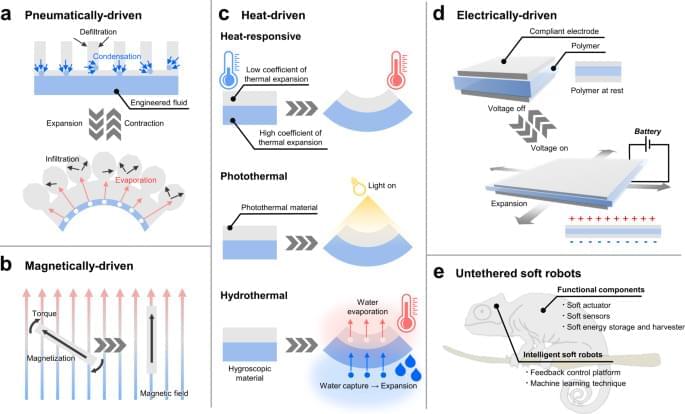
Soft actuators produce the mechanical force needed for the functional movements of soft robots, but they suffer from critical drawbacks since previously reported soft actuators often rely on electrical wires or pneumatic tubes for the power supply, which would limit the potential usage of soft robots in various practical applications. In this article, we review the new types of untethered soft actuators that represent breakthroughs and discuss the future perspective of soft actuators. We discuss the functional materials and innovative strategies that gave rise to untethered soft actuators and deliver our perspective on challenges and opportunities for future-generation soft actuators.
For pneumatic actuators, the pneumatic pumps serve an essential role in generating a mechanical force by using compressed gas or moving the liquid for the rapid fluid pressure increase. Yet, the incorporation of the pneumatic pump into the soft robotics would impair the mobility and the core functionalities of the soft robots because the pumps are usually relatively bulky and heavy when compared to the soft robots themselves. To address this issue, several recent studies demonstrated pump-less pneumatic actuation by employing the phase change materials that generate the volume change as the materials switch between liquid and gaseous states, thus resulting in the inflation and deflation of actuators. Here, the pump-less pneumatic actuators can be defined as the soft actuators that do not use the actual pump but generate a pneumatic force by the phase change of material just as if utilizing the pneumatic pump. In other words, the pump-less pneumatic actuators just reproduce the end effect of the pump by a different working mechanism without using the actual pump. The absence of the pneumatic pump in the robotic design also eliminates the need for pneumatic tubes to infuse/extract air into/from the actuator, thereby making the design completely untethered.
Likewise, external stimuli can deliver a considerable amount of mechanical displacement and force needed to actuate the soft robots in an untethered manner: the external stimuli in this article include magnetic field, heat, electricity, light, and humidity. Hence, without physically connecting the electrical tethering to the soft actuators to provide the power source, the external stimuli can enable the soft actuator to produce mechanical displacement since the materials are designed to actuate as programmed. As opposed to the pneumatics-based soft actuators that require the onboard power source (such as a battery or self-powering energy harvesting devices) to supply power to induce pneumatic force, some of these actuators receive the power to induce mechanical displacement in a completely untethered fashion. For example, systematic manipulation of a magnetic field can control the movement of the magnet-driven soft actuator as intended without any type of wiring. Similarly, if the antennas are incorporated into the soft robotic system, electromagnetic waves can be utilized to provide power wirelessly to operate the soft actuators5,6,7,8, or it also enables the remote control of the actuators via wireless communication9,10 Therefore, external stimuli-driven soft actuators retain the potential to represent the breakthrough in the field of soft robotics although there exist considerable limitations to be resolved. In this light, it would be a highly valuable resource to introduce untethered soft actuators and discuss the future perspective of new types of soft robots. There are a considerable number of review articles on soft actuators and robotics11,12,13,14,15. However, no review paper has dealt with recent advances in untethered soft actuators for soft robotics that demonstrated meaningful outcomes within a few years. Recently, roboticists and researchers proposed an explosive number of soft actuators for soft robots based on innovative structural designs and functional materials that represent breakthroughs in the field of soft robotics. Furthermore, as the field of soft actuators is relatively new and drawing a substantial amount of interest in the related fields, there exists a demand for an article that systematically reviews the current trend and informs the opportunities to contribute to the field. In this regard, we believe that the timely and thorough review of the recent advances in untethered soft actuators will be informative for the general readers who wish to draw insights and gain potential perspectives in the field.
In this article, we introduce the representative works of the untethered soft actuators that serve as breakthroughs in soft robotics and further discuss the imminent challenges of the soft actuators to be addressed. Soft actuators can also be applied to rigid robots since the actuators reviewed in this paper operate in an untethered configuration. However, we intentionally circumscribed the scope and focused mainly on soft actuators for soft robots because the incorporation of soft actuators into the soft robot can make the entire robot soft and compliant. There exist specific applications where the soft robots exhibit comparative strengths over rigid robots such as navigating through the tortuous space16,17, exploring deep-sea at extremely high pressure18, or minimally invasive surgery19. Furthermore, to present these works systematically, the paper categorizes the soft actuators by four representative working mechanisms (1. pneumatically/hydraulically-driven, 2. magnetically-driven, 3. heat-driven, and 4. electrically-driven) and further examines each actuating mechanism in relation to the untethered soft robots as illustrated in Fig. 1. The paper examines the strengths and limitations of each actuating method and concludes with the future perspective of untethered soft actuators for soft robotics. Box 1 provides the general summary that addresses the strategies to provide the power source for actuation control of the soft robots. Additionally, Table 1 draws the overall comparison of each soft actuating method to highlight the strengths, weaknesses, and other key features such as response time and output force range. On the other hand, Table 2 captures key highlights of representative soft actuators that operate based on a variety of mechanisms and thus delivers a more specific comparison.