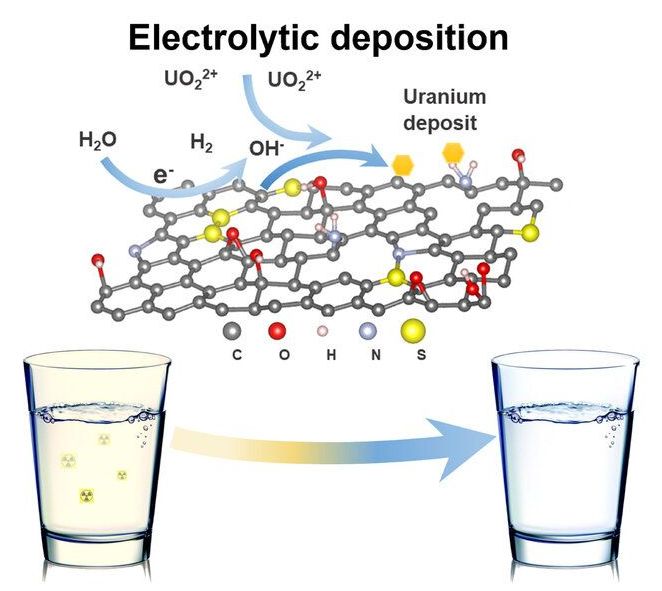
Some kinds of water pollution, such as algal blooms and plastics that foul rivers, lakes, and marine environments, lie in plain sight. But other contaminants are not so readily apparent, which makes their impact potentially more dangerous. Among these invisible substances is uranium. Leaching into water resources from mining operations, nuclear waste sites, or from natural subterranean deposits, the element can now be found flowing out of taps worldwide.
In the United States alone, “many areas are affected by uranium contamination, including the High Plains and Central Valley aquifers, which supply drinking water to 6 million people,” says Ahmed Sami Helal, a postdoc in the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering. This contamination poses a near and present danger. “Even small concentrations are bad for human health,” says Ju Li, the Battelle Energy Alliance Professor of Nuclear Science and Engineering and professor of materials science and engineering.
Now, a team led by Li has devised a highly efficient method for removing uranium from drinking water. Applying an electric charge to graphene oxide foam, the researchers can capture uranium in solution, which precipitates out as a condensed solid crystal. The foam may be reused up to seven times without losing its electrochemical properties. “Within hours, our process can purify a large quantity of drinking water below the EPA limit for uranium,” says Li.