Volatile anesthetics reversibly abolish consciousness or motility in animals, plants, and single-celled organisms (Kelz and Mashour, 2019; Yokawa et al., 2019). For humans, they are a medical miracle that we have been benefiting from for over 150 years, but the precise molecular mechanisms by which these molecules reversibly abolish consciousness remain elusive (Eger et al., 2008; Hemmings et al., 2019; Kelz and Mashour, 2019; Mashour, 2024). The functionally relevant molecular targets for causing unconsciousness are believed to be one or a combination of neural ion channels, receptors, mitochondria, synaptic proteins, and cytoskeletal proteins.
The Meyer–Overton correlation refers to the venerable finding that the anesthetic potency of chemically diverse anesthetic molecules is directly correlated with their solubility in lipids akin to olive oil (S. R. Hameroff, 2018; Kelz and Mashour, 2019). The possibility that general anesthesia might be explained by unitary action of all (or most) anesthetics on one target protein is supported by the Meyer–Overton correlation and the additivity of potencies of different anesthetics (Eger et al., 2008). Together these results suggest that anesthetics may act on a unitary site, via relatively nonspecific physical interactions (such as London/van der Waals forces between induced dipoles).
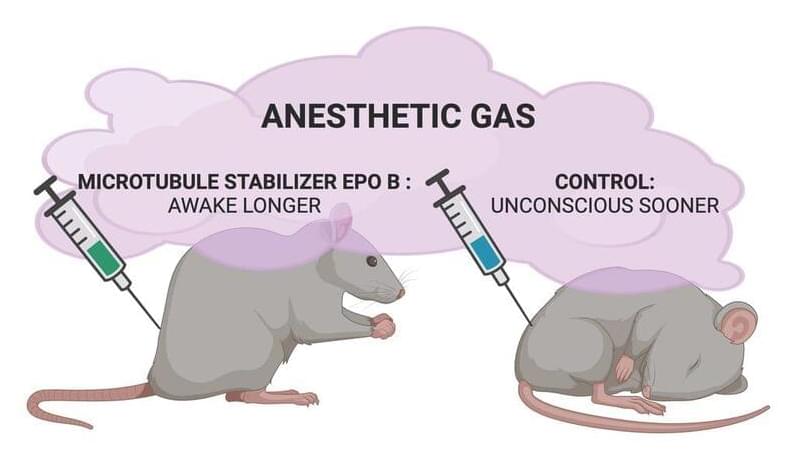
Cytoskeletal microtubules (MTs) have been considered as a candidate target of anesthetic action for over 50 years (Allison and Nunn, 1968; S. Hameroff, 1998). Other membrane receptor and ion channel proteins were ruled out as possible unitary targets by exhaustive studies culminating in Eger et al. (2008). However, MTs (composed of tubulin subunits) were not ruled out and remain a candidate for a unitary site of anesthetic action. MTs are the major components of the cytoskeleton in all cells, and they also play an essential role in cell reproduction—and aberrant cell reproduction in cancer—but in neurons, they have additional specialized roles in intracellular transport and neural plasticity (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2015). MTs have also been proposed to process information, encode memory, and mediate consciousness (S. R. Hameroff et al., 1982; S. Hameroff and Penrose, 1996; S. Hameroff, 2022). While classical models predict no direct role of MTs in neuronal membrane and synaptic signaling, Singh et al. (2021a) showed that MT activities do regulate axonal firing, for example, overriding membrane potentials. The orchestrated objective reduction (Orch OR) theory proposes that anesthesia directly blocks quantum effects in MTs necessary for consciousness (S. Hameroff and Penrose, 2014). Consistent with this hypothesis, volatile anesthetics do bind to cytoskeletal MTs (Pan et al., 2008) and dampen their quantum optical effects (Kalra et al., 2023), potentially contributing to causing unconsciousness.