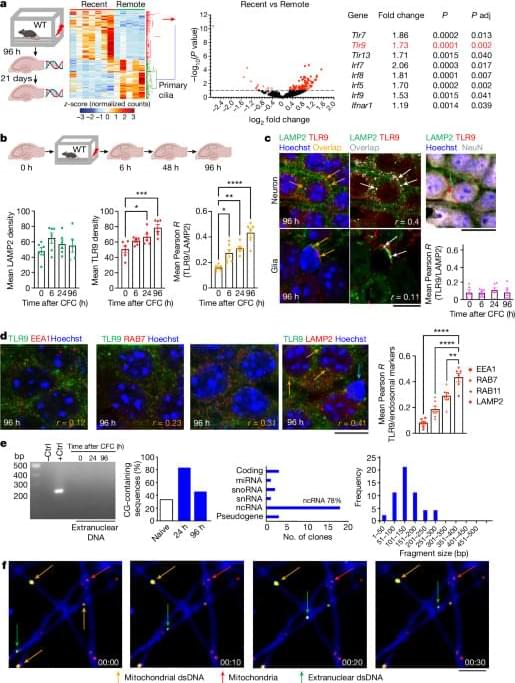
Learning results in persistent double-stranded DNA breaks, nuclear rupture and release of DNA fragments and histones within hippocampal CA1 neurons that, following TLR9-mediated DNA damage repair, results in their recruitment to memory circuits.

Generative A.I. technologies can write poetry and computer programs or create images of teddy bears and videos of cartoon characters that look like something from a Hollywood movie.
Now, new A.I. technology is generating blueprints for microscopic biological mechanisms that can edit your DNA, pointing to a future when scientists can battle illness and diseases with even greater precision and speed than they can today.
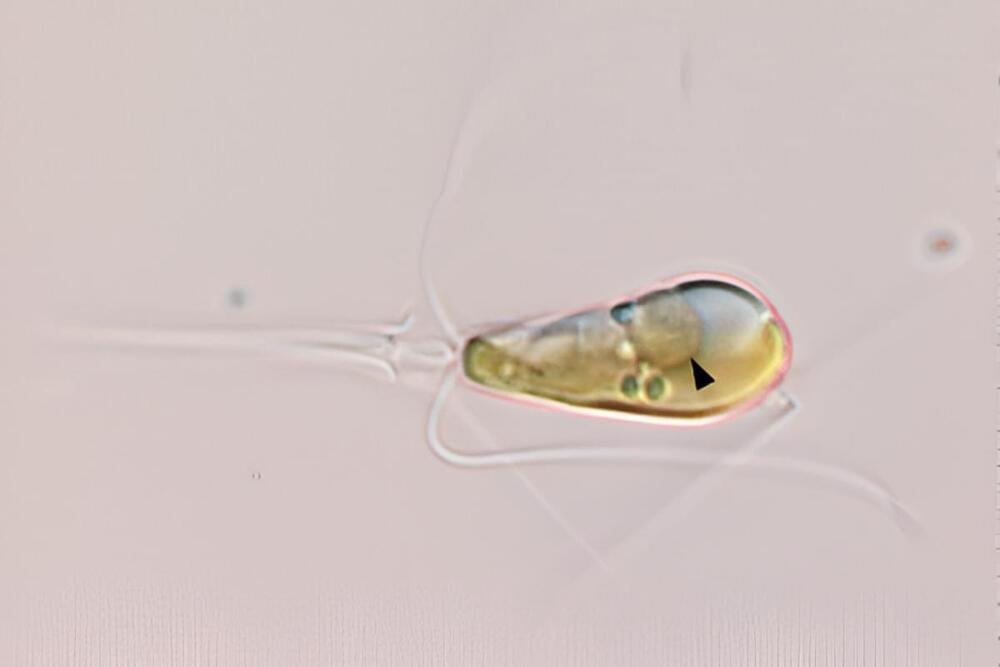
The process, called primary endosymbiosis, has only happened twice in the history of the Earth, with the first time giving rise to all complex life as we know it through mitochondria. The second time that it happened saw the emergence of plants.
Now, an international team of scientists have observed the evolutionary event happening between a species of algae commonly found in the ocean and a bacterium.
“The first time we think it happened, it gave rise to all complex life,” said Tyler Coale, a postdoctoral researcher at University of California, Santa Cruz, who led the research on one of two recent studies that uncovered the phenomenon.


“We want to better understand what causes cancer to resist or respond to immunotherapy to help design more effective strategies for patients,” said senior author Gregory Beatty, MD, PhD, an associate professor of hematology-oncology and the director of clinical and translational research for the Penn Pancreatic Cancer Research Center. “Our findings show that liver cells—with their release of SAA proteins—effectively serve as an immune checkpoint regulating anticancer immunity, making them a promising therapeutic target.”
The study builds on previous research from the team, including co-lead authors Meredith Stone, PhD, a research associate, and Jesse Lee, a graduate student, into liver inflammation in cancer: In a 2019 study, they showed how it promotes pancreatic tumor metastasis to that organ. In 2021, researchers from the Beatty Lab observed that systemic inflammation, involving many of the same molecules implicated in liver metastasis, is associated with worse responses to immunotherapies in pancreatic cancer patients.
The latest study was designed to investigate in more detail how liver inflammation may block the effects of these immune-boosting therapies.

I found this on NewsBreak:
The crew of the International Space Station has stumbled upon a drug-resistant bacteria on board, leaving them baffled as to how it arrived.
Scientists working in the low orbit lab have confirmed the discovery, which raises concerns about the potential evolution of more robust bacteria that could defy current treatments. The unique microgravity environment of the ISS is suspected to be a factor in the bacteria’s persistence.
The origin of the bacteria remains a mystery to the team, who can’t recall how it might have been introduced to the station. Life in space presents different growth conditions for organisms, leading to alternative evolutionary paths compared to their Earth-bound counterparts.

People who have obesity, or are tall with fat accumulation around their middle, are at an increased risk of colorectal cancer, regardless of their ancestry.
Repeated studies have made the link between obesity and height and increased cancer risk, including colorectal cancer. For example, a study published in 2022 showed that people of European ancestry who are tall and centrally obese, as well as people with general obesity, have a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.