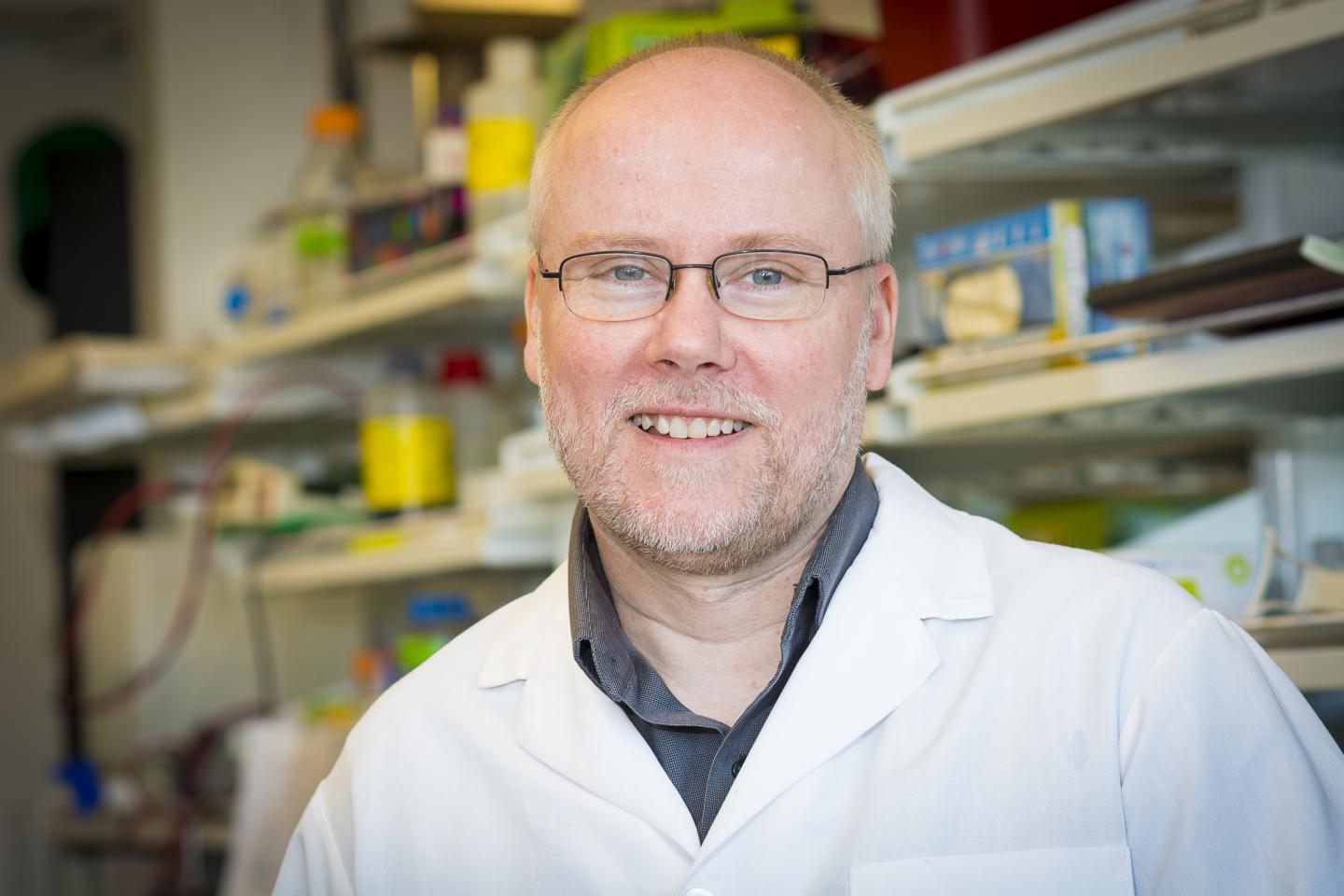
Our guest for this show is Aubrey de Grey, Ph.D., and he refuses to accept aging as something we can not change. Aubrey is a Biomedical Gerontologist and Chief Scientific Officer of The SENS Research Foundation. I talk more about his background and the SENS Foundation in the interview. Aubrey has put forth a model for aging based on seven types of damage that occur as a product of aging. We discuss this model and the techniques the possibly address each category of damage. This interview is longer than the other thus far but it had me gripped the entire time so enjoy!
MEDIA
Soundcloud :: https://soundcloud.com/humanOSRadio
ITunes :: https://goo.gl/SDAiNm
Stitcher :: https://goo.gl/LaERkp
YouTube Channel :: https://goo.gl/egvdpb
Image Credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aubrey_de_Grey