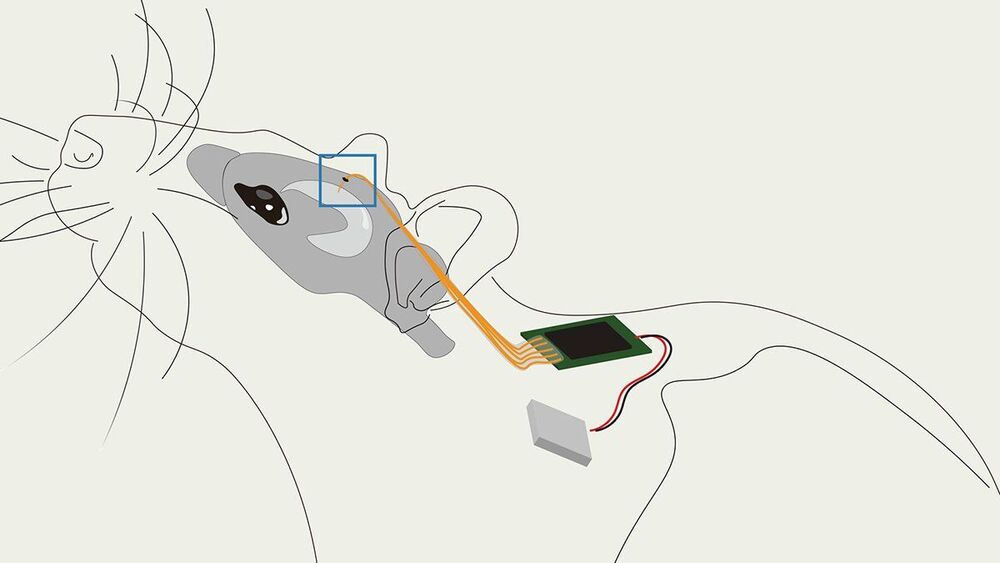
As researchers learn more about the brain, it has become clear that responsive neurostimulation is becoming increasingly effective at probing neural circuit function and treating neuropsychiatric disorders, such as epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease. But current approaches to designing a fully implantable and biocompatible device able to make such interventions have major limitations: their resolution isn’t high enough and most require large, bulky components that make implantation difficult with risk of complications.
A Columbia Engineering team led by Dion Khodagholy, assistant professor of electrical engineering, has come up with a new approach that shows great promise to improve such devices. Building on their earlier work to develop smaller, more efficient conformable bioelectronic transistors and materials, the researchers orchestrated their devices to create high performance implantable circuits that enable allow reading and manipulation of brain circuits. Their multiplex-then-amplify (MTA) system requires only one amplifier per multiplexer, in contrast to current approaches that need an equal number of amplifiers as number of channels.
“It is critical to be able to detect and intervene to treat brain-disorder-related symptoms, such as epileptic seizures, in real time,” said Khodagholy, a leader in bio-and neuroelectronics design. “Not only is our system much smaller and more flexible than current devices, but it also enables simultaneous stimulation of arbitrary waveforms on multiple independent channels, so it is much more versatile.