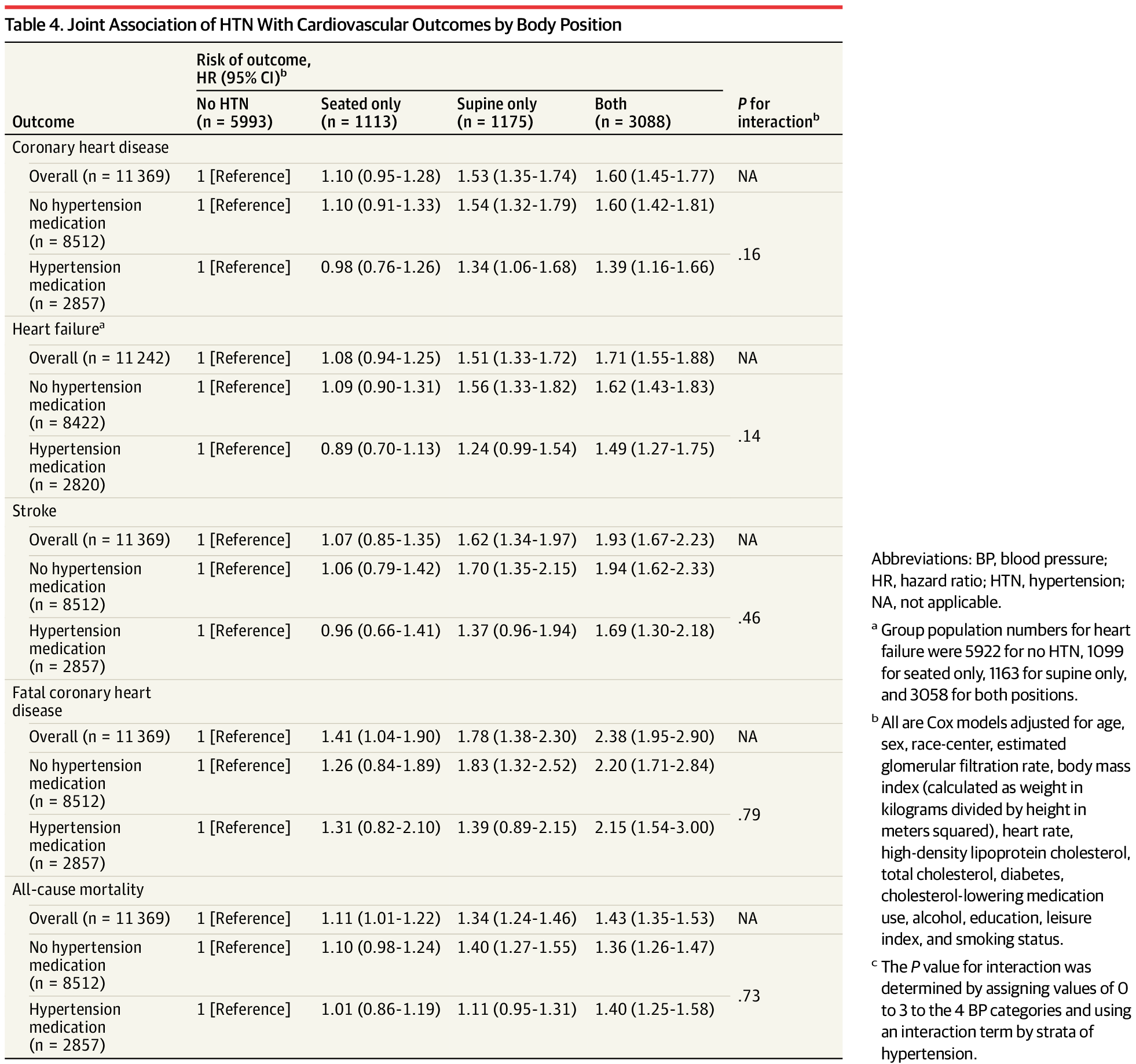
This cohort study investigates the association of supine hypertension with cardiovascular disease and mortality in middle-aged adults.

