Heart tumor or cardiac tumor is a rare condition that is prevalent in adults. Though the exact cause is unknown, genetics could play a role.
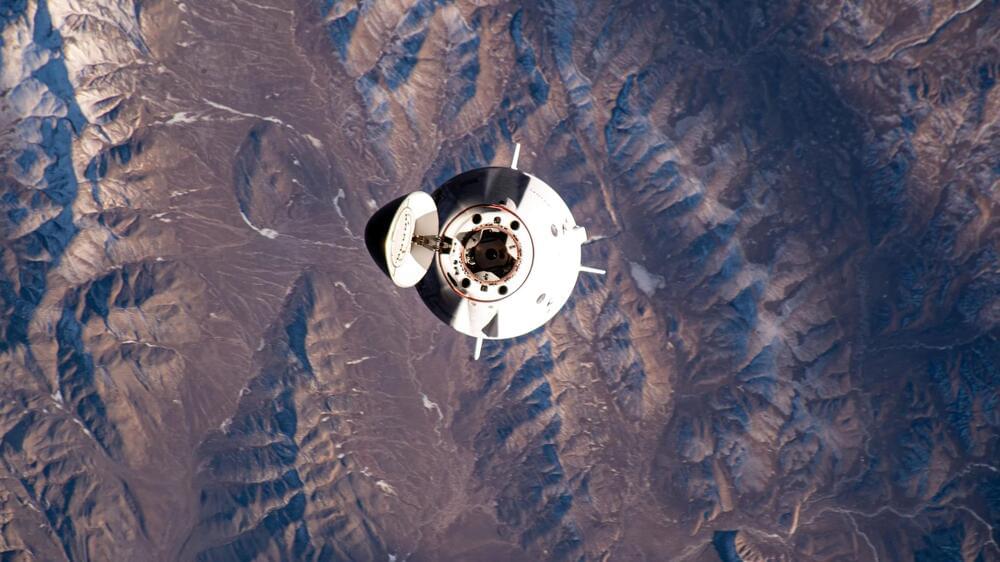



Eleven astronauts and cosmonauts from around the world are living and working together aboard the International Space Station (ISS) today, January 22. The four Axiom Mission 3 (Ax-3) private astronauts met the seven Expedition 70 crew members on Saturday beginning two weeks of dual operations.
The Ax-3 crew spent the weekend getting familiar with space station systems and emergency procedures before starting Monday with a full schedule of science and media activities. Ax-3 Commander Michael López-Alegría joined Pilot Walter Villadei and studied how microgravity affects the biochemistry of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s to improve health on Earth and in space. The duo later inserted samples into a fluorescence microscope for a study seeking to prevent and predict cancer diseases to protect crews in space and humans on Earth.
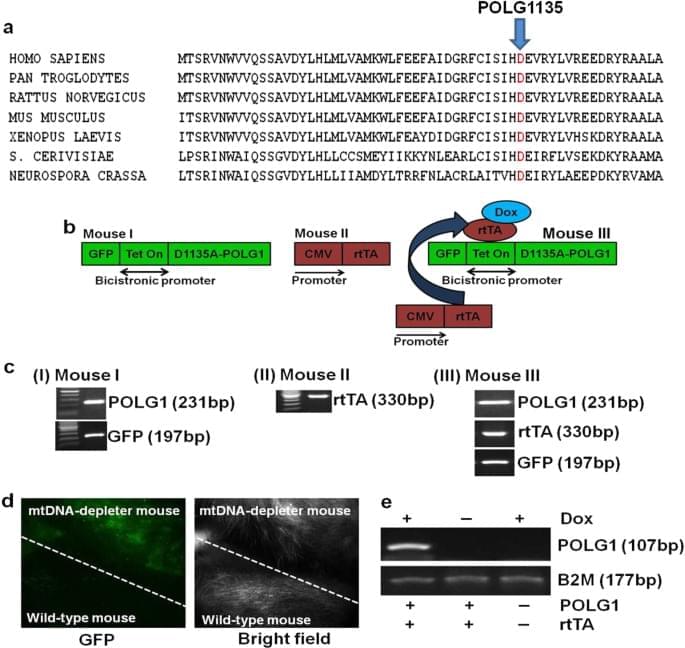
Year 2018 Age related symptoms may be even more simple to reverse by recharging the mitochondria then eventually we can have genetically engineered mitochondria to run longer so the cycles of the human body could run indefinitely.
Singh, B., Schoeb, T.R., Bajpai, P. et al. Reversing wrinkled skin and hair loss in mice by restoring mitochondrial function. Cell Death Dis 9, 735 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0765-9
With the insertion of a little math, Sandia National Laboratories researchers have shown that neuromorphic computers, which synthetically replicate the brain’s logic, can solve more complex problems than those posed by artificial intelligence and may even earn a place in high-performance computing.
The findings, detailed in a recent article in the journal Nature Electronics, show that neuromorphic simulations employing the statistical method called random walks can track X-rays passing through bone and soft tissue, disease passing through a population, information flowing through social networks and the movements of financial markets, among other uses, said Sandia theoretical neuroscientist and lead researcher James Bradley Aimone.
“Basically, we have shown that neuromorphic hardware can yield computational advantages relevant to many applications, not just artificial intelligence to which it’s obviously kin,” said Aimone. “Newly discovered applications range from radiation transport and molecular simulations to computational finance, biology modeling and particle physics.”
What if AI could tell us we have cancer before we show a single symptom? Steve Quake, head of science at the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, explains how AI can revolutionize science.
Up next, Harvard professor debunks the biggest exercise myths ► • Harvard professor debunks the biggest…
AI can help us understand complex systems like our cells. better. The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative is committed to building one of the world’s biggest non-profit life science AI computing clusters to help build digital models of what goes wrong in cells when we get diseases like diabetes or cancer and more.
Read the video transcript ► https://bigthink.com/sponsored/future…
We created this video in partnership with the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative.
Go Deeper with Big Think:

