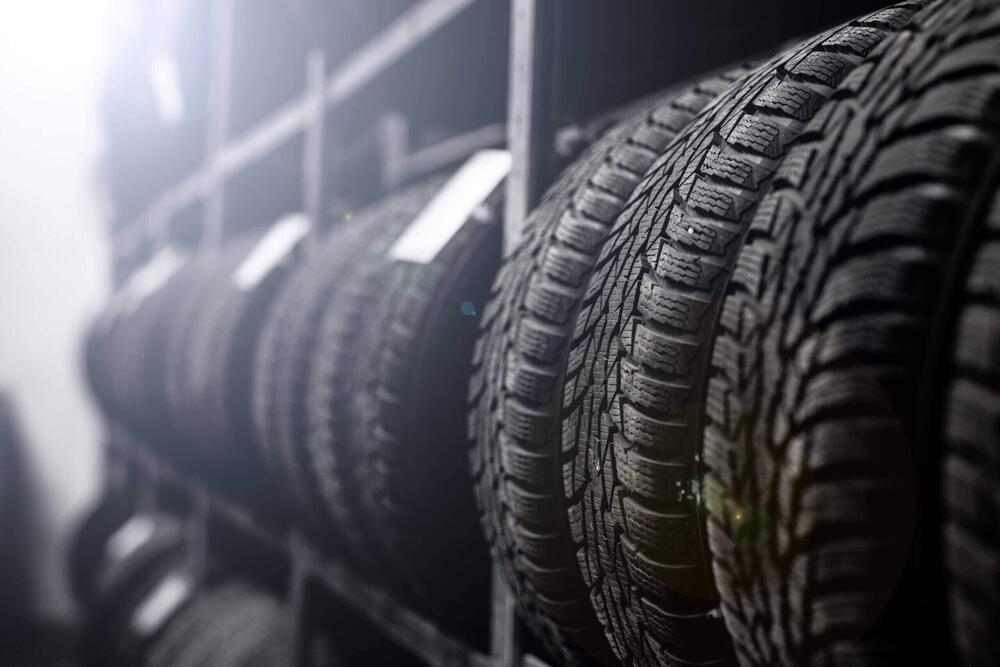
Canada-based Tyromer is building a pilot factory in Arnhem to bring its circular rubber products to the European market. Specializing in the devulcanization of rubber from scrap tires, Tyromer will fine-tune and exhibit its recycling technology at its new Dutch facility in order to sell the process to third parties. The company is one of the first in the Netherlands to give this hard-to-process residual product a high-quality new life, making it a valuable addition to the Dutch circular economy.
Located at Kleefse Waard Industrial Park (IPKW) in Arnhem, the factory is currently being set up. “We expect to be able to start early in the summer [of 2021],” said Jos van Son, managing director of Tyromer Europe. Tyromer will employ approximately 12 people in Arnhem.
“Tyromer has a unique solution to a major problem: mountains of car tire rubber that cannot be reused. Companies such as Tyromer, which have solutions for societal challenges with smart technologies, are a welcome addition to the East Netherlands ecosystem. The fact that Tyromer is establishing itself at IPKW, where many companies are involved with energy and circularity issues, is good news for the activity in our region,” added René Brama, investment manager of Tech at Oost NL.