Musk said he thinks Neuralink will “solve a lot of brain-related diseases,” naming autism and schizophrenia as examples. Autism is not a disease.



Tissues take shape during development through a series of morphogenetic movements guided by local cell-scale forces. While current in vitro approaches subjecting tissues to homogenous stresses, it is currently no possible to recapitulate highly local spatially varying forces. Here we develop a method for local actuation of organoids using embedded magnetic nanoparticles. Sequential aggregation of magnetically labelled human pluripotent stem cells followed by actuation by a magnetic field produces localized magnetic clusters within the organoid. These clusters impose local mechanical forces on the surrounding tissue in response to applied global magnetic fields. We show that precise, spatially defined actuation provides short-term mechanical tissue perturbations as well as long-term cytoskeleton remodeling. We demonstrate that local magnetically-driven actuation guides asymmetric growth and proliferation, leading to enhanced patterning in human neural organoids. We show that this approach is applicable to other model systems by observing polarized patterning in paraxial mesoderm organoids upon local magnetic actuation. This versatile approach allows for local, controllable mechanical actuation in multicellular constructs, and is widely applicable to interrogate the role of local mechanotransduction in developmental and disease model systems.
The authors have declared no competing interest.

Choanoflagellates, animals’ closest relatives, have pluripotency genes, reshaping views on their evolution.
The research highlights how evolution repurposes existing genetic tools, turning them into versatile drivers of innovation. This adaptability underscores how foundational processes in unicellular organisms laid the groundwork for the development of complex life forms.
Beyond rewriting evolutionary biology, the findings could revolutionize regenerative medicine. Understanding how ancient genes enabled pluripotency offers new pathways to refine stem cell therapies and enhance cell reprogramming techniques.
For instance, synthetic versions of these genes might outperform native animal genes, opening possibilities for more efficient treatments for diseases or tissue damage.
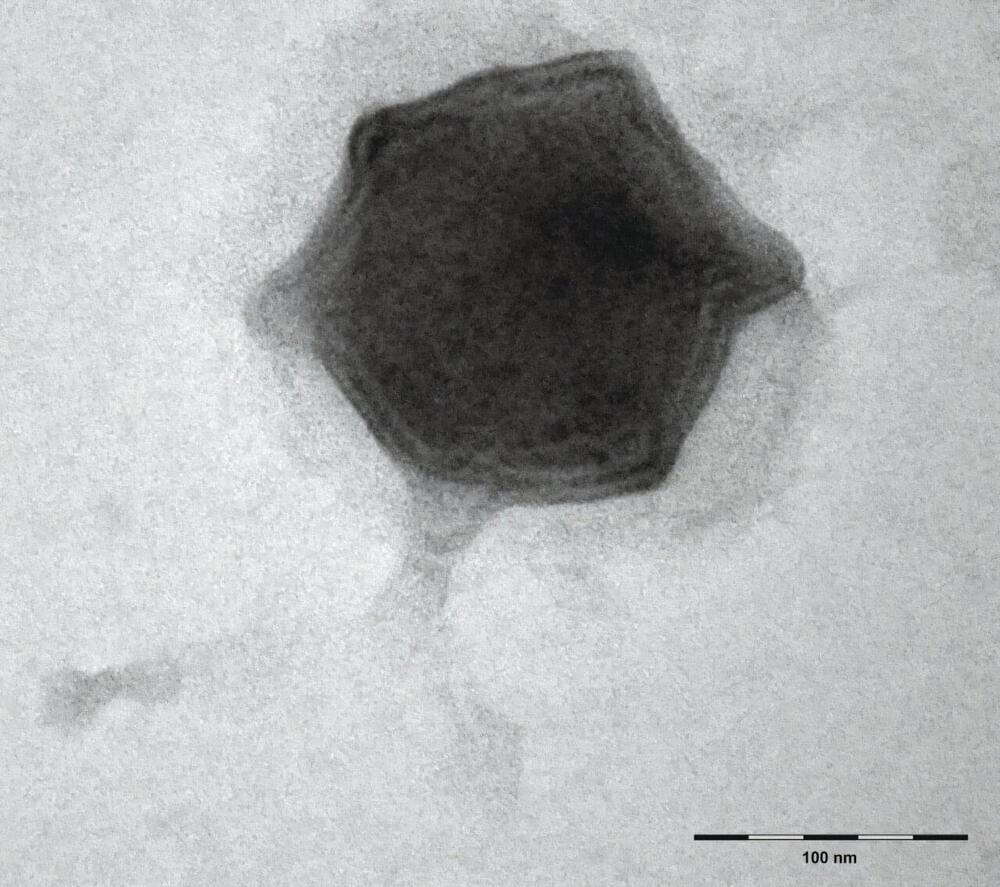
Scientists from the Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences found forty new freshwater viruses infecting aquatic microorganisms this year. The first one, which they isolated and described in detail, was named Budvirus after the South Bohemian capital České Budějovice. It belongs to “Giant Viruses” and it infects unicellular algae called cryptophytes.
Researchers have confirmed that this virus has an important role in the ecosystem, as it controls algal bloom, helping to maintain balance in the aquatic environment. The discoveries of all the viruses were made at the Římov reservoir near České Budějovice, which has been regularly monitored by South Bohemian hydrobiologists for five decades and is one of the most studied freshwater reservoirs in Europe. The work is published in The ISME Journal.
Although we have freshwater ecosystems such as lakes, ponds, reservoirs and rivers all around us, their microscopic representatives, especially viruses and bacteria, are still a little-explored area. A drop of water can contain a million bacteria and ten times more viruses, but only a handful of them have been described. Recent methods, such as environmental DNA analysis, are making great strides in the study of the aquatic microworld. This is also one of the methods used by the Czech scientific team.
