In biology textbooks and beyond, the human genome and DNA therein typically are taught in only one dimension. While it can be helpful for learners to begin with the linear presentation of how stretches of DNA form genes, this oversimplification undersells the significance of the genome’s 3D structure.
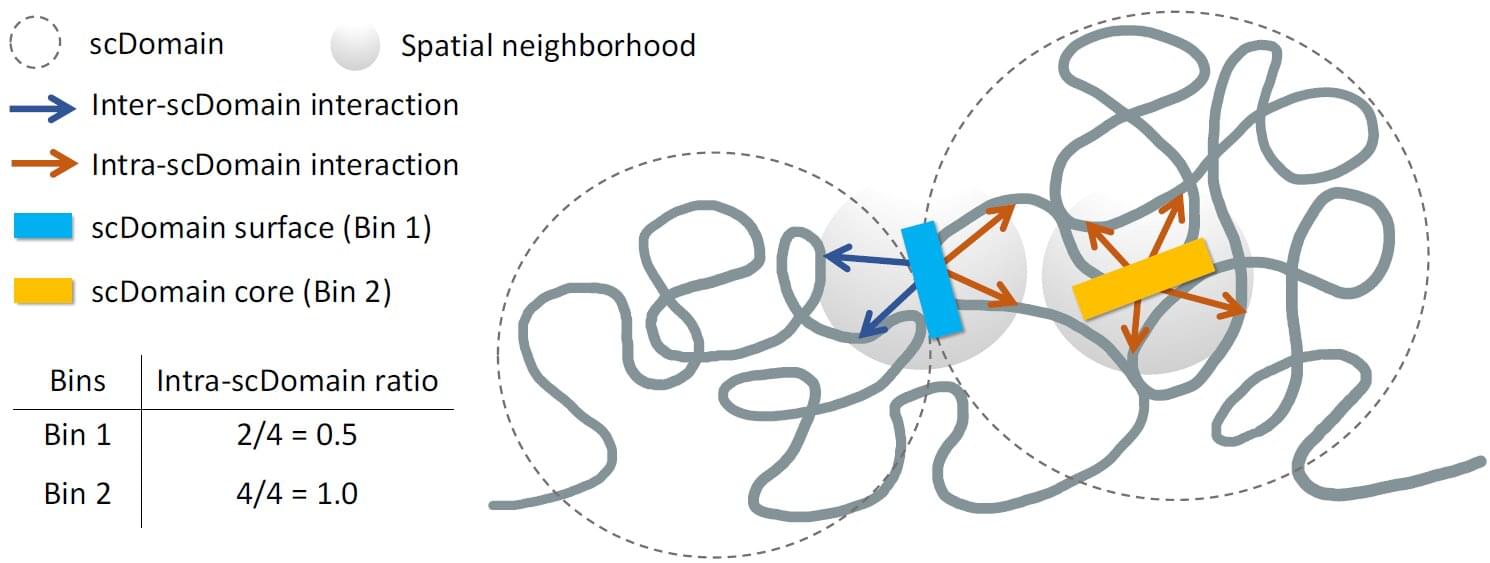
To fit in the nucleus of our cells, six feet of DNA is wound up like thread on protein spools called histones. In its packaged form called chromatin, coiled up DNA features many loops and clumps. While it may look random and messy to the untrained eye, these tumbleweed-like shapes bring certain genomic regions into close contact while sheltering others.
Problems with this 3D structure are associated with many diseases including developmental disorders and cancer. Almost 12% of genomic regions in breast cancer cells have incurred issues with their chromatin structure, while other structural issues are known to cause T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.