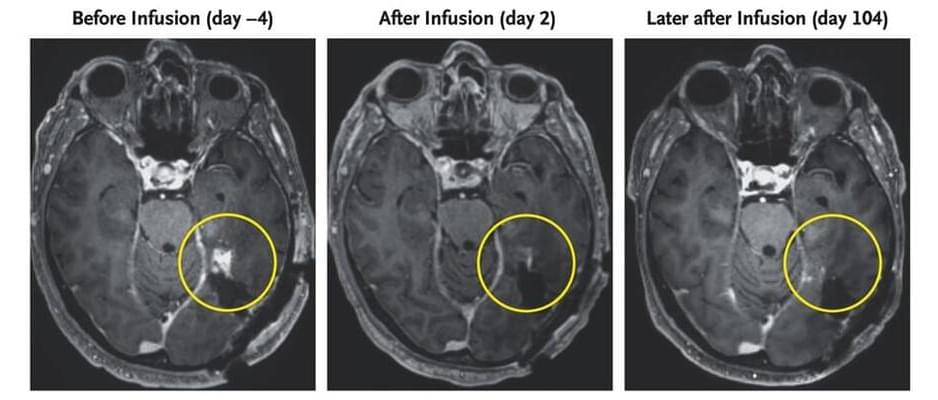
Brain scans of a 72-year-old man diagnosed with a highly aggressive form of cancer known as a glioblastoma have revealed a remarkable regression in his tumor’s size within days of receiving an infusion of an innovative new treatment.
Though the outcomes of two other participants with similar diagnoses were somewhat less positive, the case’s success still bodes well for the search for a way to effectively cure what is currently an incurable disease.
Glioblastomas are typically about as deadly as cancers can get. Emerging from supporting cells inside the central nervous system, they can rapidly develop into malignant masses that claim up to 95 percent of patient lives within five years.