New Customers Exclusive – Get A Free 240gb SSD at Micro Center: https://micro.center/f73724
Check out the Micro Center x ASUS Custom PC Builder: https://micro.center/929cf7
Get your Crucial P5 Plus NVMe SSD today at:
https://crucial.gg/LinusTechTips.
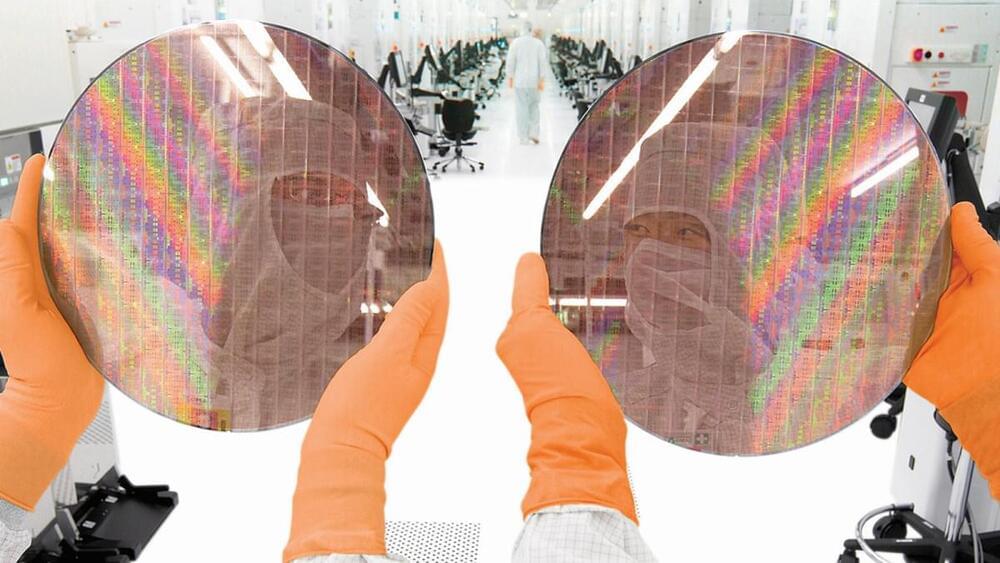
It’s not a microbrewery, it’s the Nanosys manufacturing facility where quantum dots are made! James takes on a tour of the chemical reactors and cool color science that are creating industry leading HDR experiences on our TVs and monitors.
Buy Samsung 32″ Odyssey G7 Curved Gaming Monitor.
On Amazon: https://geni.us/wZGJ2b.
On Best Buy: https://geni.us/BasHQ
On Newegg: https://geni.us/pB6v.
Purchases made through some store links may provide some compensation to Linus Media Group.
Discuss on the forum: https://linustechtips.com/topic/1396266-this-boiling-liquid-…lity-tour/