We are learning more about fungal infection and neurological diseases. Recently we learned of gingival diseases and Alzheimer’s. My wonder is how plants such as Moringa in one’s diet, that have antifungal properties, can help.
Fungal infections are emerging as a major medical challenge, and a team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine has developed a mouse model to study the short-term consequences of fungal infection in the brain.
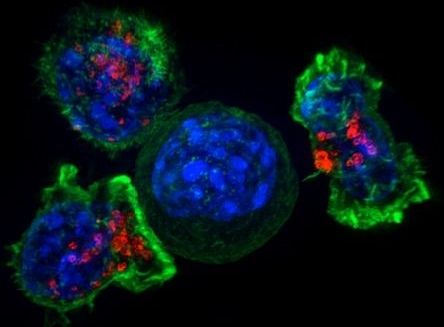
The researchers report in the journal Nature Communications the unexpected finding that the common yeast Candida albicans, a type of fungus, can cross the blood-brain barrier and trigger an inflammatory response that results in the formation of granuloma-type structures and temporary mild memory impairments in mice. Interestingly, the granulomas share features with plaques found in Alzheimer’s disease, supporting future studies on the long-term neurological consequences of sustained C. albicans infection.
“An increasing number of clinical observations by us and other groups indicates that fungi are becoming a more common cause of upper airway allergic diseases such as asthma, as well as other conditions such as sepsis, a potentially life-threatening disease caused by the body’s response to an infection,” said corresponding author Dr. David B. Corry, professor of medicine-immunology, allergy and rheumatology and Fulbright Endowed Chair in Pathology at Baylor College of Medicine.