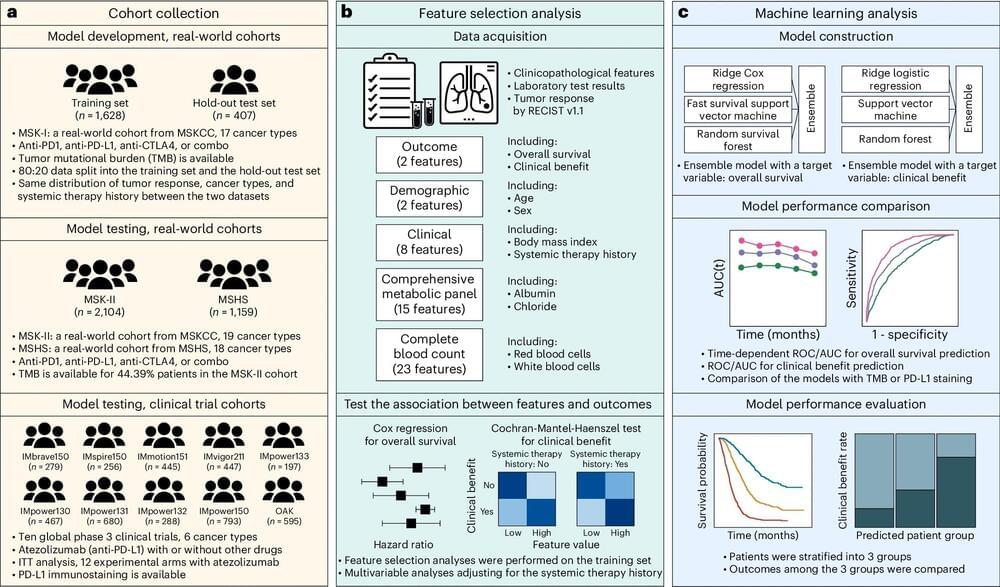
Doctors around the world may soon have access to a new tool that could better predict whether individual cancer patients will benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors—a type of immunotherapy—using only routine blood tests and clinical data.
The artificial intelligence–based model, dubbed SCORPIO, was developed by a team of researchers from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and the Tisch Cancer Institute at Mount Sinai.
The model is not only cheaper and more accessible, it’s significantly better at predicting outcomes than the two current biomarkers approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), according to findings published in Nature Medicine.