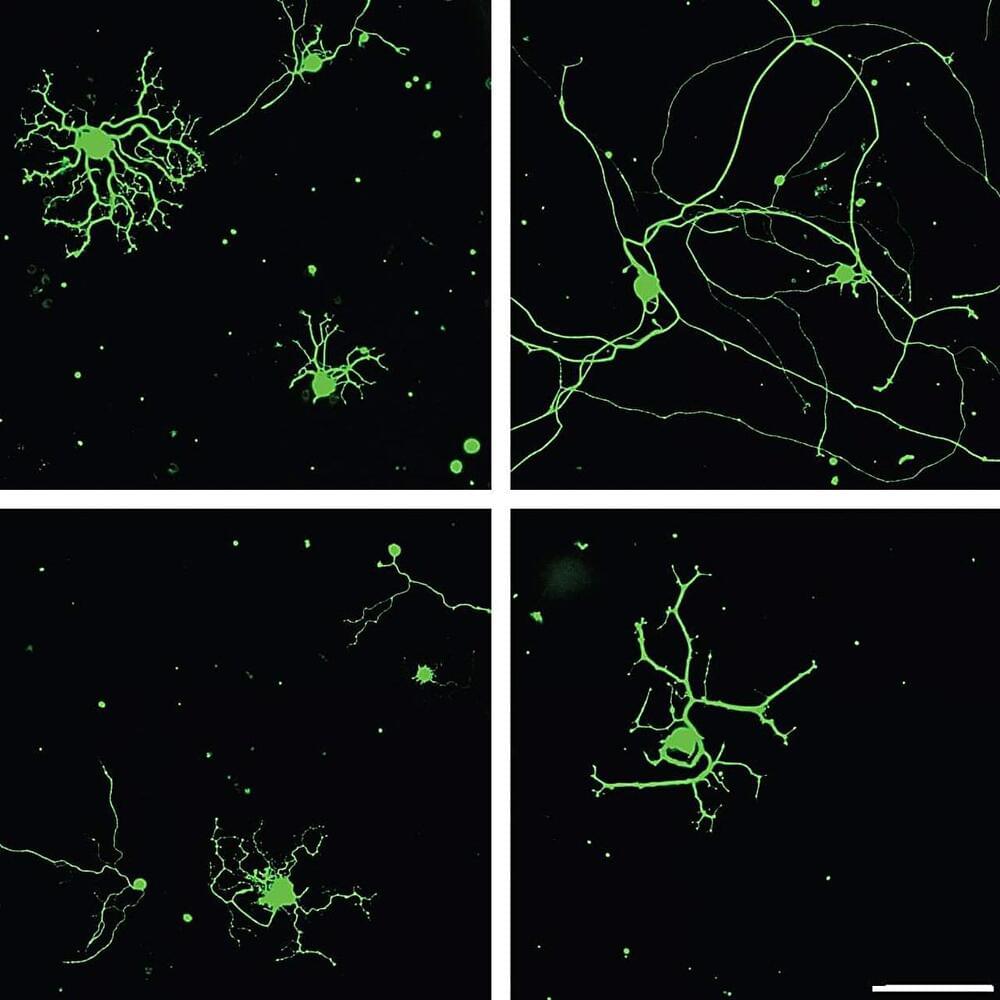
Just like a gecko that regrows a broken tail, our peripheral nervous system knows how to regenerate the branches of its cells after an injury. Unfortunately, the cells in our central nervous system—our brain and spinal cord—are far more limited when it comes to regeneration.
Accordingly, diseases that lead to the degeneration and death of brain neurons, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and ALS, are irreversible and incurable. So, what is it about the peripheral nervous system, which connects our brain and spinal cord to the other organs, that gives it the power to regenerate itself so readily?
In a new study, researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science have discovered that a protein, previously known to be expressed only during embryonic development, plays a key role in regenerating adult neurons in the peripheral nervous system.