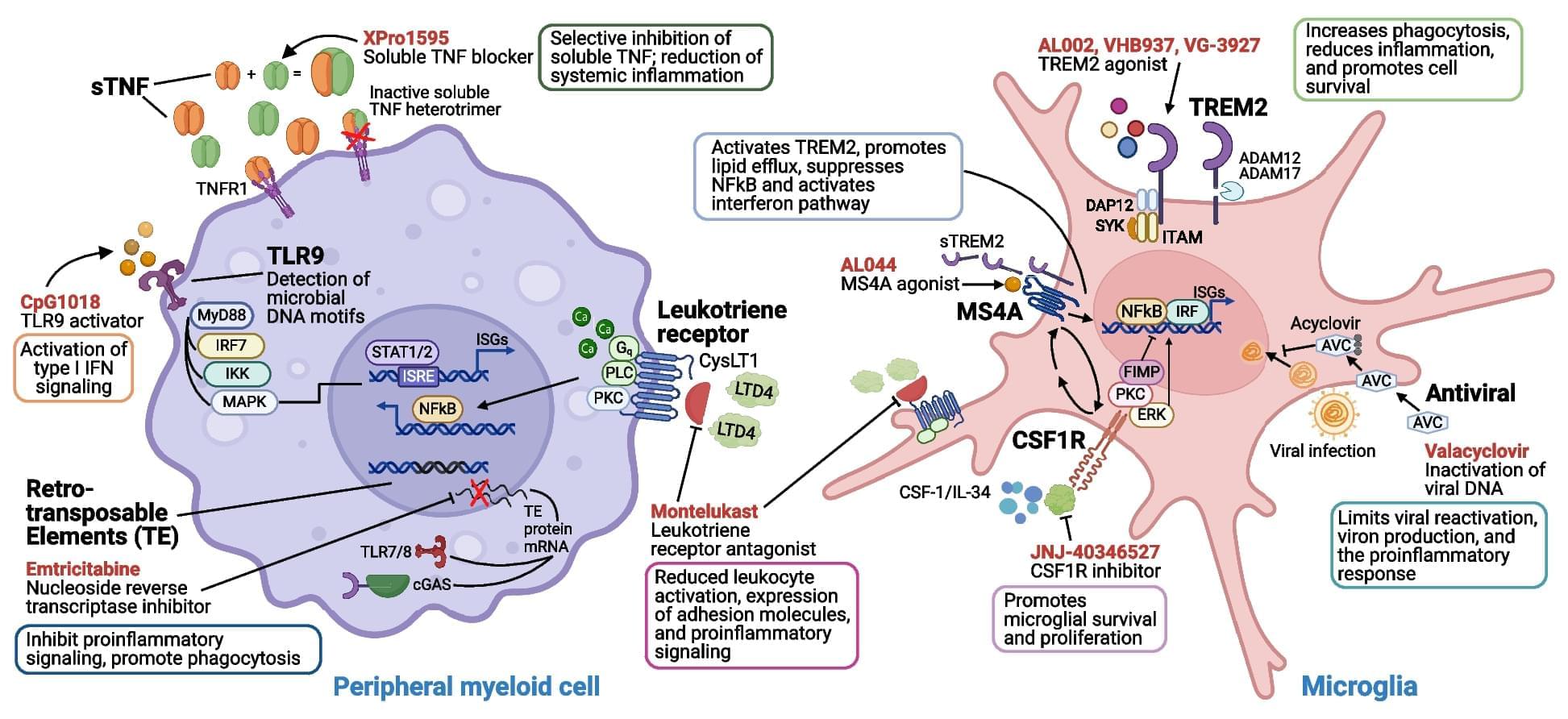
Immune mechanisms play a fundamental role in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis, suggesting that approaches which target immune cells and immunologically relevant molecules can offer therapeutic opportunities beyond the recently approved amyloid beta monoclonal therapies. In this review, we provide an overview of immunomodulatory therapeutics in development, including their preclinical evidence and clinical trial results. Along with detailing immune processes involved in AD pathogenesis and highlighting how these mechanisms can be therapeutically targeted to modify disease progression, we summarize knowledge gained from previous trials of immune-based interventions, and provide a series of recommendations for the development of future immunomodulatory therapeutics to treat AD.
