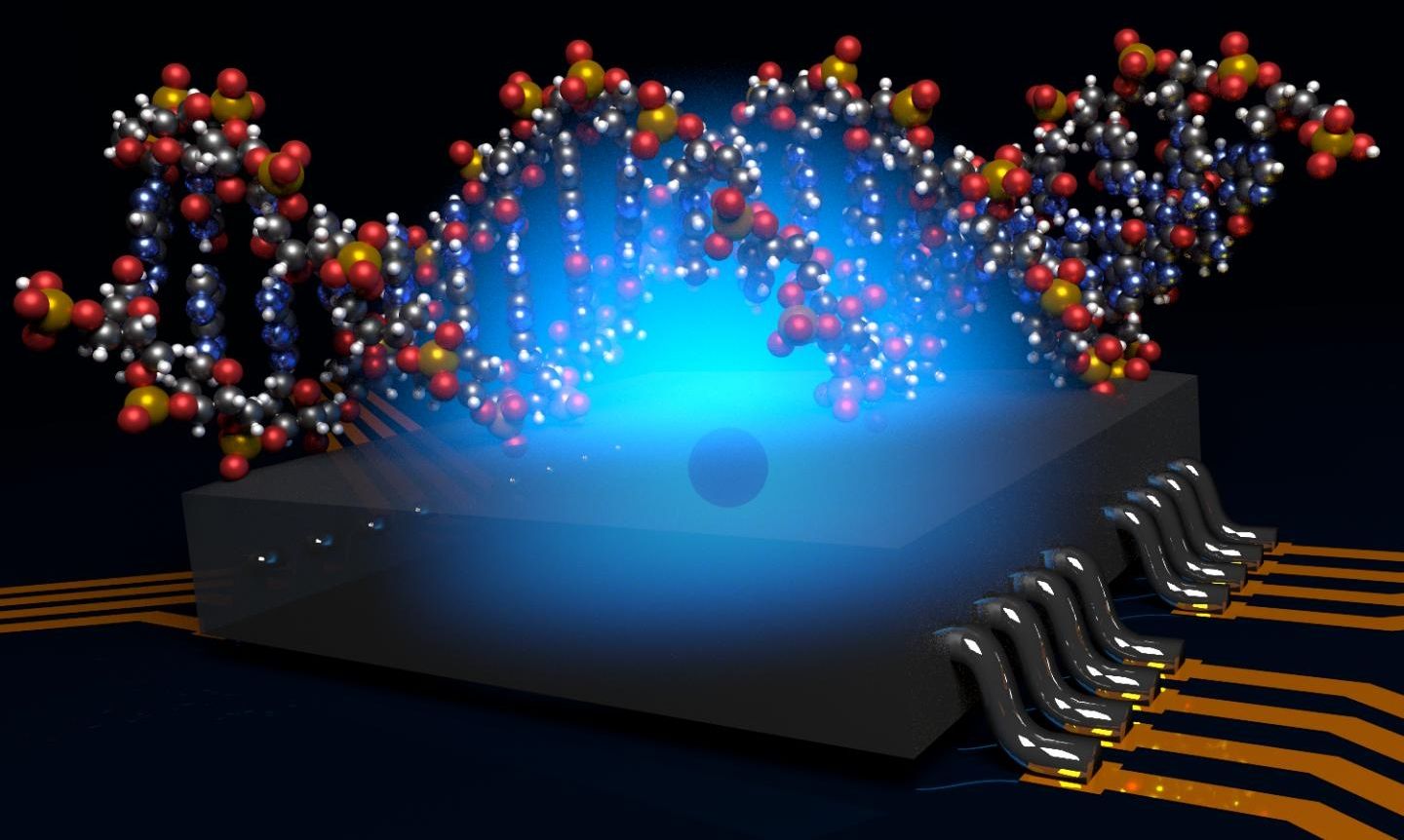
Researchers at the University of Melbourne have developed a way to radically miniaturise a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine using atomic-scale quantum computer technology.
Capable of imaging the structure of a single bio-molecule, the new system would overcome significant technological challenges and provide an important new tool for biotechnology and drug discovery.
The work was published today in Nature Communications, and was led by Prof Lloyd Hollenberg at the University of Melbourne, working closely with researchers at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T) to design the quantum molecular microscope.