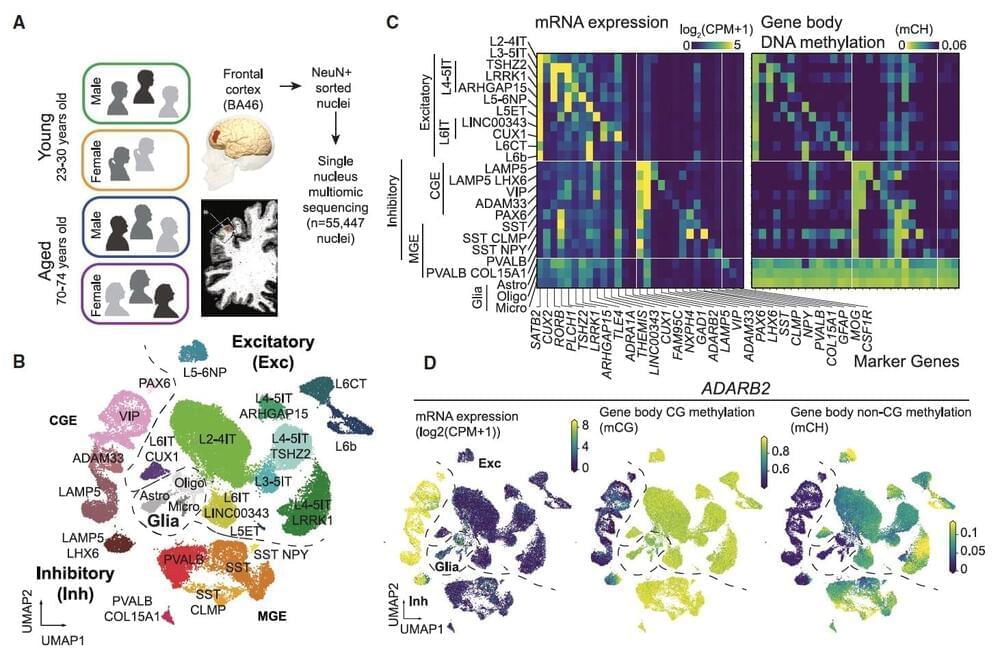
Aging is known to have profound effects on the human brain, prompting changes in the composition of cells and the expression of genes, while also altering aspects of the interaction between genes and environmental factors. While past neuroscience studies have pinpointed many of the molecular changes associated with aging, the age-related genetic factors influencing specific neuron populations remains poorly understood.
Recent studies on flies, mice, primates and human brain tissue utilizing single-cell or single-nucleus RNA-sequencing and genetic experimental techniques shed new light on these cell-type-specific changes. For instance, they unveiled the effects of aging on glial cells in the mouse and human brain, associations between cell-specific changes and modified chromatin proteins, and the influence of DNA methylation in the aging of various tissues.
Researchers at University of California (UC) San Diego and Salk Institute recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how both age and sex impact human cortical neurons at a single-cell level. Their findings, published in Neuron, offer new insights into how aging affects cell composition, gene expression and DNA methylation across human brain cell types, while also uncovering differences between gene expression and DNA methylation in females and males.