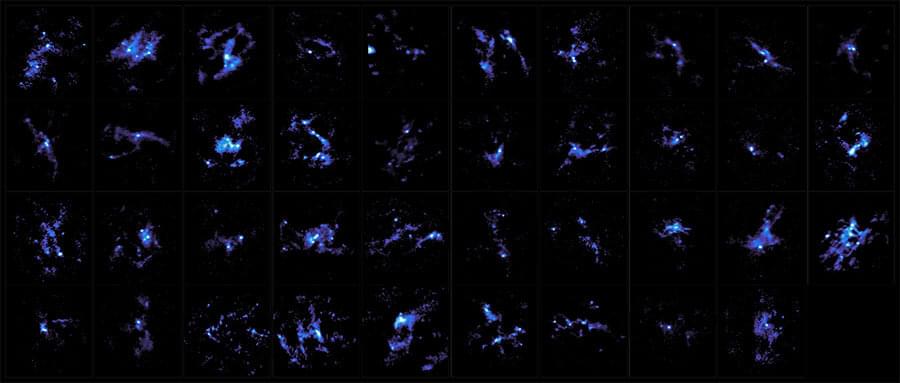
Astronomers have mapped 39 interstellar clouds where high-mass stars are expected to form. This large data set shows that the accepted model of low-mass star formation needs to be expanded to explain the formation of high-mass stars. This suggests the formation of high-mass stars is fundamentally different from the formation of low-mass stars, not just a matter of scale.
High-mass stars play an important role in the evolution of the universe through the release of heavy elements and the shock waves produced when a massive star explodes in a supernova. Despite their importance, the way massive stars form remains poorly understood due to their rarity.
To better understand massive star formation a team led by Kaho Morii, Patricio Sanhueza, and Fumitaka Nakamura used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to observe 39 infrared dark clouds (IRDCs). IRDCs are massive, cold, and dense clouds of gas and dust; and are thought to be the sites of massive star formation. The team focused on clouds showing no signs of star formation, to understand the beginning of the formation process before young stars ignite. In the 39 clouds, the team found more than 800 stellar seeds, referred to as molecular cloud cores, which astronomers think will evolve into stars.