The supermassive black hole at the heart of our galaxy has suddenly started flashing brighter than we have ever seen it, and astronomers don’t know why.
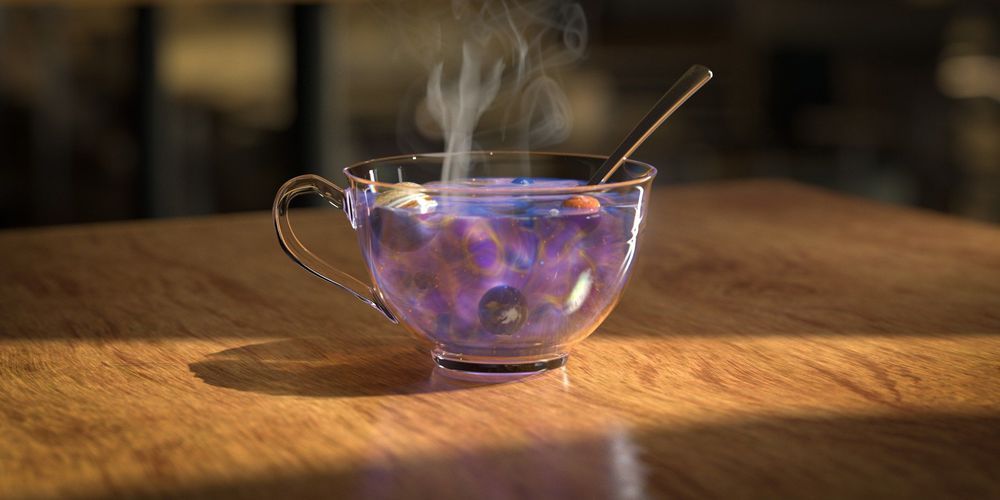



Pour milk in coffee, and the eddies and tendrils of white soon fade to brown. In half an hour, the drink cools to room temperature. Left for days, the liquid evaporates. After centuries, the cup will disintegrate, and billions of years later, the entire planet, sun and solar system will disperse. Throughout the universe, all matter and energy is diffusing out of hot spots like coffee and stars, ultimately destined (after trillions of years) to spread uniformly through space. In other words, the same future awaits coffee and the cosmos.
This gradual spreading of matter and energy, called “thermalization,” aims the arrow of time. But the fact that time’s arrow is irreversible, so that hot coffee cools down but never spontaneously heats up, isn’t written into the underlying laws that govern the motion of the molecules in the coffee. Rather, thermalization is a statistical outcome: The coffee’s heat is far more likely to spread into the air than the cold air molecules are to concentrate energy into the coffee, just as shuffling a new deck of cards randomizes the cards’ order, and repeat shuffles will practically never re-sort them by suit and rank. Once coffee, cup and air reach thermal equilibrium, no more energy flows between them, and no further change occurs. Thus thermal equilibrium on a cosmic scale is dubbed the “heat death of the universe.”
But while it’s easy to see where thermalization leads (to tepid coffee and eventual heat death), it’s less obvious how the process begins. “If you start far from equilibrium, like in the early universe, how does the arrow of time emerge, starting from first principles?” said Jürgen Berges, a theoretical physicist at Heidelberg University in Germany who has studied this problem for more than a decade.


How do galaxies such as our Milky Way come into existence? How do they grow and change over time? The science behind galaxy formation has remained a puzzle for decades, but a University of Arizona-led team of scientists is one step closer to finding answers thanks to supercomputer simulations.
Observing real galaxies in space can only provide snapshots in time, so researchers who want to study how galaxies evolve over billions of years have to revert to computer simulations. Traditionally, astronomers have used this approach to invent and test new theories of galaxy formation, one-by-one. Peter Behroozi, an assistant professor at the UA Steward Observatory, and his team overcame this hurdle by generating millions of different universes on a supercomputer, each of which obeyed different physical theories for how galaxies should form.
The findings, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, challenge fundamental ideas about the role dark matter plays in galaxy formation, how galaxies evolve over time and how they give birth to stars.
Dark matter might well be the biggest mystery in the Universe. We know there’s something out there making things move faster than they should. But we don’t know what it is, and we sure as heck don’t know where it came from.
According to a new paper, the origins of dark matter may be more peculiar than we know. Perhaps, they were particles that appeared in a very brief period of time, just fractions of fractions of a second, before the Big Bang.
This doesn’t just suggest a new connection between particle physics and astronomy; if this hypothesis holds, it could indicate a new way to search for the mysterious stuff.

The Universe is thought to have popped into existence some 13.8 billion years ago when an infinitesimal point expanded billions of lightyears across in just a fraction of a second. The Big Bang theory has stood for the best part of 100 years after Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître first proposed in 1927 the expansion of the Universe could be traced back to a single point. However, the well-accepted model is now under the microscope after a team of researchers found a star which appears to be older than the cosmos.

Black holes can get pretty big, but there’s a special class that is the biggest of the big, absolute yawning monster black holes. And astronomers seem to have found an absolute specimen, clocking in at 40 billion times the mass of the Sun.
It’s at the centre of a galaxy called Holmberg 15A, a supergiant elliptical galaxy around 700 million light-years away, which in turn sits at the centre of the Abell 85 galaxy cluster.
The object is one of the biggest black holes ever found, and the biggest found by tracking the movement of the stars around it.


This week’s podcast features an interview with Ray LaPierre, who heads up the department of engineering physics at McMaster University in Canada. Ray talks to fellow Canadian Hamish Johnston about his research in semiconductor nanowires, in particular for use in photonics and quantum computers, and also shares his experiences of working at JDS Uniphase during the telecoms boom.
Physics World’s Anna Demming also joins the podcast to describe a flurry of new results in the emerging field of twistronics – where two layers of graphene are stacked on top of each other but twisted at a slight angle to each other. The discovery last year that bilayer graphene can become a superconductor if the two graphene layers are twisted at the so-called magic angle of 1.1º won Physics World’s 2018 Breakthrough of the Year, and since then the race has been on to investigate other angle-dependent properties of twisted bilayer graphene. Anna describes how different research teams are now trying to work out what causes these intriguing effects.
We also talk to industry editor Margaret Harris about the importance of technology and engineering for scientific progress. Margaret shares her own “light-bulb” moment, when she realized that new laser technology could have saved hours of experimental time during her PhD, and also highlights several articles in the latest Physics World Focus on Instruments and Vacuum that highlight how breakthrough scientific discoveries rely on developments in the enabling technologies – including the first images of a black hole that were revealed in April.
Atish Dabholkar, a theoretical physicist from India, has been appointed as the new director of Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) in Trieste, Italy.
He is currently the head of ICTP’s high energy, cosmology and astroparticle physics section. He joined the centre in 2014 on secondment from Sorbonne Université and the National Center for Scientific Research, where he has been a research director since 2007. Mr. Dabholkar will take up his duties as ICTP director with the rank of Assistant Director General of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). He will succeed Fernando Quevedo, who has led the centre since 2009.
“It’s an honour and a great responsibility to be chosen as ICTP’s next director. ICTP is a one-of-a-kind institution with a very high level of research and a unique global mission for international cooperation through science. It was envisioned as an international hub for excellence in science and as an anchor to build scientific capacity and a culture of science around the globe. This vision remains valid today even after five decades, but needs to be implemented keeping in mind changing realities and priorities,” he said in a statement.