Our bodies divest themselves of 60 billion cells every day through a natural process of cell culling and turnover called apoptosis.
These cells — mainly blood and gut cells — are all replaced with new ones, but the way our bodies rid themselves of material could have profound implications for cancer therapies in a new approach developed by Stanford Medicine researchers.
They aim to use this natural method of cell death to trick cancer cells into disposing of themselves. Their method accomplishes this by artificially bringing together two proteins in such a way that the new compound switches on a set of cell death genes, ultimately driving tumor cells to turn on themselves. The researchers describe their latest such compound in a paper published Oct. 4 in Science.
Sometimes there are slightly different versions, or sequences of genes. There are several versions of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene, for example. One of them, called APOE4, has been linked to a much higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, and carriers often have worse forms of the disease compared to carriers of other forms like APOE3. There are immune cells in the brain called microglia that help protect the brain from damage and harm. But when APOE4 is expressed, microglia seem to start to cause inflammation, and misfolded proteins to form in the brain, which can lead to serious problems. The findings have been reported in Cell Stem Cell.
In this work, the researchers developed a mouse model that could generate the human APOE4 protein in their brains. Next, the investigators eliminated microglia from these mouse brains. The formation of two misfolded proteins that are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s diseases: amyloid and tau, was halted.
There are many processes and proteins that help the body fight a flu infection. One of them is known as IFITM3. Researchers have now shown that this protein can help prevent viruses from mutating after they have infected a new host. But some people are deficient in IFITM3, which can raise their risk of a severe flu infection. That deficiency is not unusual in some groups. For example, around twenty percent of Chinese people and four percent of people with European ancestry carry variants in IFITM3 that can interfere with the protein’s expression. This study has shown that these genetic variants can allow flu viruses to establish infections even when the virus is present at very low levels that would not usually cause infection. The findings have been reported in Nature Communications.
The IFITM3 (interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3) protein is part of the innate immune system, and is generated at high levels after the detection of a flu infection. It can sequester viral particles so that they are not able to replicate, which reduces the severity of flu infections. Mouse models that are IFITM3 deficient are extremely vulnerable to the flu.

Summary: AI models trained on MRI data can now distinguish brain tumors from healthy tissue with high accuracy, nearing human performance. Using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning from tasks like camouflage detection, researchers improved the models’ ability to recognize tumors.
This study emphasizes explainability, enabling AI to highlight the areas it identifies as cancerous, fostering trust among radiologists and patients. While slightly less accurate than human detection, this method demonstrates promise for AI as a transparent tool in clinical radiology.