Black holes are some of the most mysterious and awe-inspiring celestial objects in science, and while pairs of black holes or a black hole orbiting another object like a star, known as binary black holes, have been confirmed to exist, what about triple systems? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) announced the discovery of a “black hole triple”, meaning three black holes are orbiting each other simultaneously. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of black holes and what this can teach us about the universe, overall.
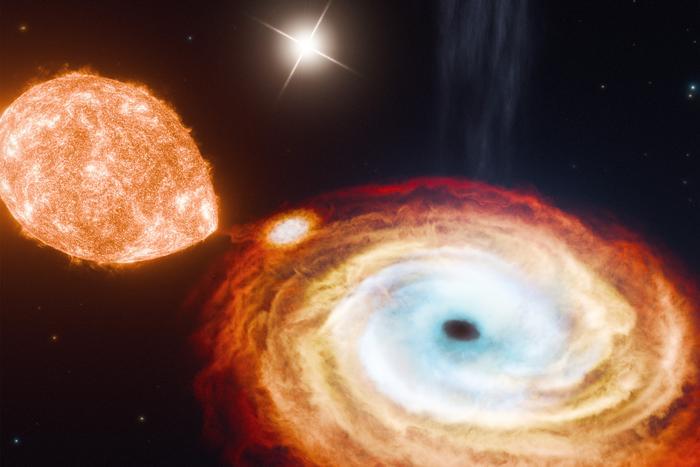
For the study, the researchers examined the binary black hole system V404 Cygni, which consists of a central black hole being orbited by two stars, with one orbiting in 6.5 days while the other takes approximately 70,000 years to complete one orbit. It is this second object that has scientists scratching their heads, as it is confounding how an object so far away can be influenced by a black hole’s gravity. While black holes are often created from a supernova, or the collapse and explosion of a large star, this means the explosion should have pushed away the farther star in this system. Therefore, the team postulates this black hole was formed by what’s known as a “direct collapse”, which is a smaller and gentler process when a star collapses in on itself as opposed to producing an outward explosion.
“We think most black holes form from violent explosions of stars, but this discovery helps call that into question,” said Dr. Kevin Burdge, who is a Pappalardo Fellow in the MIT Department of Physics and lead author of the study. “This system is super exciting for black hole evolution, and it also raises questions of whether there are more triples out there.”