https://www.spreaker.com/user/xzoneradiotv/xzrs20180108epaemirapastor



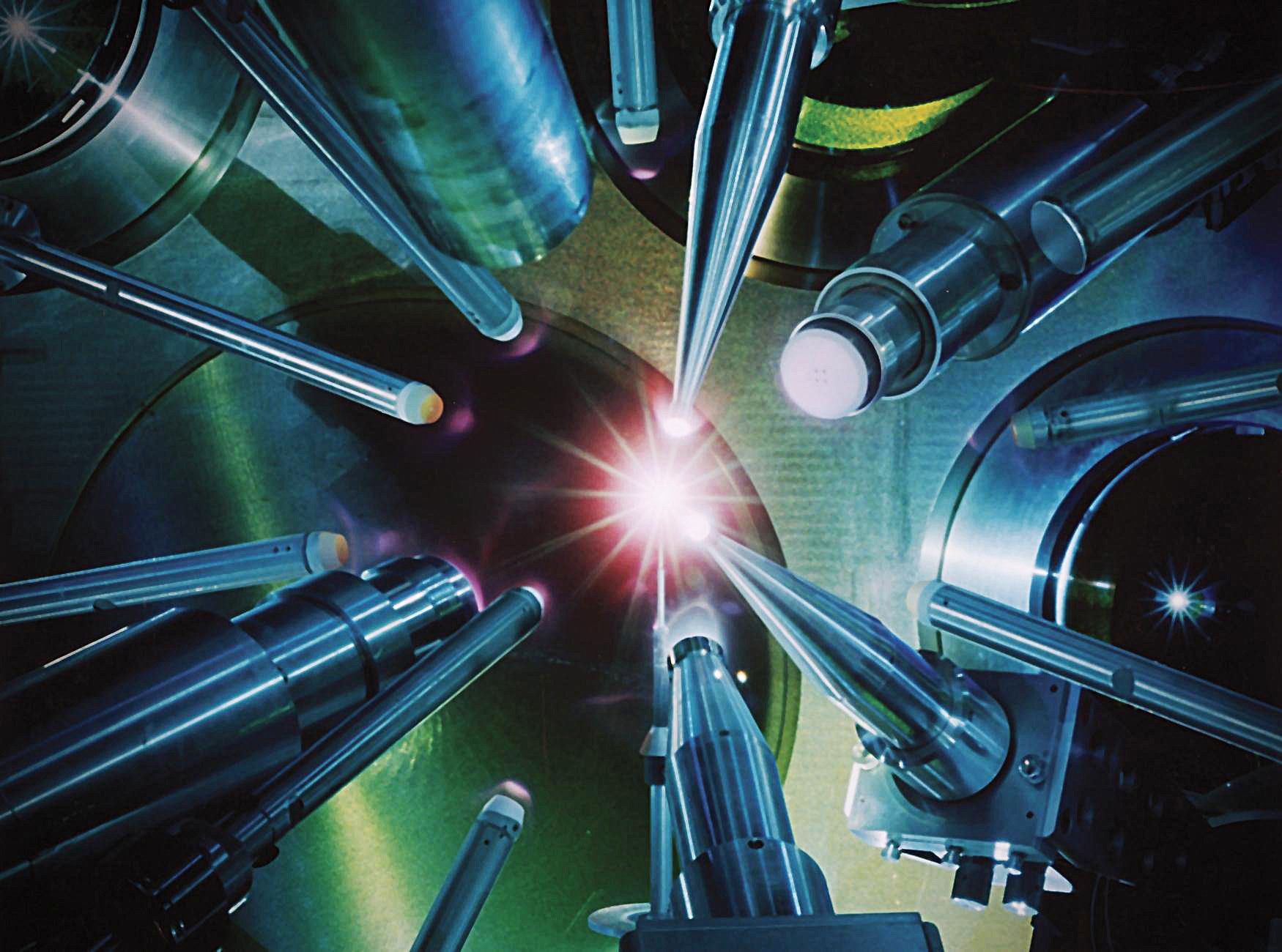
The development of ultra-intense lasers delivering the same power as the entire U.S. power grid has enabled the study of cosmic phenomena such as supernovae and black holes in earthbound laboratories. Now, a new method developed by computational astrophysicists at the University of Chicago allows scientists to analyze a key characteristic of these events: their powerful and complex magnetic fields.
In the field of high-energy density physics, or HEDP, scientists study a wide range of astrophysical objects—stars, supermassive black holes at the center of galaxies and galaxy clusters—with laboratory experiments as small as a penny and lasting only a few billionths of a second. By focusing powerful lasers on a carefully designed target, researchers can produce plasmas that reproduce conditions observed by astronomers in our sun and distant galaxies.
Planning these complex and expensive experiments requires large-scale, high-fidelity computer simulation beforehand. Since 2012, the Flash Center for Computational Science of the Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics at UChicago has provided the leading open computer code, called FLASH, for these HEDP simulations, enabling researchers to fine-tune experiments and develop analysis methods before execution at sites such as the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory or the OMEGA Laser Facility in Rochester, N.Y.




