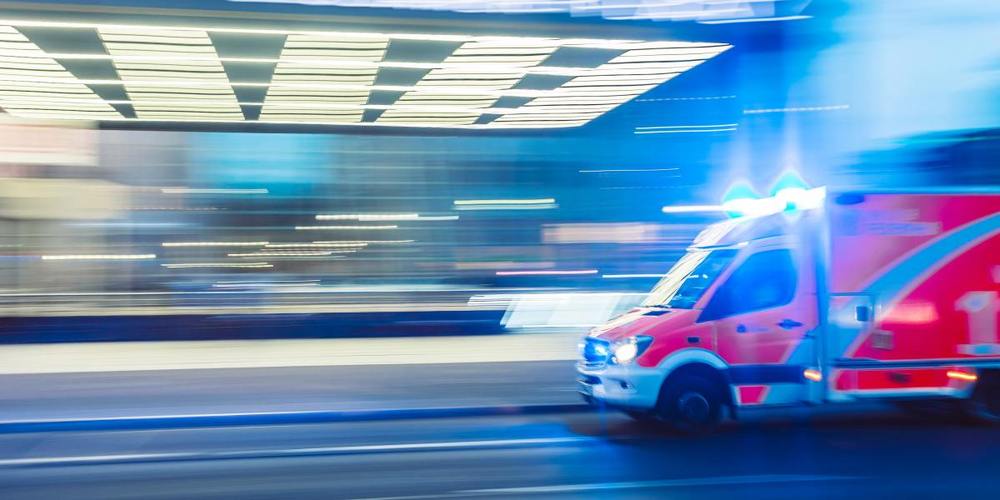
For the first time ever, a patient’s death has been linked directly to a cyberattack. Police have launched a “negligent homicide” investigation after ransomware disrupted emergency care at Düsseldorf University Hospital in Germany.
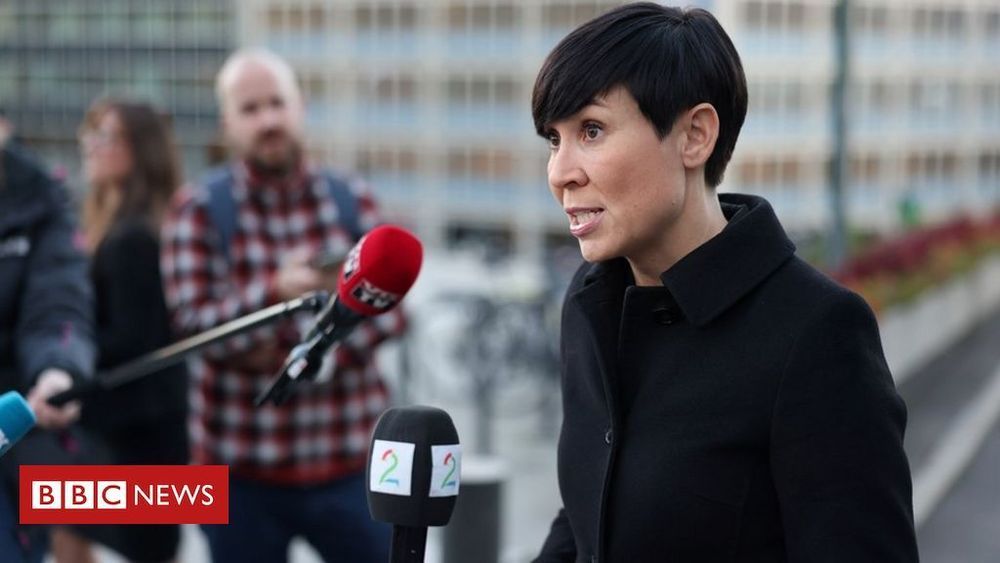
The victim: Prosecutors in Cologne say a female patient from Düsseldorf was scheduled to undergo critical care at the hospital when the September 9 attack disabled systems. When Düsseldorf could no longer provide care, she was transferred 19 miles (30 kilometers) away to another hospital. The hackers could be held responsible by German police, the BBC reports.
A tragic first: “If confirmed, this tragedy would be the first known case of a death directly linked to a cyberattack,” Ciaran Martin, formerly the chief executive of the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre, said in a speech at the Royal United Services Institute. “Although the purpose of ransomware is to make money, it stops systems working. So if you attack a hospital, then things like this are likely to happen. There were a few near misses across Europe earlier in the year, and this looks, sadly, like the worst might have come to pass.”
 In the race to launch smallsats into low earth orbit quickly and cost-effectively, operators and manufacturers have compromised on security and left themselves vulnerable to cyber attacks. Let’s not make Newspace a paradise for hackers.
In the race to launch smallsats into low earth orbit quickly and cost-effectively, operators and manufacturers have compromised on security and left themselves vulnerable to cyber attacks. Let’s not make Newspace a paradise for hackers.