Google’s new Willow quantum processor has reignited discussions around blockchain security and their ability to withstand rapid advancements.

A team of cybersecurity researchers at Stony Brook University has uncovered a new way for scammers to steal from unsuspecting cryptocurrency users. They have posted a paper to the arXiv preprint server describing the new crypto scam and how users can protect themselves.
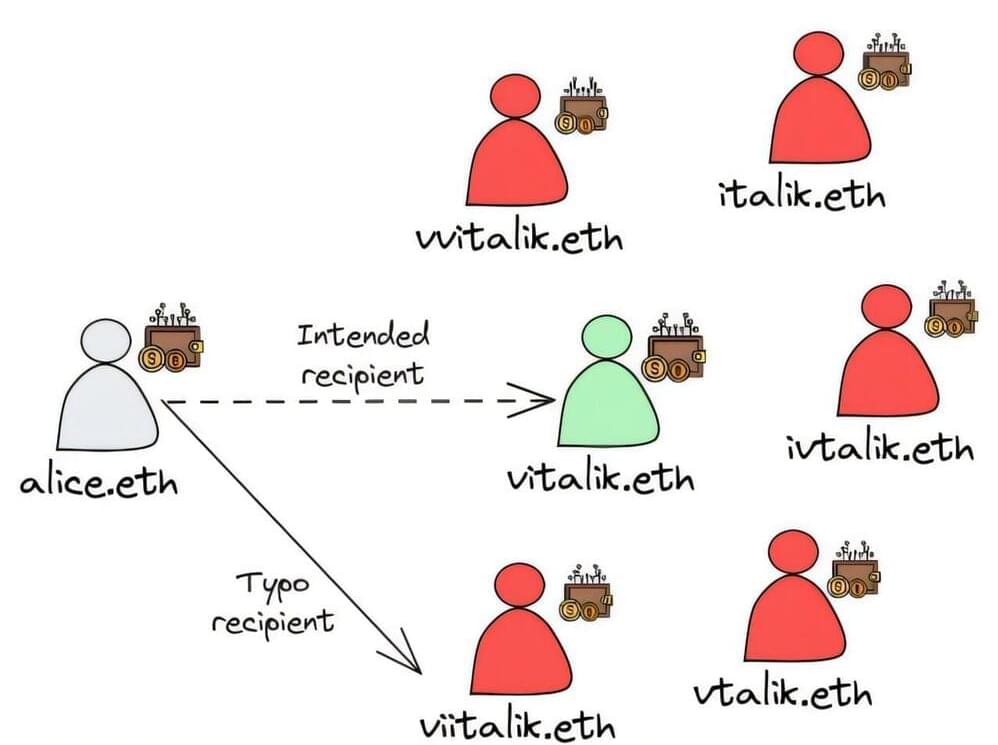
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital currency run on a secure online platform. One example is Coinbase. Crypto currency is stored in a crypto wallet. In this new study, the team in New York reports that scammers have found a way to get people to redirect crypto payments away from intended recipients and toward wallets held by the scammers.
The researchers call the scam typosquatting. It involves setting up Blockchain Naming Systems (BNS) domain names that are similar to those used by well-known entities. It exploits the use of simple word-based addresses rather than the complicated and hard-to-remember letter and digit codes commonly associated with crypto wallets.
🚀 Q: How might Trump’s administration impact AI development in the US? A: Trump aims to make America “first in AI” by dismantling Biden’s policy framework and reducing government regulation, potentially leading to skyrocketing growth in AI, cryptocurrencies, blockchain, Web3, and augmented reality.
🔓 Q: What’s J.D. Vance’s stance on AI development? A: Trump’s potential VP J.D. Vance supports open source AI and decentralized power, aiming to prevent large tech companies from steering regulation and allowing smaller innovators to compete.