A team of researchers who helped shape our understanding of the origin, evolution and nature of the cosmos is now $3 million richer.
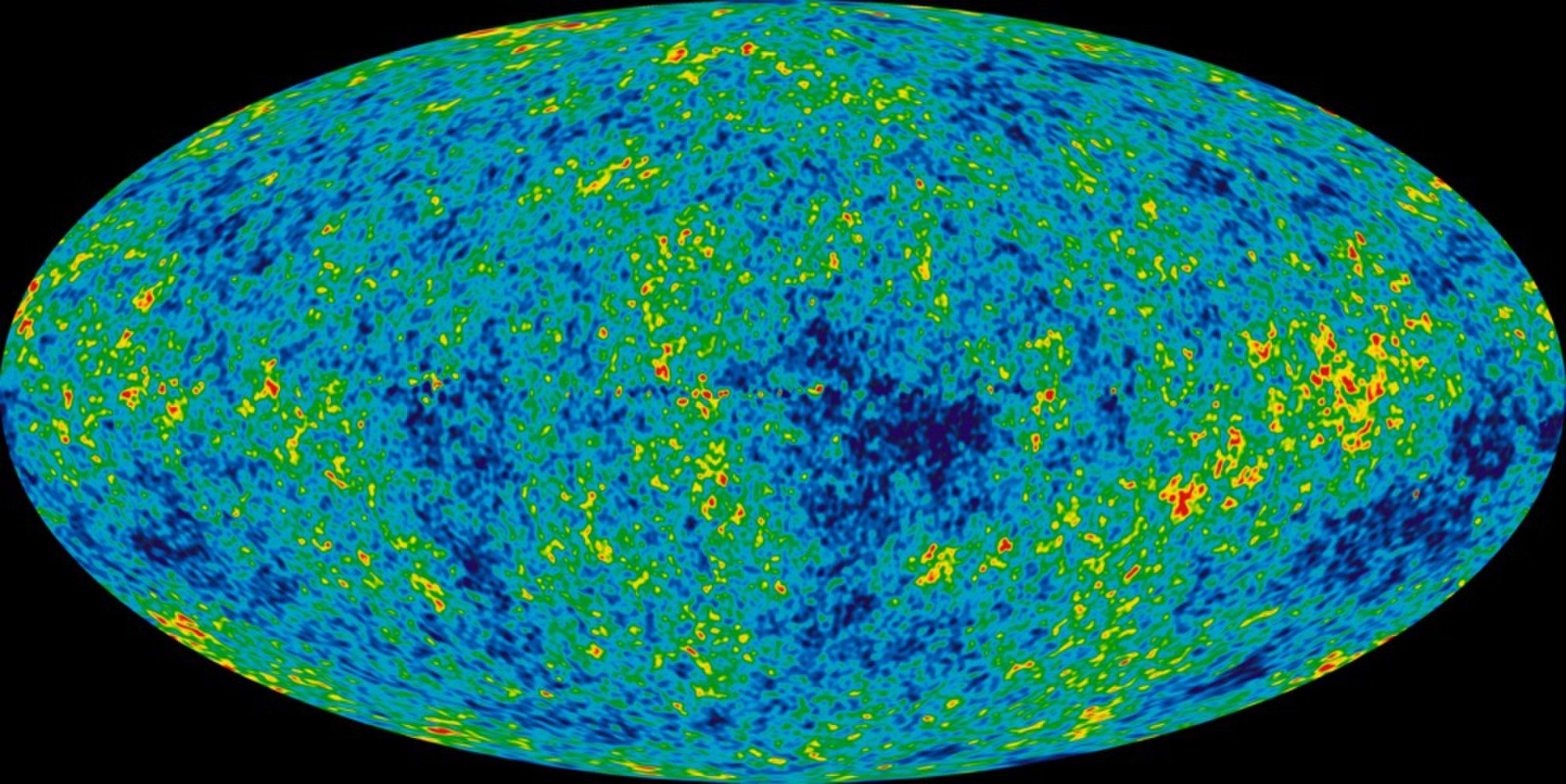
Those folks worked on NASA’s WMAP space mission, which was awarded the 2018 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics today (Dec. 3) during a ceremony in Palo Alto, California.
From 2001 to 2009, WMAP mapped the cosmic microwave background (CMB) — the light left over from the Big Bang — with unprecedented precision. This work allowed scientists to nail down the age of the universe (about 13.8 billion years), its rate of accelerating expansion (roughly 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec) and its basic composition (about 5 percent “normal” matter, 24 percent dark matter and 71 percent dark energy). [Dark Matter and Dark Energy: The Mystery Explained (Infographic)].

“Imminent upgrades to contemporary asteroid survey instruments and improved data processing techniques are likely to produce more interstellar objects in the upcoming years.”
As the common tropes of science fiction continue to break out into reality, from humanoid robots to self-driving cars, there’s one concept that has seemingly remained beyond our grasp: time travel.
But, jumping through time might not be impossible, after all, according to one astrophysicist.
By the rules of theoretical physics, certain conditions exist that would allow for the construction of elaborate wormholes, which could transport humans back to different eras.
While scientists have yet to discover the conditions needed to travel back in time, and construction a system large enough for humans certainly wouldn’t be easy, ‘there’s nothing forbidding it’ in the laws of theoretical physics, explains astrophysicist Ethan Siegel of Lewis & Clark College in the Forbes blog Starts With A Bang.
Backward time travel would rely on the elusive counterpart to the known positive energy / positive or zero mass particles found all throughout the universe – the negative mass/energy particles, which have long been theorized but never yet found.