Scientists have identified more than 9,000 of these synthetic chemicals. Study reveals concerning link between everyday household products and childhood c

Magnesium is a common chemical element, an alkaline earth metal, which is highly chemically reactive and is very light (even lighter than aluminum). Magnesium is abundant in plants and minerals and plays a role in human physiology and metabolism. In the cosmos, it is produced by large aging stars.
Among its physical properties, while it is a good conductor of electricity, magnesium is not known to be a superconductor. Superconductors are particularly promising materials with the potential to revolutionize energy transmission, medical imaging, and quantum computing, and are defined by their ability to conduct electricity without resistance below a certain critical temperature.
Recently, with my colleague Giovanni Ummarino from Turin Polytechnic, I have started challenging the textbook paradigm that states only certain elements in the periodic table can be superconductors. In particular, my colleague and I have shown that the phenomenon of quantum confinement can turn non-superconducting elements into superconductors. Our research is published in Condensed Matter.
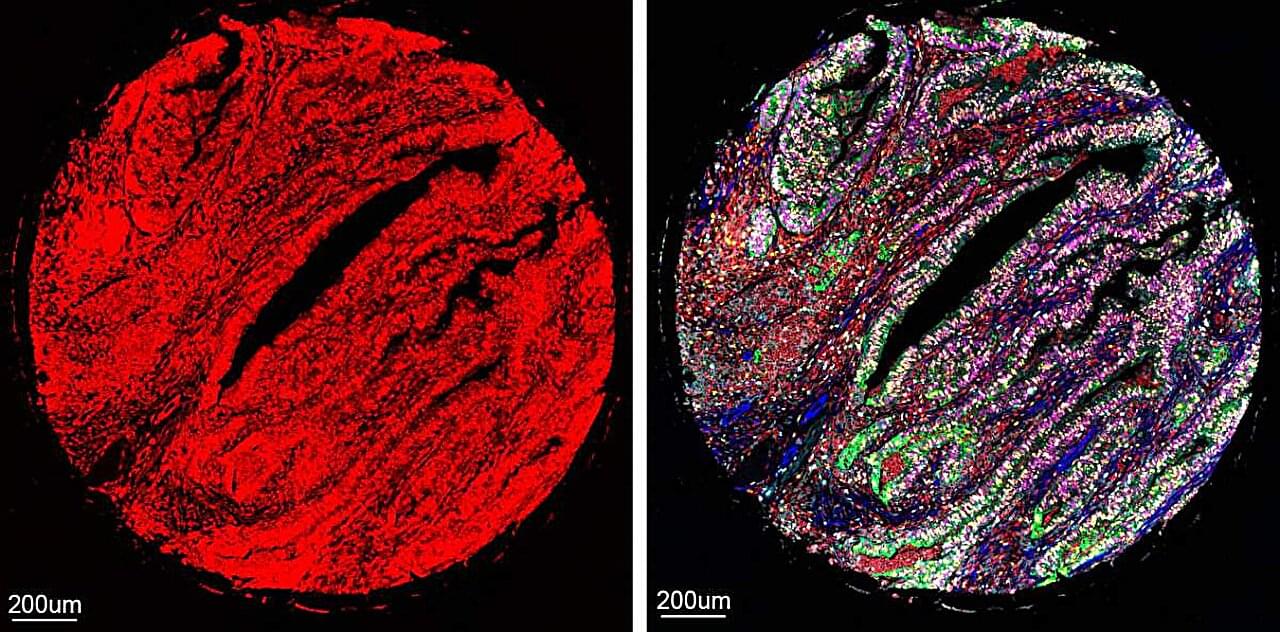
AI systems already work their magic in many areas of biomedical science, helping to solve protein structure, discover hidden patterns in the genome and process massive amounts of biological data. Now, an AI-assisted technology developed at the Weizmann Institute of Science and published in Nature Biotechnology may grant researchers and physicians an unprecedented means of peering deep into the body’s tissues by making it possible to simultaneously view more proteins than ever before, in a tissue sample.
“To understand how any particular tissue works, it’s crucial to measure lots of its proteins at the same time,” says Dr. Leeat Keren of Weizmann’s Molecular Cell Biology Department, who headed the research team. “This gives us an idea of which cells are present in the tissue and how they communicate and interact with one another.”