Tumors constantly shed DNA from dying cells, which briefly circulates in the patient’s bloodstream before it is quickly broken down.
Caption :
A new way to recover significantly more circulating tumor DNA in a blood sample could improve the sensitivity of liquid biopsies used to detect, monitor, and guide treatment of tumors.
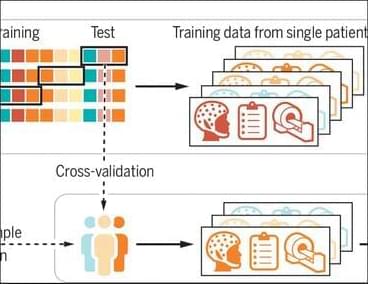
MachineLearning clinical prediction models fail to generalize across trial data, a new Science study finds. The results “require reexamination of the practical challenges that precision medicine is facing.” Learn more in a new Science Perspective:
The prediction of individual treatment responses with machine learning faces hurdles.
Frederike H. Petzschner [email protected] Authors Info & Affiliations
Science.

https://www.news-medical.net/news/20240123/New-study-reveals…tment.aspx ASMicrobiology
In a recent study published in the American Society for Microbiology, researchers developed a novel rabbit infection model to investigate meropenem’s resistance development potential and antibacterial efficacy.
Study: Molecular pharmacodynamics of meropenem for nosocomial pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Image Credit: Sam Rana/Shutterstock.com.
Background
Meropenem is an antibacterial drug representing the current gold standard in hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) care.
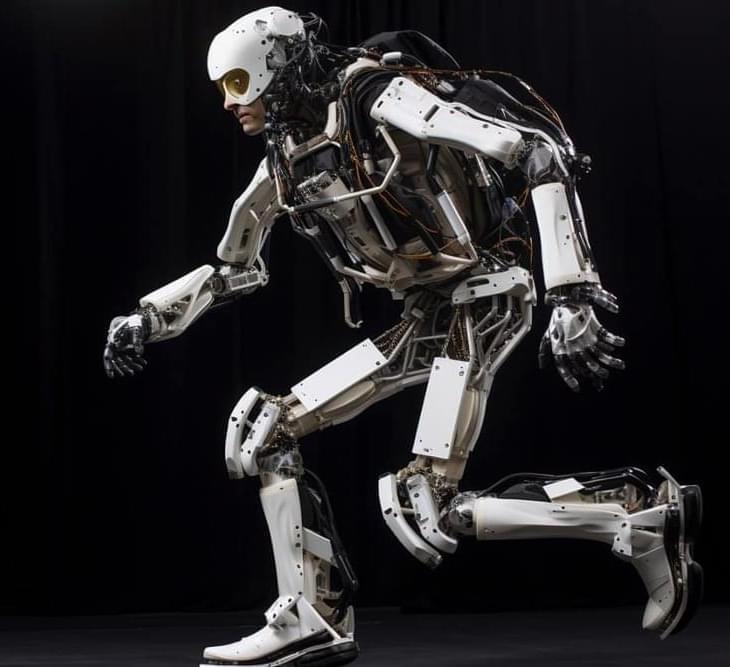

The article repeats itself a bit but there’s some good parts about an exoskeleton, advanced algorithm and bipedal robots and prosthetics. It’ll basically apply to those future industries.
We typically don’t think about it whilst doing it, but walking is a complicated task. Controlled by our nervous system, our bones, joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues (i.e., the musculoskeletal system) must move in coordination and respond to unexpected changes or disturbances at varying speeds in a highly efficient manner. Replicating this in robotic technologies is no small feat.
Now, a research group from Tohoku University Graduate School of Engineering has replicated human-like variable speed walking using a musculoskeletal model – one steered by a reflex control method reflective of the human nervous system. This breakthrough in biomechanics and robotics sets a new benchmark in understanding human movement and paves the way for innovative robotic technologies.