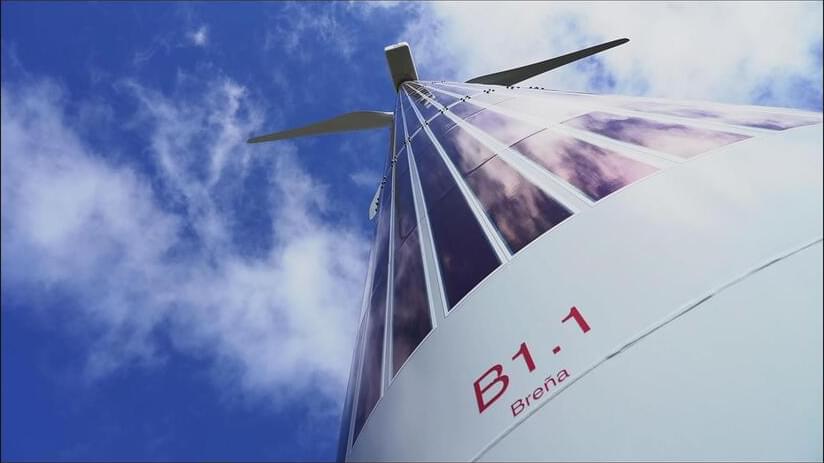
In November 2021, while the municipal utility in Marburg, Germany, was performing scheduled maintenance on a hot water storage facility, engineers glued 18 solar panels to the outside of the main 10-meter-high cylindrical tank. It’s not the typical home for solar panels, most of which are flat, rigid silicon and glass rectangles arrayed on rooftops or in solar parks. The Marburg facility’s panels, by contrast, are ultrathin organic films made by Heliatek, a German solar company. In the past few years, Heliatek has mounted its flexible panels on the sides of office towers, the curved roofs of bus stops, and even the cylindrical shaft of an 80-meter-tall windmill. The goal: expanding solar power’s reach beyond flat land. “There is a huge market where classical photovoltaics do not work,” says Jan Birnstock, Heliatek’s chief technical officer.
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) such as Heliatek’s are more than 10 times lighter than silicon panels and in some cases cost just half as much to produce. Some are even transparent, which has architects envisioning solar panels not just on rooftops, but incorporated into building facades, windows, and even indoor spaces. “We want to change every building into an electricity-generating building,” Birnstock says.
Heliatek’s panels are among the few OPVs in practical use, and they convert about 9% of the energy in sunlight to electricity. But in recent years, researchers around the globe have come up with new materials and designs that, in small, labmade prototypes, have reached efficiencies of nearly 20%, approaching silicon and alternative inorganic thin-film solar cells, such as those made from a mix of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium (CIGS). Unlike silicon crystals and CIGS, where researchers are mostly limited to the few chemical options nature gives them, OPVs allow them to tweak bonds, rearrange atoms, and mix in elements from across the periodic table. Those changes represent knobs chemists can adjust to improve their materials’ ability to absorb sunlight, conduct charges, and resist degradation. OPVs still fall short on those measures. But, “There is an enormous white space for exploration,” says Stephen Forrest, an OPV chemist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.