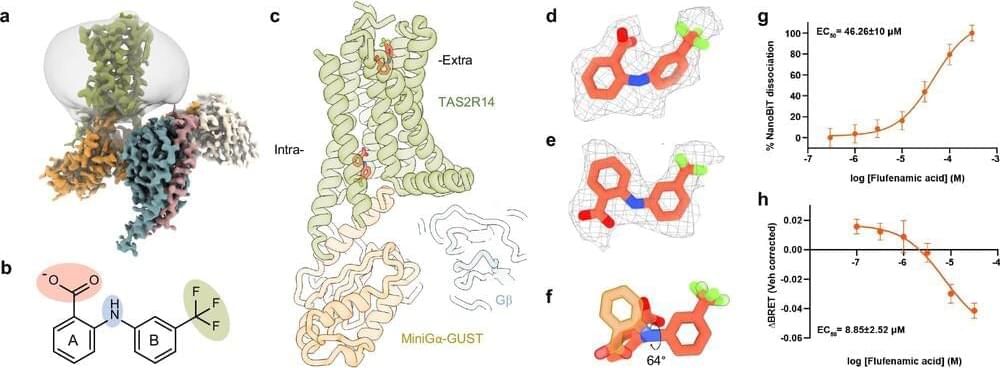
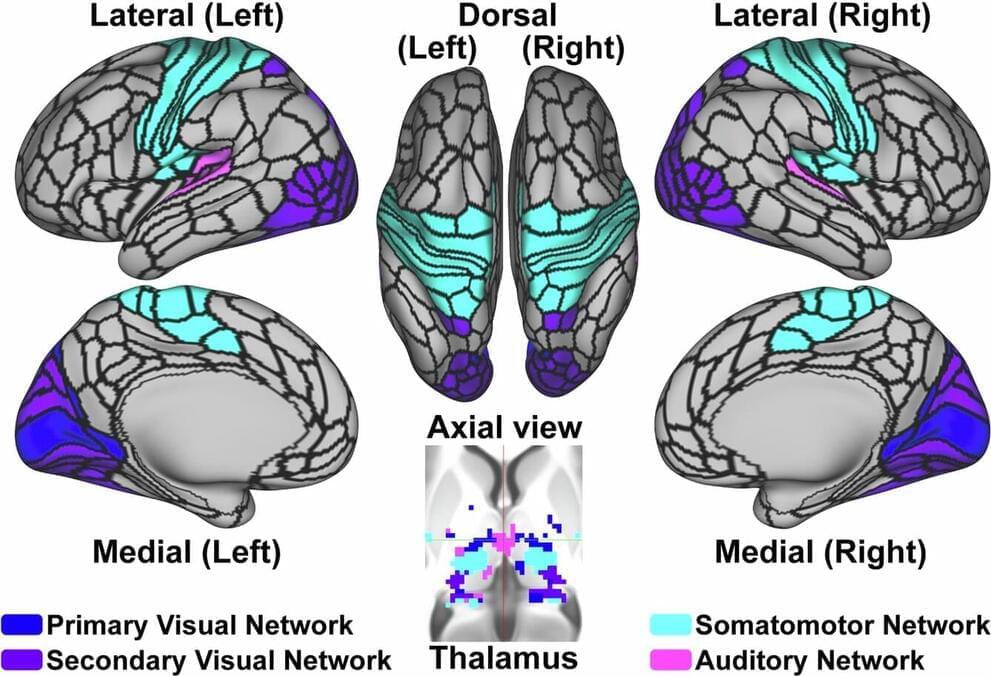
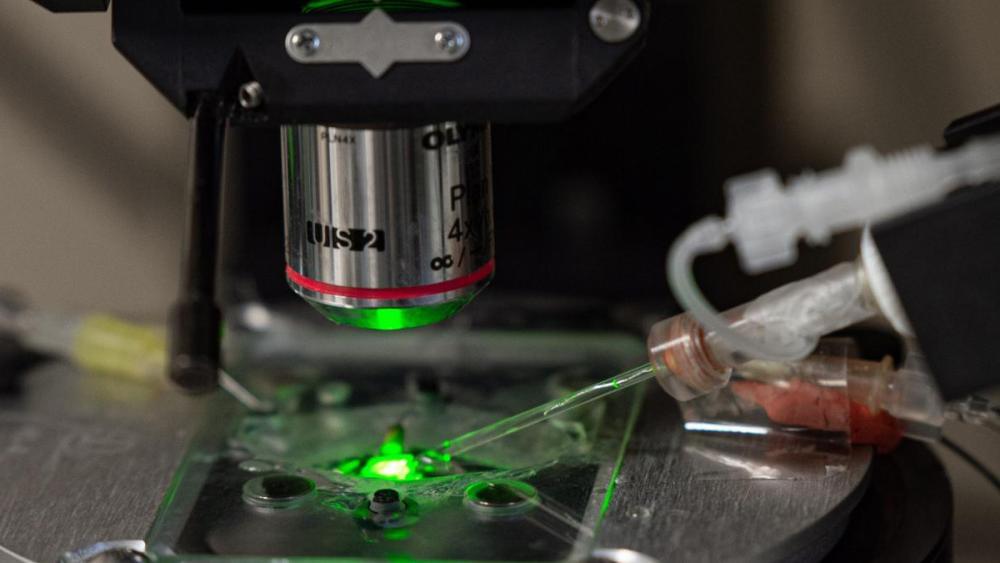
Advance paves the way for broad applications in medicine and biotech. Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering and the University of Rome Tor Vergata in Italy have developed synthetic genes that function like the genes in living cells.
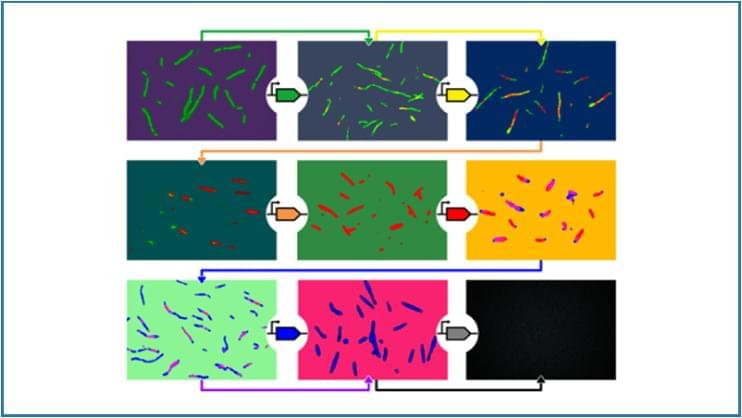
The artificial genes can build intracellular structures through a cascading sequence that builds self-assembling structures piece by piece. The approach is similar to building furniture with modular units, much like those found at IKEA. Using the same parts, one can build many different things and it’s easy to take the set apart and reconstruct the parts for something else. The discovery offers a path toward using a suite of simple building blocks that can be programmed to make complex biomolecular materials, such as nanoscale tubes from DNA tiles. The same components can also be programmed to break up the design for different materials.
The research study was recently published in Nature Communications and led by Elisa Franco, a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering and bioengineering at UCLA Samueli. Daniela Sorrentino, a postdoctoral scholar in Franco’s Dynamic Nucleic Acid Systems lab, is the study’s first author.