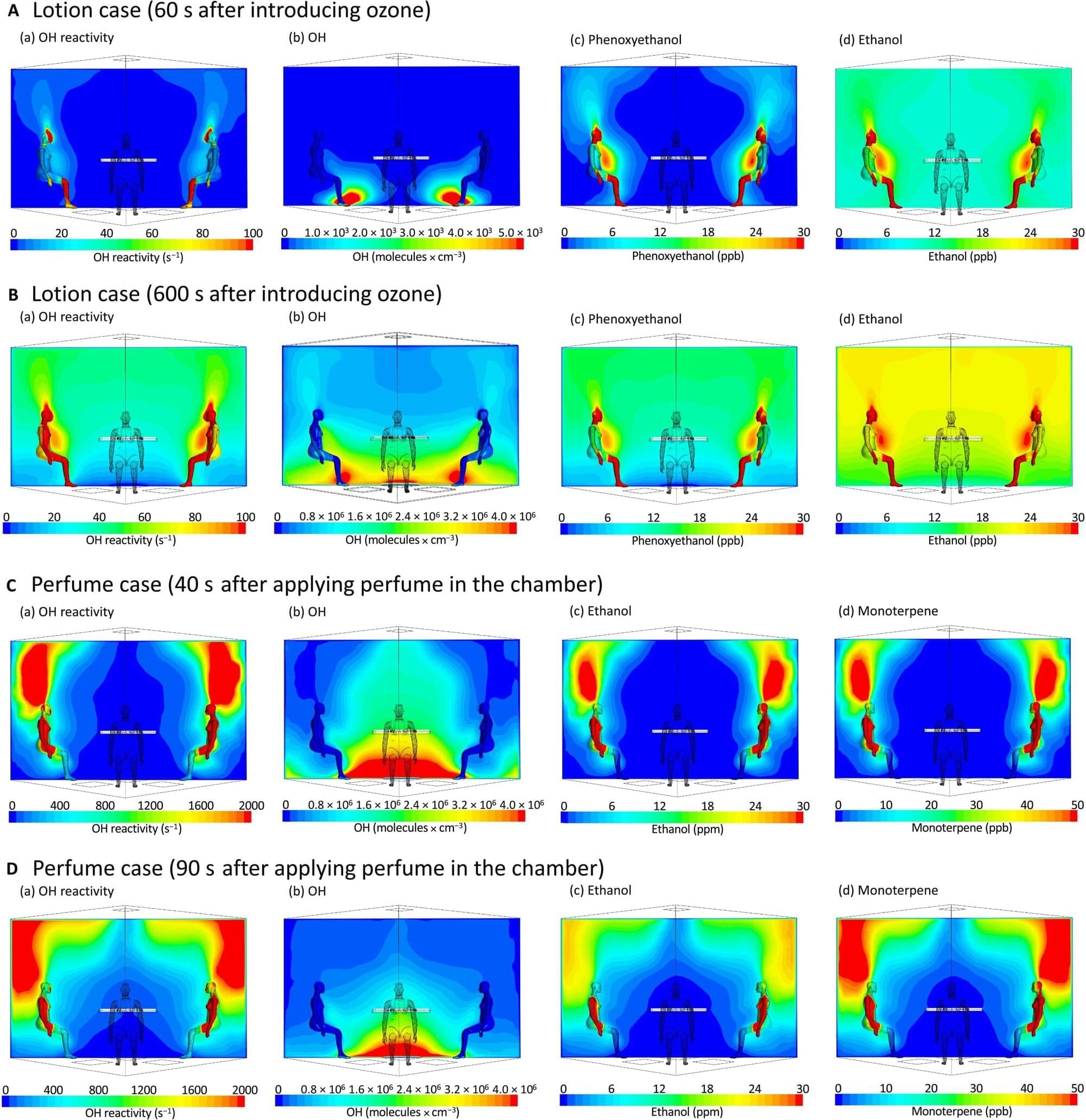
The indoor environment contains multiple sources of chemical compounds. These include continuous emissions from housing materials such as furniture, floors and furnishings, but also periodic intense emissions from human activities such as cooking, smoking, and cleaning.
Outdoor air chemicals can also enter indoor environments through infiltration and ventilation. Ozone (O3) from outdoors can react with compounds indoors to create a complex chemical cocktail within the indoor living space. Since people spend up to 90% of their time indoors, exposure to this diverse array of chemical compounds over extended periods is cause for concern, particularly as the human-health impacts of many such chemicals remain poorly understood.
On the basis of their findings in 2022, Jonathan Williams’s research group from the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry took a closer look at how the human oxidation field might be influenced by personal care products. The study is published in the journal Science Advances.