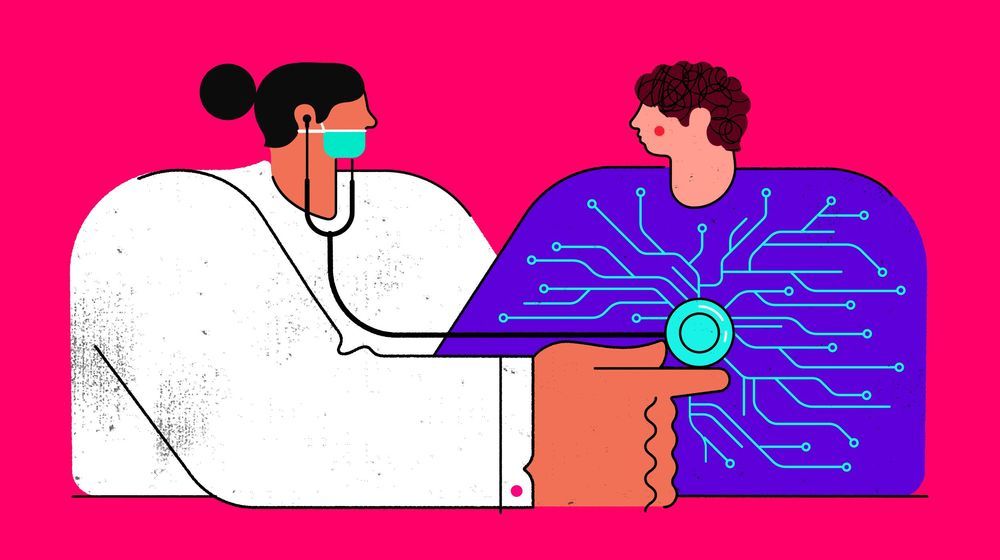
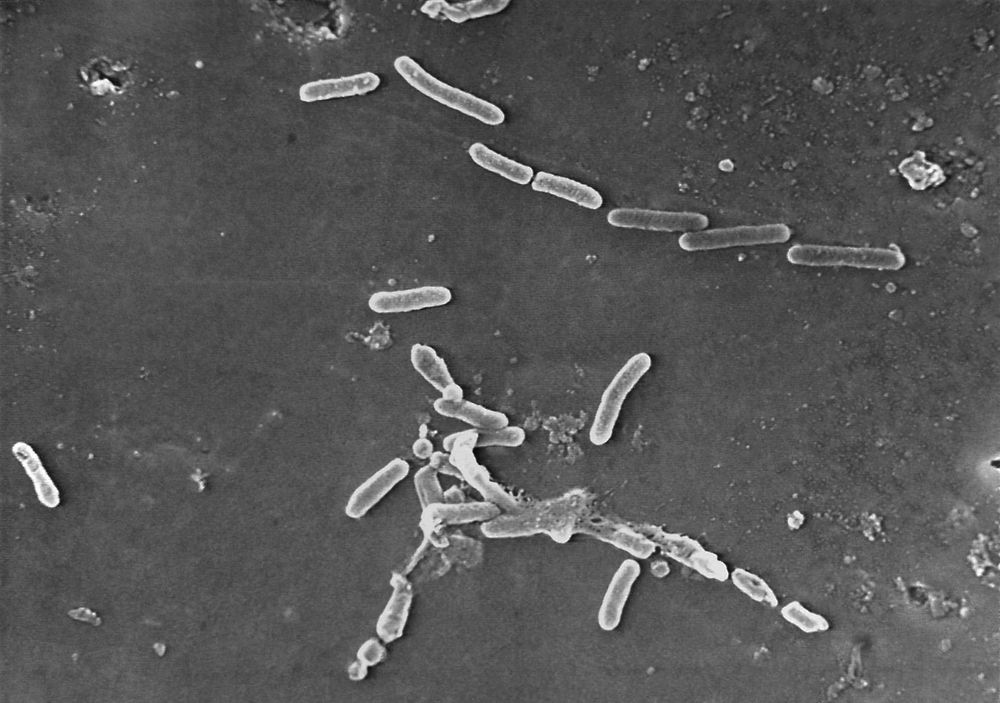
1. The 4 main things happening in Hyperbaric oxygen treatment: 1.- A decrease of inflammation 2.- An increase in the amount of oxygen in circulation and reversing hypoxia. 3.- Stimulate the release of stem cells from the brain along with the bone-derived stem cells. 4.- Kill infection. Why it matters for regenerative and dementia treatment? Listen to Dr. Scott Sherr explaining in detail in http://www.mendelhaim.com/podcast/2. For more information on Dr. Scott’s work go to https://www.hyperbaricmedicalsolutions.com/integrative-hbot/scott-sherr.
2. Raising money for academic research is a hard point, according to all of my guests, but even when we talk about Hyperbaric treatment there is a lack of money and the number of chambers declines in u.s. In Israel by the way, the demand is increasing and it takes a few months waiting in lines to start getting the treatment, this can turn into a big business opportunity in my opinion as to the risk for such research on participants is not as big as other medical research.
3. Longevity investment is a relatively new field and is lack of a method to invest by, the Three criteria that Sergey Young from the Longevity Vision Fund examine before investing in new companies are 1- will the product be affordable to touch millions of people’s lives and not only help the rich. 2- Looking for sectors that enjoy the technological exponential development paste such as AI, early diagnostics, stem cells, warbles, and organ transplants. 3 — Network, if you are a new startup and trying to raise from The Longevity vision fund, question yourself before, Do you have partners that can market your product such as big pharma or health care chain or a big manufacturer, do you collaborate with the best academic institutes in the longevity research. Go listen to the full episode Mission Alpha with Sergey Young on http://www.mendelhaim.com/podcast/3