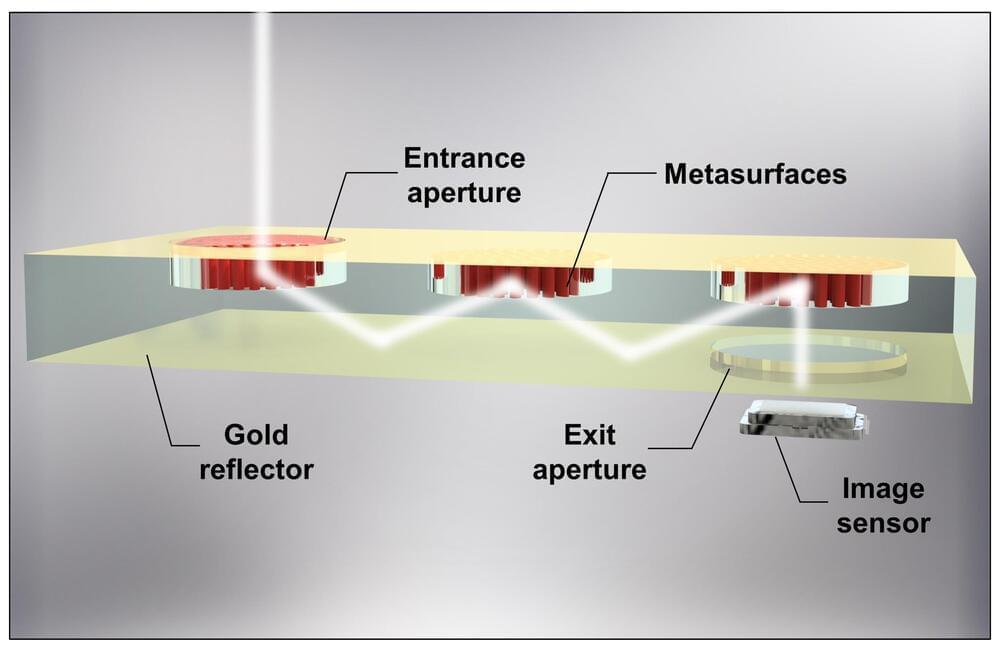
Researchers from Seoul National University College of Engineering announced they have developed an optical design technology that dramatically reduces the volume of cameras with a folded lens system utilizing “metasurfaces,” a next-generation nano-optical device.
By arranging metasurfaces on the glass substrate so that light can be reflected and moved around in the glass substrate in a folded manner, the researchers have realized a lens system with a thickness of 0.7mm, which is much thinner than existing refractive lens systems. The research was published on Oct. 30 in the journal Science Advances.
Traditional cameras are designed to stack multiple glass lenses to refract light when capturing images. While this structure provided excellent high-quality images, the thickness of each lens and the wide spacing between lenses increased the overall bulk of the camera, making it difficult to apply to devices that require ultra-compact cameras, such as virtual and augmented reality (VR-AR) devices, smartphones, endoscopes, drones, and more.