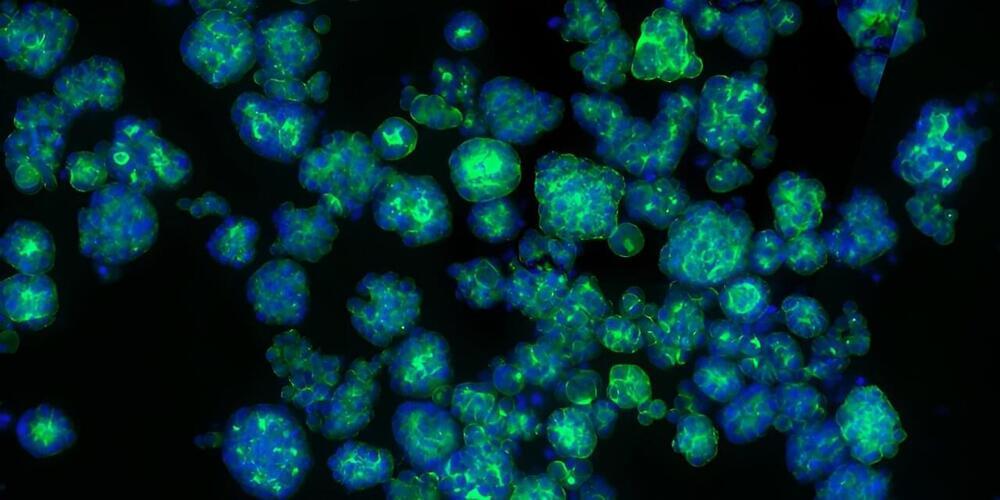
Cancer cells are chameleons. They completely change their metabolism to grow continuously. University of Basel scientists have discovered that high levels of the amino acid arginine drive metabolic reprogramming to promote tumor growth. This study suggests new avenues to improve liver cancer treatment.
The liver is a vital organ with many important functions in the body. It metabolizes nutrients, stores energy, regulates the blood sugar level, and plays a crucial role in detoxifying and removing harmful components and drugs. Liver cancer is one of the world’s most lethal types of cancer. Conditions that cause liver cancer include obesity, excessive alcohol consumption and hepatitis C infection. Early diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic strategies are crucial for improving treatments in liver cancer.
In the past decade, scientists have made much progress in understanding the multiple facets of cancer. Historically, it has long been viewed as a disorder in cell proliferation. However, there is growing evidence that cancer is a metabolic disease.