STEPHEN HAWKING’s “most unexpected discovery” was revealed by the legendary scientist himself during a rare glimpse into the mind of a genius.


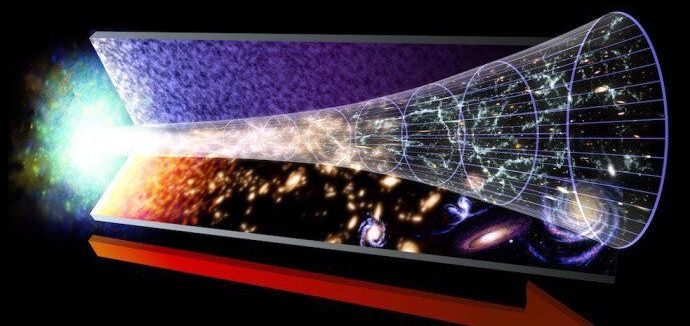
The universe bathes in a sea of light, from the blue-white flickering of young stars to the deep red glow of hydrogen clouds. Beyond the colors seen by human eyes, there are flashes of X-rays and gamma rays, powerful bursts of radio, and the faint, ever-present glow of the cosmic microwave background. The cosmos is filled with colors seen and unseen, ancient and new. But of all these, there was one color that appeared before all the others, the first color of the universe.
The universe began 13.8 billion years ago with the Big Bang. In its earliest moment, it was more dense and hot than it would ever be again. The Big Bang is often visualized as a brilliant flash of light appearing out of a sea of darkness, but that isn’t an accurate picture. The Big Bang didn’t explode into empty space. The Big Bang was an expanding space filled with energy.
At first, temperatures were so high that light didn’t exist. The cosmos had to cool for a fraction of a second before photons could appear. After about 10 seconds, the universe entered the photon epoch. Protons and neutrons had cooled into the nuclei of hydrogen and helium, and space was filled with a plasma of nuclei, electrons and photons. At that time, the temperature of the universe was about 1 billion degrees Kelvin.
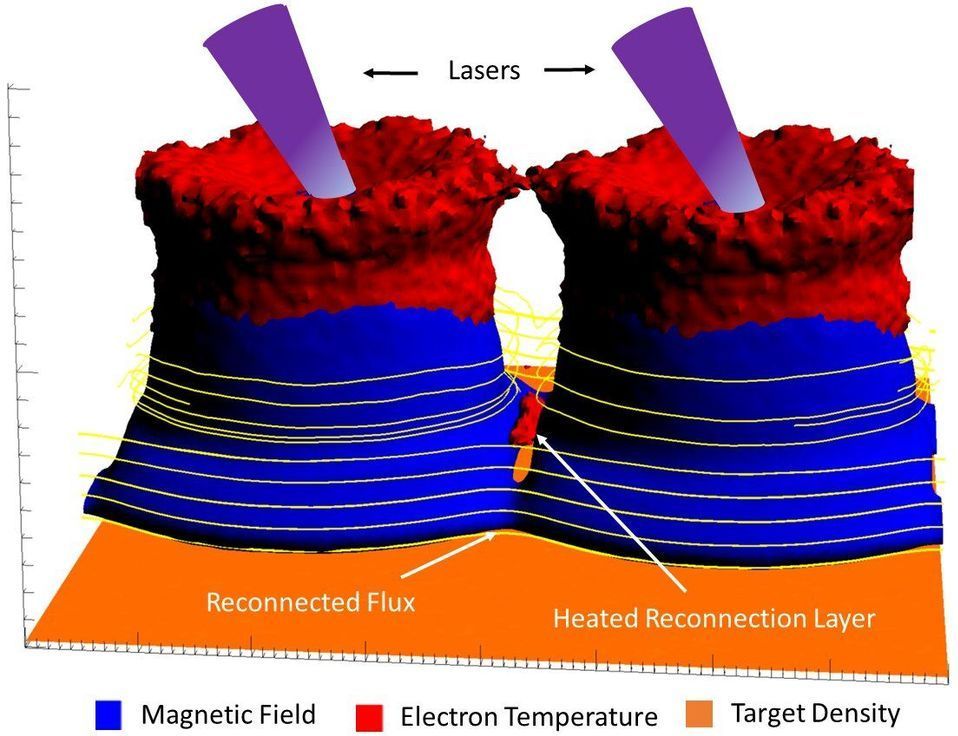
Magnetic reconnection, a process in which magnetic field lines tear and come back together, releasing large amounts of kinetic energy, occurs throughout the universe. The process gives rise to auroras, solar flares and geomagnetic storms that can disrupt cell phone service and electric grids on Earth. A major challenge in the study of magnetic reconnection, however, is bridging the gap between these large-scale astrophysical scenarios and small-scale experiments that can be done in a lab.
Researchers have now overcome this barrier through a combination of clever experiments and cutting-edge simulations. In doing so, they have uncovered a previously unknown role for a universal process called the “Biermann battery effect,” which turns out to impact magnetic reconnection in unexpected ways.
The Biermann battery effect, a possible seed for the magnetic fields pervading our universe, generates an electric current that produces these fields. The surprise findings, made through computer simulations, show the effect can play a significant role in the reconnection occurring when the Earth’s magnetosphere interacts with astrophysical plasmas. The effect first generates magnetic field lines, but then reverses roles and cuts them like scissors slicing a rubber band. The sliced fields then reconnect away from the original reconnection point.

