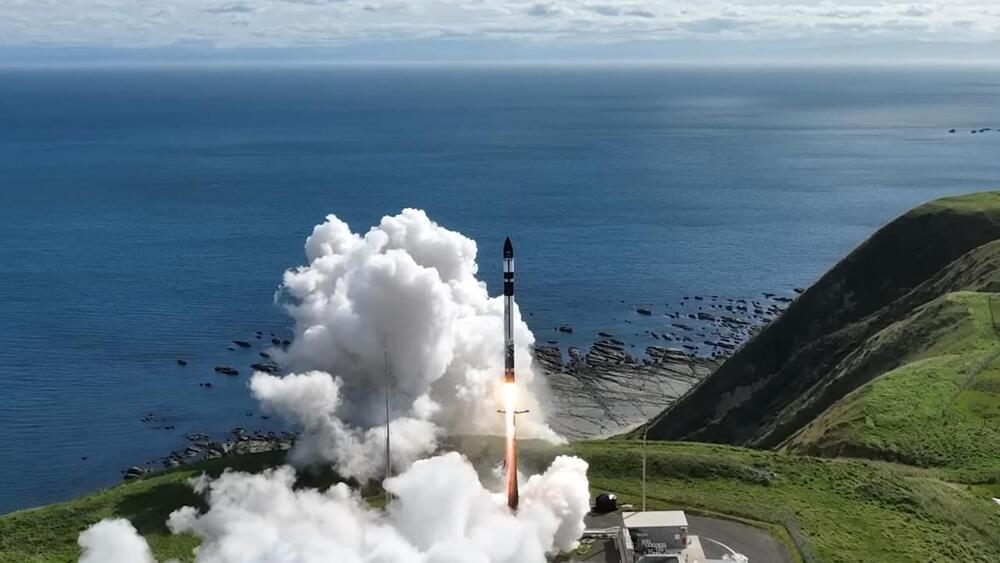
Electron, Rocket Lab’s small satellite launch vehicle, launched twice, just ~2 weeks apart from the companies Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand to deliver the 4 CubeSat constellation to orbit.
Payload deployment confirmed! Congratulations to the launch team on our 37th Electron launch, and to our mission partners at @NASA @NASA_LSP @NASAAmes: the TROPICS constellation is officially on orbit! pic.twitter.com/xAy7ltg7m1
The two missions, dubbed ‘Rocket Like a Hurricane’ and ‘Coming to a Storm Near You,’ contain two 11.8-lb (5.34 kg) CubeSats each delivered to a 30-degree orbital inclination in order for the constellation to monitor tropical systems forming in the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean and will be capable of performing scans about once every hour.