Designed to train students to practice responsible technology development, the Social and Ethical Responsibilities of Computing (SERC) publishes a collection of original pedagogical materials developed for instructional use on MIT OpenCourseWare.



To classify as a DTC, a system also needs to be truly many-body, and its coherence times (that is, the time over which fragile quantum states persist without being destroyed by interactions with their environment) must be long enough that its periodic variations are not mistaken for a short-term system change. Finally, one must be able to prepare the system in arbitrary initial states and show that all of them result in similar DTC behaviour.
A major milestone
The Melbourne team’s work, which is described in Science Advances, builds on earlier reports of DTCs that used quantum processors based on nine nuclear spins in diamond and 20 superconducting qubits. As in these previous experiments, the team turned a quantum computer into an experimental platform — a quantum simulator – in which all the requirements of DTCs could be met.
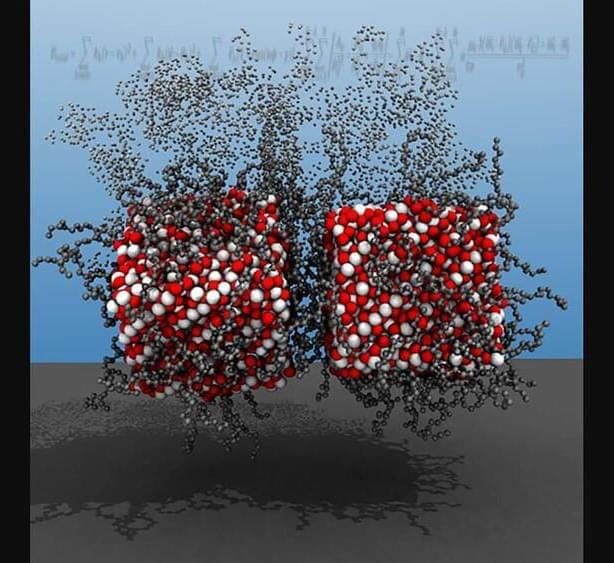
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new computational tool that allows users to conduct simulations of multi-functional magnetic nanoparticles in unprecedented detail. The advance paves the way for new work aimed at developing magnetic nanoparticles for use in applications from drug delivery to sensor technologies.
“Self-assembling magnetic nanoparticles, or MNPs, have a lot of desirable properties,” says Yaroslava Yingling, corresponding author of a paper on the work and a Distinguished Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at NC State. “But it has been challenging to study them, because computational models have struggled to account for all of the forces that can influence these materials. MNPs are subject to a complicated interplay between external magnetic fields and van der Waals, electrostatic, dipolar, steric, and hydrodynamic interactions.”
Many applications of MNPs require an understanding of how the nanoparticles will behave in complex environments, such as using MNPs to deliver a specific protein or drug molecule to a targeted cancer affected cell using external magnetic fields. In these cases, it is important to be able to accurately model how MNPs will respond to different chemical environments. Previous computational modeling techniques that looked at MNPs were unable to account for all of the chemical interactions MNPs experience in a given colloidal or biological environment, instead focusing primarily on physical interactions.

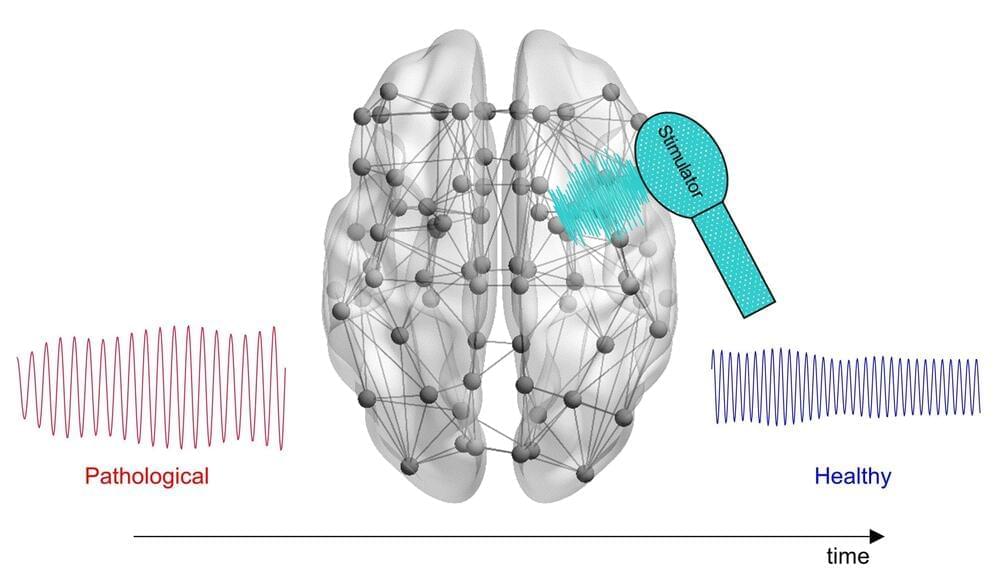
Scientists have developed a novel computational approach that incorporates individual patients’ brain activity to calculate optimal, personalized brain stimulation treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Lazaro Sanchez-Rodriguez of the University of Calgary, Canada, and colleagues present their new framework in PLOS Computational Biology.
Electrical stimulation of certain parts of the brain could help promote healthy activity in neural circuits impaired by Alzheimer’s disease, a neurodegenerative condition. This experimental treatment has shown some promise in clinical trials. However, all patients currently receive identical treatment protocols, potentially leading to different outcomes according to individual variations in brain signaling.
To investigate the possibility of personalized brain stimulation, Sanchez-Rodriguez and colleagues took a theoretical approach. They built a computational tool that incorporates patients’ MRI scans and physiological brain signaling measurements to calculate optimal brain stimulation signals, with the goal of delivering efficient, effective personalized treatment.
Superconductors—metals in which electricity flows without resistance—hold promise as the defining material of the near future, according to physicist Brad Ramshaw, and are already used in medical imaging machines, drug discovery research and quantum computers being built by Google and IBM.
However, the super-low temperatures conventional superconductors need to function—a few degrees above absolute zero—make them too expensive for wide use.
In their quest to find more useful superconductors, Ramshaw, the Dick & Dale Reis Johnson Assistant Professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), and colleagues have discovered that magnetism is key to understanding the behavior of electrons in “high-temperature” superconductors. With this finding, they’ve solved a 30-year-old mystery surrounding this class of superconductors, which function at much higher temperatures, greater than 100 degrees above absolute zero. Their paper, “Fermi Surface Transformation at the Pseudogap Critical Point of a Cuprate Superconductor,” published in Nature Physics March 10.
The sensor sends out electromagnetic waves in a broad beam, which are intercepted and reflected back by objects (or people) in their path.
Circa 2015
Stanford bioengineer Manu Prakash and his students have developed a synchronous computer that operates using the unique physics of moving water droplets.
Computers and water typically don’t mix, but in Manu Prakash’s lab, the two are one and the same. Prakash, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Stanford, and his students have built a synchronous computer that operates using the unique physics of moving water droplets.
The computer is nearly a decade in the making, incubated from an idea that struck Prakash when he was a graduate student. The work combines his expertise in manipulating droplet fluid dynamics with a fundamental element of computer science – an operating clock.