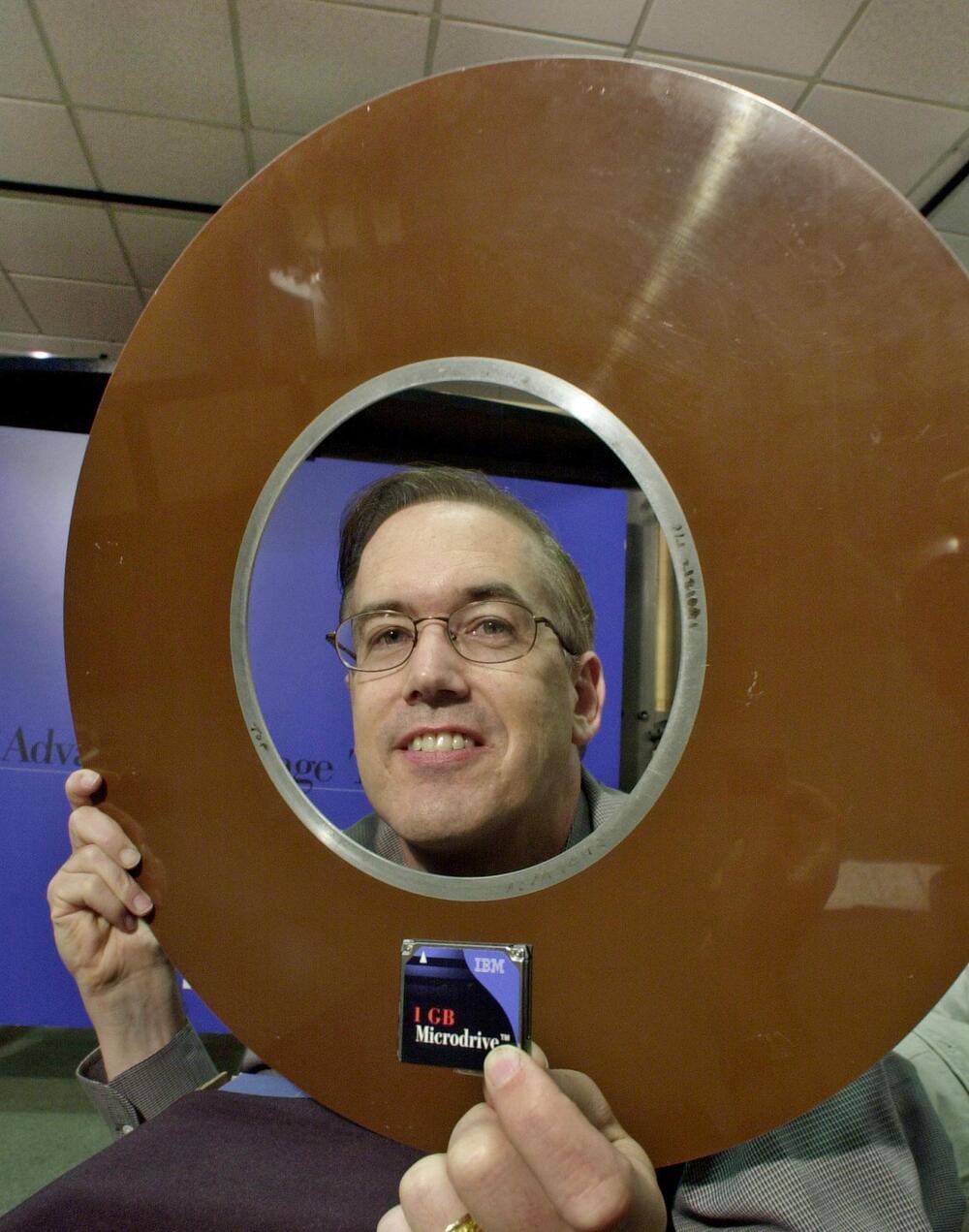
On September 14, 1956, IBM announced the 305 and 650 RAMAC (Random Access Memory Accounting) “data processing machines,” incorporating the first-ever disk storage product. The 305 came with fifty 24-inch disks for a total capacity of 5 megabytes, weighed 1 ton, and could be leased for $3,200 per month.
In 1953, Arthur J. Critchlow, a young member of IBM’s advanced technologies research lab in San Jose, California, was assigned the task of finding a better data storage medium than punch-cards.
The information explosion (a term first used in 1941, according to the Oxford English Dictionary) has turned into the big digital data explosion. And the data explosion enabled deep learning, an advanced data analysis method, to perform today’s AI breakthroughs in image identification and natural language processing.
The RAMAC became obsolete within a few years of its introduction as the vacuum tubes powering it were replaced by transistors. Today, disk drives still serve as the primary containers for digital data, but solid-state drives (flash memory), first used in mobile devices, are fast replacing disk drives even in today’s successors of the RAMAC, supporting large-scale business operations.
Whatever form the storage takes, IBM created in 1956 new markets and businesses based on fast access to digital data. As Seagate’s Mark Kryder asserted in 2006: “Instead of Silicon Valley, they should call it Ferrous Oxide Valley. It wasn’t the microprocessor that enabled the personal video recorder, it was storage. It’s enabling new industries.”