Keren explains that this knowledge is vital to the study of disease processes. Cancerous growths, for example, contain, in addition to tumor cells, various other cell types, including healthy cells of the tissue the tumor is growing on and of the immune system. The cellular makeup of the tumor and how those cell types interact with one another can determine the effectiveness of therapies or be used to predict which patients have a better prognosis and which are likely to develop metastases. Such findings, in turn, can lead to improved personalized treatments.


Chronic kidney disease (CKD) populations face an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), yet many remain undertreated with statins for primary prevention of CVD despite meeting eligibility criteria. We examined trends in statin use for primary prevention among individuals with CKD before and after the release of the 2013 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guideline recommending statin use for lipid management in selected adults with CKD.

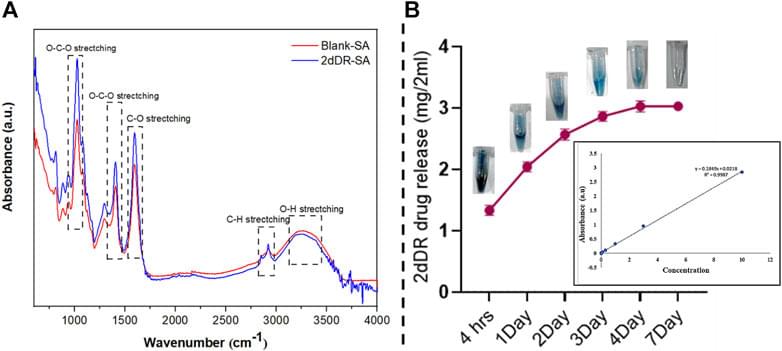
Androgenic alopecia (AGA) affects both men and women worldwide. New blood vessel formation can restore blood supply and stimulate the hair regrowth cycle. Recently, our group reported that 2-deoxy-D-ribose (2dDR) is 80%–90% as effective as VEGF in the stimulation of neovascularization in in vitro models and in a chick bioassay. In this study, we aimed to assess the effect of 2dDR on hair growth. We prepared an alginate gel containing 2dDR, polypropylene glycol, and phenoxyethanol. AGA was developed in C57BL6 mice by intraperitoneally injecting testosterone (TE). A dihydrotestosterone (DHT)-treated group was used as a negative control, a minoxidil group was used as a positive control, and we included groups treated with 2dDR gel and a combination of 2dDR and minoxidil. Each treatment was applied for 20 days. Both groups treated with 2dDR gel and minoxidil stimulated the morphogenesis of hair follicles. H&E-stained skin sections of C57BL/6 mice demonstrated an increase in length, diameter, hair follicle density, anagen/telogen ratio, diameter of hair follicles, area of the hair bulb covered in melanin, and an increase in the number of blood vessels. Masson’s trichrome staining showed an increase in the area of the hair bulb covered in melanin. The effects of the FDA-approved drug (minoxidil) on hair growth were similar to those of 2dDR (80%–90%). No significant benefit were observed by applying a combination of minoxidil with 2dDR. We conclude that 2dDR gel has potential for the treatment of androgenic alopecia and possibly other alopecia conditions where stimulation of hair regrowth is desirable, such as after chemotherapy. The mechanism of activity of 2dDR remains to be established.
Alopecia can occur due to hormonal imbalance, thyroid problems, certain medications, and autoimmune diseases. It can be induced by blood thinning medications, contraceptives, antidepressants, steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, beta and calcium-channel blockers, retinoids, and chemotherapeutics (Vicky et al., 2018). Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenic alopecia (AGA), is one of the most widespread hair loss conditions in the world (Yohei et al., 2018). In the pathophysiology of AGA, testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by 5α-reductase. DHT then binds to androgen receptors in the dermal papilla cells (DPCs) of sensitive hair follicles and prolongs the telogen phase, causing hair loss before the growth of new hair (Izabela et al., 2014). AGA is said to affect 30% of Asian men by age 30 and 50% by age 50 (Yohei et al., 2018). It also affects 80% of White men and 40% of White women by age 70 (Pietro et al., 2019).
Dr. Sean Tucker, Ph.D. is the Founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Vaxart Inc. ( https://vaxart.com/ ), a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing…