Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links/Affiliates: Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.u…
Category: biotech/medical – Page 317
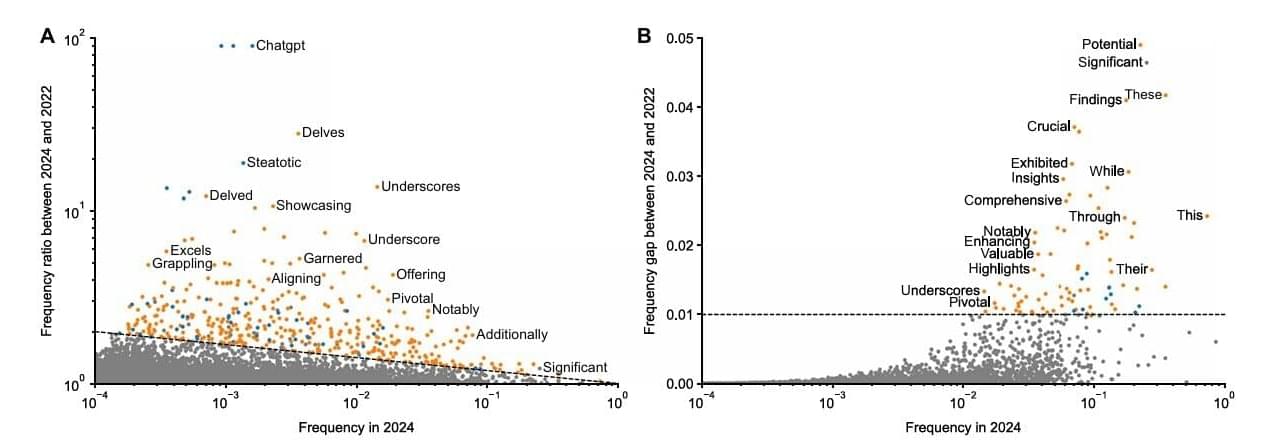
Massive study detects AI fingerprints in millions of scientific papers
Chances are that you have unknowingly encountered compelling online content that was created, either wholly or in part, by some version of a Large Language Model (LLM). As these AI resources, like ChatGPT and Google Gemini, become more proficient at generating near-human-quality writing, it has become more difficult to distinguish between purely human writing from content that was either modified or entirely generated by LLMs.
This spike in questionable authorship has raised concerns in the academic community that AI-generated content has been quietly creeping into peer-reviewed publications.
To shed light on just how widespread LLM content is in academic writing, a team of U.S. and German researchers analyzed more than 15 million biomedical abstracts on PubMed to determine if LLMs have had a detectable impact on specific word choices in journal articles.
AI Detects Hidden Lung Tumors Doctors Miss — And It’s Fast
Trained on multi-hospital data, iSeg spots moving tumors doctors sometimes miss, edging radiation treatment toward pinpoint perfection.
First large-scale stem cell bank enables worldwide studies on genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common, debilitating neurodegenerative disease affecting about 10% of people over the age of 65 and one third of people aged 85 and above. Besides environmental factors, the genes have a strong influence on whether or not a person develops AD during their lifetime.
Through genome sequencing of DNA from large groups of healthy people and people with AD, some naturally occurring small changes in the DNA, known as genetic variants, were found to be more frequent in AD patients than in healthy people.
As more and more of these AD-associated genetic “risk” variants are discovered, it is now possible to calculate a person’s individual polygenic risk score (PRS), meaning the likelihood of the person developing AD, with high accuracy.
Neuroscientist: Brain Surgery Can Create “Two Conscious Entities”
Christof’s idea that split brain patients have split consciousness doesn’t really make sense and doesn’t correspond to the evidence. Consciousness is metaphysically simple — that is, my thoughts and sense of self can’t be split with a knife like the brain or a material thing can be split. What would it mean to say that I have “split” consciousness? Instead of Mike, there would be Mike and Joe, which wouldn’t be “split,” it would just be two people.
A category error
‘Split consciousness’ is an oxymoron, a category error. Consciousness is not the kind of thing that can be split, and there’s no evidence that one person can ever become two people. It’s science fiction, not science.

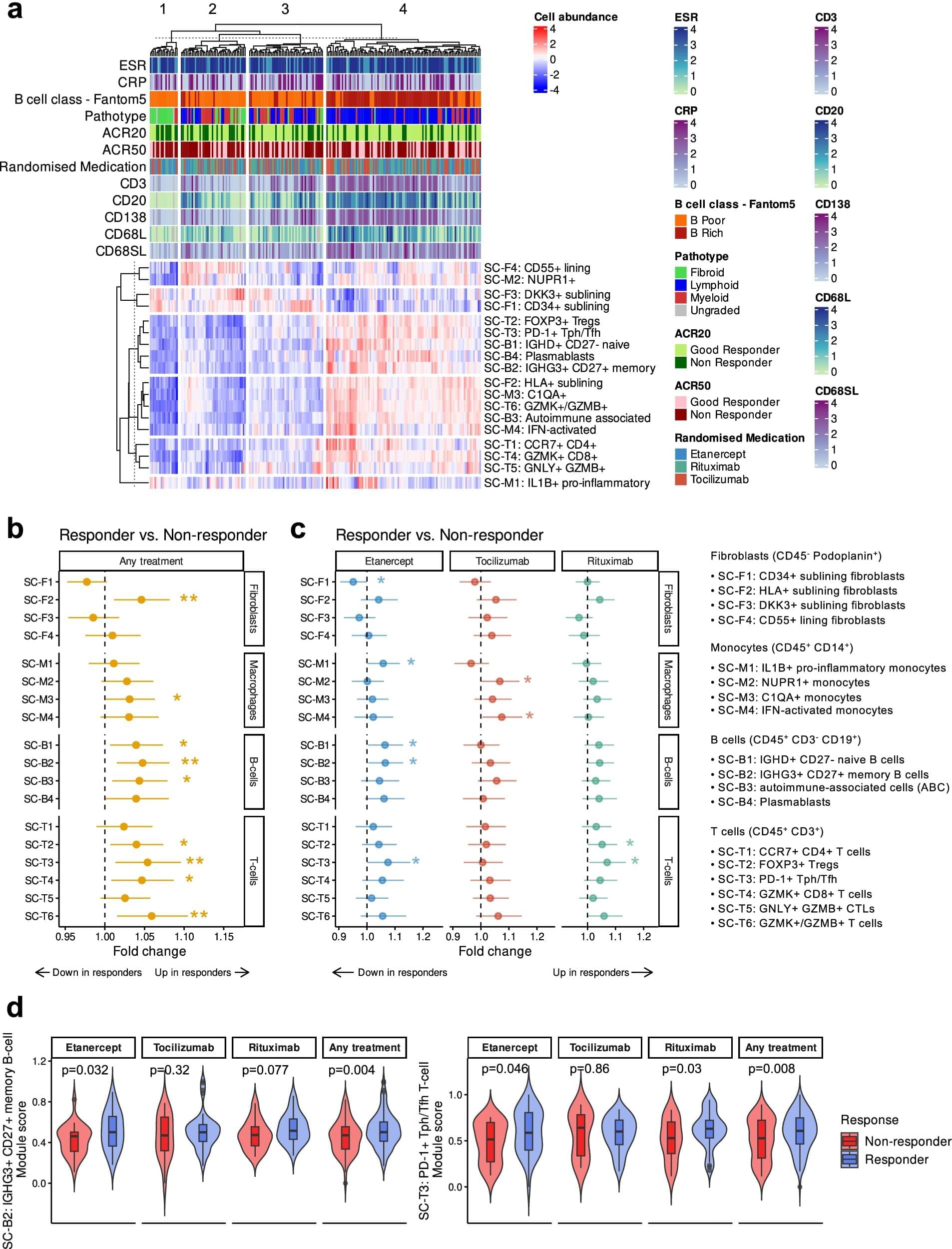
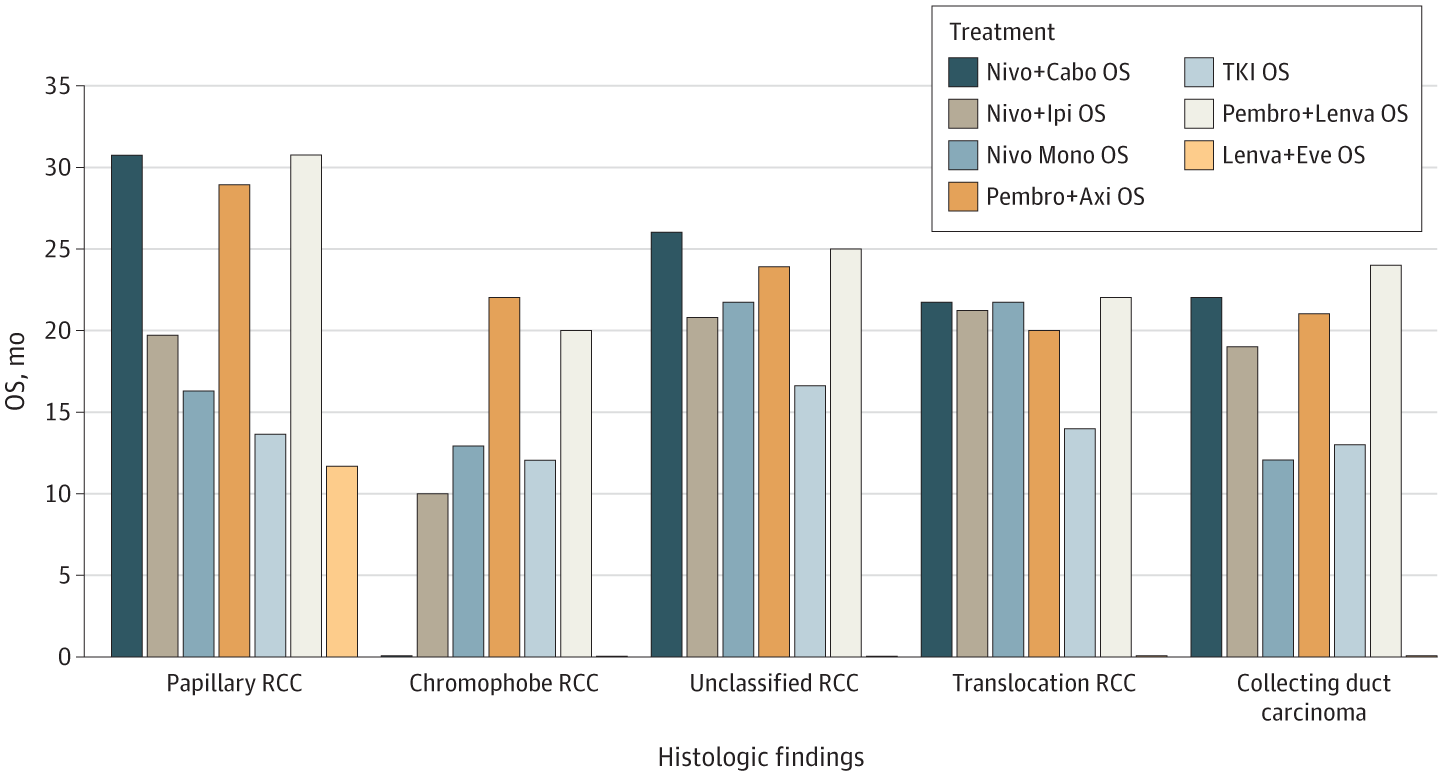
Clinical test predicts best rheumatoid arthritis treatment on first try
1 in 100 people in Britain today live with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Unlike osteoarthritis (OA), RA is caused not by wear and tear but by the body’s immune system attacking its own joints. RA can strike quickly at any age—but is most common for people aged 40–60.
Biological therapies are the leading treatment. Clinicians use engineered proteins made from living cells to slow the disease by targeting the specific parts of the immune system that are going rogue. Over the past 20 years they have led to major improvements in helping patients to live with RA.
However, different patients will react differently to different biological therapies depending upon their genetics. This means individual therapies have a failure rate of approximately 40%.

Natural compounds and strategies for fighting against drug resistance in cancer: a special focus on phenolic compounds and microRNAs
Bioactive phytochemicals, phenolic compounds, terpenoids, and alkaloids, exert antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antigenotoxic, and anticancer effects, simultaneously showing minimal or no toxicity on normal, healthy cells. Phytochemicals targeting various signaling pathways and multiple mechanisms underlying intrinsic and acquired multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells make them invaluable tools for the development of novel strategies for fighting against anticancer drug resistance in different types of cancer, which is one of the ultimate goals of modern oncology research. As MDR is described to be a simultaneous development of resistance to multiple drugs with different chemical structures, mechanisms of action, and targets it is not surprising that multiple factors, such as genetic and epigenetic changes, as well as noncoding RNAs, including microRNAs may significantly contribute to the development MDR in cancer cells, and its targeting and modulation of their expression to sensitize cells to treatment. This review implies that some natural compounds, such as curcumin, resveratrol, kaempferol, allicin, and quercetin, have the potential to interact with highly oncogenic and/or proinflammatory miRNAs, such as miR-21/155/663/146a, significantly influencing the response to cancer therapy. This article aims to point out how natural compounds may be used, accompanied by miRNAs mimics or miRNA inhibitors to treat specific types of cancer and its subtypes to overcome multidrug resistance. The main challenge is to determine the proper doses and concentrations of both miRNAs and compounds.