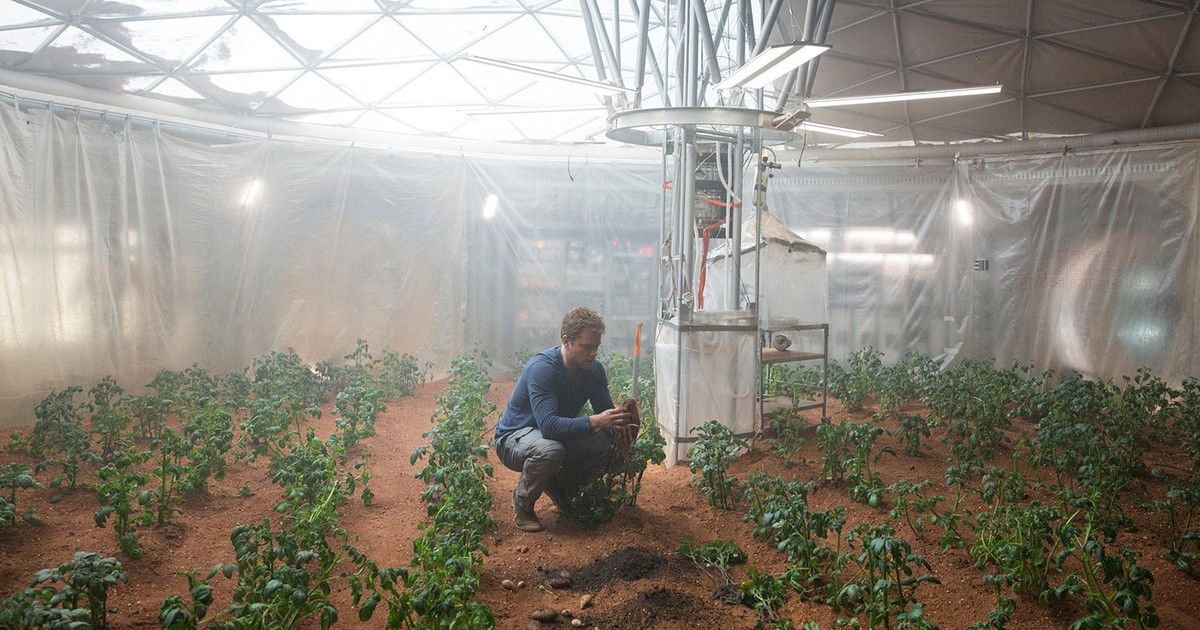
Just like checking your bag on a commercial airline, space travel comes with some pretty big weight restrictions. How big? According to estimates, reaching space costs a whopping $10,000 per pound, which means that every ounce saved has a big impact on the bottom line.
That’s where a group of Danish researchers comes in. The team is working on a synthetic biology project called CosmoCrops, which hopes to use bacteria to make it possible to 3D print everything needed for a respectable space mission, using a cutting-edge co-culturing system. And it could even make life better for those of us back on Earth in the process.
“We are trying to make space exploration cheaper, because many inventions we use in our daily life were invented because of space exploration, like Velcro and solar energy,” Joachim Larsen, one of the students working on the project, told Digital Trends. “The way we want to achieve this is to [be] able to produce everything from food to medicine and bioplastic for 3D printers out in space — making the space rocket a lot lighter.”