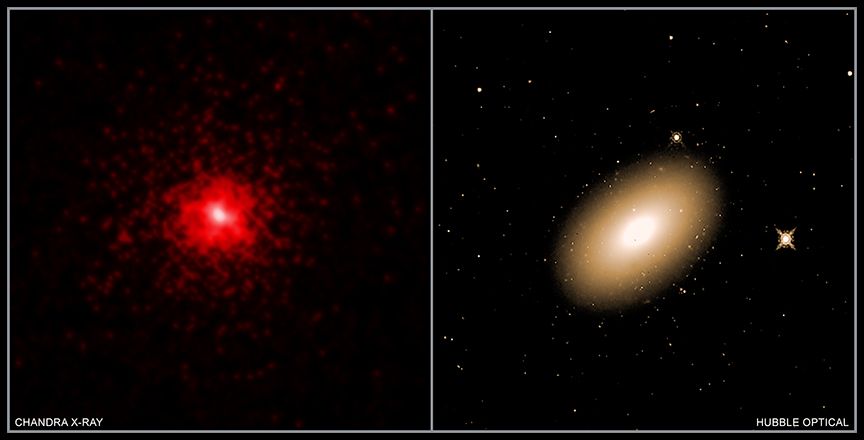
In recent years, cosmologists peering back to the very dawn of our Universe have discovered something peculiar. A whole bunch of supermassive black holes — in a time thought way too early for such massive objects to have formed.
Exactly how they got to be so freaking huge so quickly is a heck of a puzzle — but a new surprise discovery might have delivered an answer. The disc of dust and gas around a supermassive black hole is moving in such a way that it’s slurping down material faster than it would normally.
That means it’s gaining mass faster than expected — which in turn could explain what happened in the earliest days of our Universe.

Scientists believe they may have caught a glimpse of a parallel universe bumping up against ours.
They’ve seen hints in signals from the most distant points of the universe that suggest the fabric of our universe has been disrupted by another incredibly different universe. Their analysis may be the proof for the multiverse theory.
According to researchers: “Dr Ranga-Ram Chary examined the noise and residual signals in the cosmic microwave background left over from the Big Bang (pictured) and found a number of scattered bright spots which he believes may be signals of another universe bumping into our own billions of years ago.”
At least that’s the tentative conclusion researchers have come to. According to some cosmological theories, collisions of alternative universes should be possible. Theories conclude that our universe is like a bubble among many.




