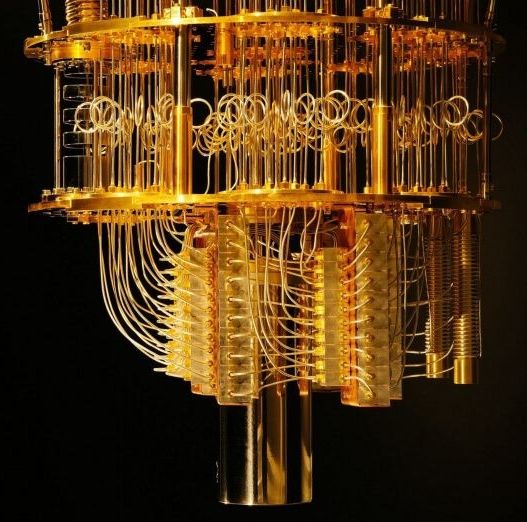
IonQ was founded on a gamble that ‘trapped ion quantum’ computing could outperform the silicon-based quantum computers that Google and others are building. As of right now, it does. IonQ has constructed a quantum computer that can perform calculations on a 79-qubit array, beating the previous king Google’s efforts by 7 qubits.
Their error rates are also the best in the business, with their single-qubit error rate at 99.97% while the nearest competitors are around the 99.5 mark, and a two-qubit error rate of 99.3% when most competitors are beneath 95%. But how does it compare to regular computers?
According to IonQ, in the kinds of workloads that quantum computers are being built for, it’s already overtaking them. The Bernstein-Vazirani Algorithm, a benchmark IonQ is hoping will take off, tests a computer’s ability to determine a single encoded number (called an oracle) when the computer can only ask a single yes/no question.