Quantum, Blockchain & AI | Sarah Baldeo, Founder, ID Quotient Advisory Group. Sarah will be presenting at the upcoming Fin+AI 2024 Conference.
Register with code EARLYBIRD until July 15th — www.finaiconference.com.
Sarah Baldeo is an experienced neuroscientist, technologist, corporate strategist and entrepreneur, closing on 20 years of leadership experience. Sarah shares her experience in working with banks, payment providers, insurance, and other enterprise organizations. Sarah shares her perspective on AI, Quantum, Blockchain and other technologies.
In 2023 Sarah graced more than 50 stages, and gave 24 keynotes, was featured on 960AM radio, and most recently nominated for the DMZ 2024 Women of the Year Award & the Top 25 Women of Influence Award. You may have even seen her on TV during the Wimbledon Open Commercials!
Sarah On LinkedIn:
Chris delves into the transformative impact of digital money and AI on financial services, predicting major changes by 2030. The conversation explores key themes like personalization, automation, and the tension between centralization and decentralization. Chris highlights how AI and blockchain are shaping the future of finance, emphasizing the need for smart data use. He also shares insights on the evolving role of fintech startups and traditional banks. Tune in for a deep dive into the future of money and technology, and get inspired by one of fintech’s most influential voices. Don’t miss this enlightening discussion on how intelligent money is set to revolutionize our lives!
Follow Chris Skinner: https://thefinanser.com/ / https://www.linkedin.com/in/cmskinner/
Chris Skinner, a top fintech influencer and award-winning speaker, is the author of 18 books, including “Intelligent Money.” He blogs daily at The Finanser.com and co-founded one of the first mobile banks. Skinner advises global leaders and organizations like the UN and the World Economic Forum. He also writes children’s books and co-founded The Portrait Foundation. In 2023, he received a Lifetime Achievement Award from the Payments Association.
Paolo Sironi: https://www.linkedin.com/in/thepsironi/
IBM FinTech Strategy and Author.
In this interview I speak with Chris Fronda, CEO of Logictry.
In this interview Bruce Burke speaks with Chris Fronda, CEO of Logictry. Scaling the world’s wisdom to help everyone make better decisions faster. Chris is presenting at Fin+AI 2024 Conference, October 2–4, 2024 at Le Meridien in Dania Beach, Florida. Meet Chris and other leaders at Fin+AI.
https://www.finaiconference.com/chris…
Chris Fronda is a former Enterprise Product Manager, 4X startup founder, and 15+ year full stack software architect with experience building web apps, native mobile apps, blockchain dapps, scalable cloud architectures, expert systems, and custom large language models.
Chris is a proven expert in technology and innovation having worked with clients ranging from small businesses to Fortune 10 companies and helps organizations systematize and scale their business leveraging the latest technological advancements.
Join Randal Koene, a computational neuroscientist, as he dives into the intricate world of whole brain emulation and mind uploading, while touching on the ethical pillars of AI. In this episode, Koene discusses the importance of equal access to AI, data ownership, and the ethical impact of AI development. He explains the potential future of AGI, how current social and political systems might influence it, and touches on the scientific and philosophical aspects of creating a substrate-independent mind. Koene also elaborates on the differences between human cognition and artificial neural networks, the challenge of translating brain structure to function, and efforts to accelerate neuroscience research through structured challenges.
00:00 Introduction to Randal Koene and Whole Brain Emulation.
00:39 Ethical Considerations in AI Development.
02:20 Challenges of Equal Access and Data Ownership.
03:40 Impact of AGI on Society and Development.
05:58 Understanding Mind Uploading.
06:39 Randall’s Journey into Computational Neuroscience.
08:14 Scientific and Philosophical Aspects of Substrate Independent Minds.
13:07 Brain Function and Memory Processes.
25:34 Whole Brain Emulation: Current Techniques and Challenges.
32:12 The Future of Neuroscience and AI Collaboration.
SingularityNET is a decentralized marketplace for artificial intelligence. We aim to create the world’s global brain with a full-stack AI solution powered by a decentralized protocol.
We gathered the leading minds in machine learning and blockchain to democratize access to AI technology. Now anyone can take advantage of a global network of AI algorithms, services, and agents.
Website: https://singularitynet.io.
Discord: / discord.
Forum: https://community.singularitynet.io.
Telegram: https://t.me/singularitynet.
Twitter: / singularitynet.
Facebook: / singularitynet.io.
Instagram: / singularitynet.io.
Github: https://github.com/singnet.
Linkedin: / singularitynet.
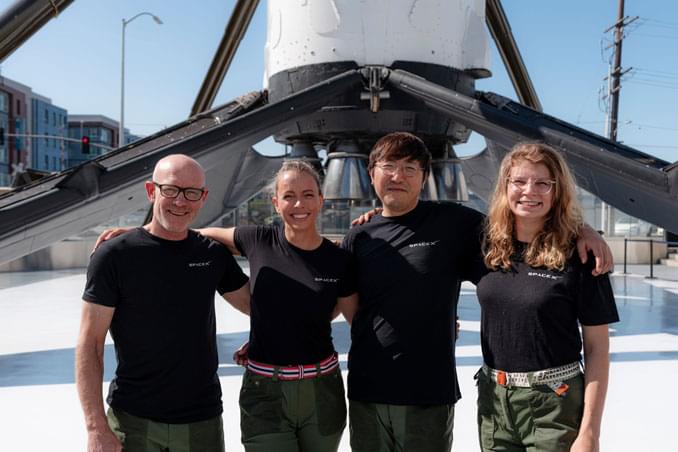

A blockchain entrepreneur, a cinematographer, a polar adventurer and a robotics researcher plan to fly around Earth’s poles aboard a SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule by end of year, becoming the first humans to observe the ice caps and extreme polar environments from orbit, SpaceX announced Monday.
The historic flight, launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, will be commanded by Chun Wang, a wealthy bitcoin pioneer who founded f2pool and stakefish, “which are among the largest Bitcoin mining pools and Ethereum staking providers,” the crew’s website says.
“Wang aims to use the mission to highlight the crew’s explorational spirit, bring a sense of wonder and curiosity to the larger public and highlight how technology can help push the boundaries of exploration of Earth and through the mission’s research,” SpaceX said on its web site.
Singularity net Ben goerzel discusses artificial and general intelligence and cosmist intelligence.
Dr. Ben Goertzel discusses artificial general, non-human and cosmist intelligences with Ed Keller at The Overview Effect Lectures, which is a series positioned as a survey of some of the key operational themes critical to post planetary and universal design.
Ed Keller’s Youtube Channel — / machinicphylum.
SingularityNET is a decentralized marketplace for artificial intelligence. We aim to create the world’s global brain with a full-stack AI solution powered by a decentralized protocol.
We gathered the leading minds in machine learning and blockchain to democratize access to AI technology. Now anyone can take advantage of a global network of AI algorithms, services, and agents.