CUTTING ROOM Scientists will soon wield the molecular scissors CRISPR/Cas9 in the human body. Some people with a form of inherited blindness will have the gene editor injected into their eyes, where researchers hope it will snip out a mutation.


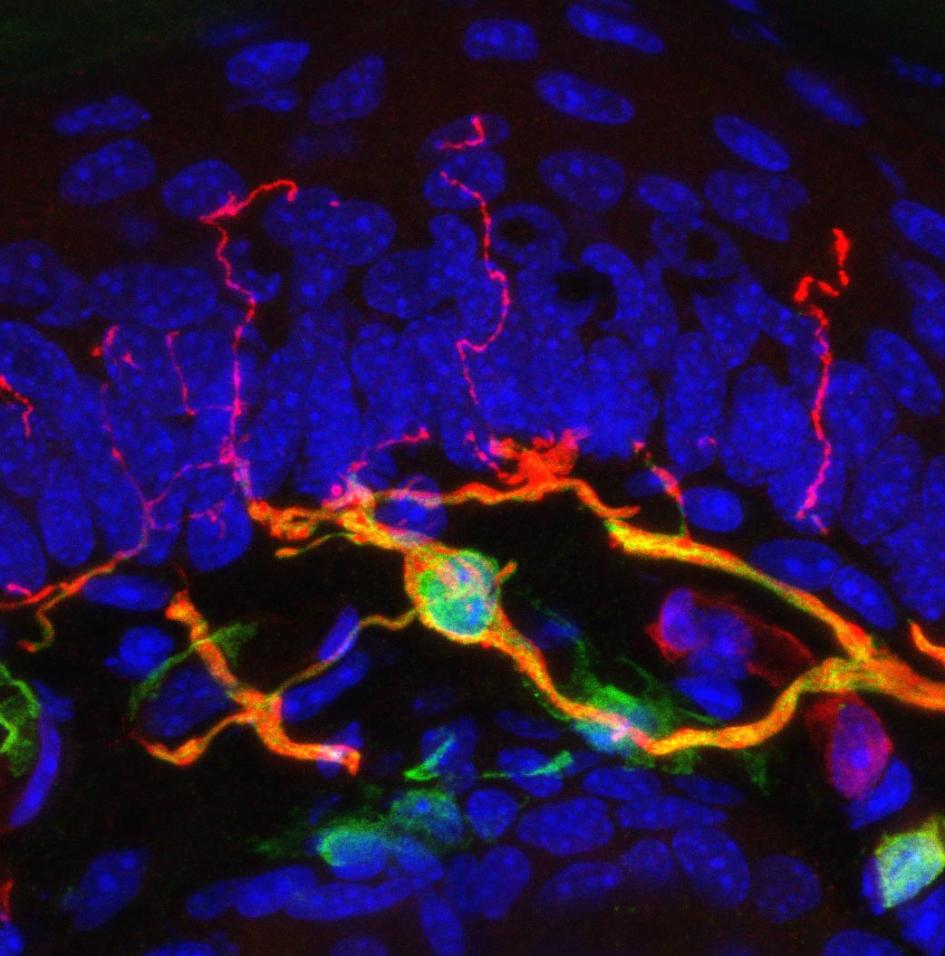
Most people who’ve been jabbed by a needle know the drill: First the pierce, then the sharp, searing pain and an urge to pull away, or at least wince. While the exact circuitry behind this nearly universal reaction is not fully understood, scientists may have just found an important piece of the puzzle: a previously unknown sensory organ inside the skin.
Dubbed the nociceptive glio-neural complex, this structure is not quite like the typical picture of a complex organ like the heart or the spleen. Instead, it’s a simple organ made up of a network of cells called glial cells, which are already known to surround and support the body’s nerve cells. In this case, the glial cells form a mesh-like structure between the skin’s outer and inner layers, with filament-like protrusions that extend into the skin’s outer layer. (Also find out about a type of simple organ recently found in humans, called the interstitium.)
As the study team reports today in the journal Science, this humble organ seems to play a key role in the perception of mechanical pain—discomfort caused by pressure, pricking, and other impacts to the skin. Until now, individual cells called nociceptive fibers were thought to be the main starting points for this kind of pain.
Dr. Michael West, CEO of AgeX Therapeutics and Founder of Geron Corporation, discusses breakthroughs in the understanding of biological regeneration and in induced tissue regeneration, through his talk “Hayflick Rewound: Somatic Restriction, Epigenetics, and the Reversibility of Human Aging”. This talk was given at the Ending Age-Related Diseases conference in NYC. Join us at http://lifespan.io/hero
►Conference Page: https://www.leafscience.org/ending-age-related-diseases-adva…prospects/
►Subscribe for more: https://www.youtube.com/user/LifespanIO?sub_confirmation=1
►This video is presented by LEAF. Please support our work by becoming a “Lifespan Hero”: http://lifespan.io/hero
► #LifeExtension #MichaelWest #AgeX
Today, we want to highlight a recent study in which a team of researchers from UT Southwestern demonstrates how adjusting the gut microbiome in mice lowers the occurrence of cancer.
What is the gut microbiome?
The microbiome describes a varied community of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that inhabit our gut. The four bacterial phyla of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria make up around 98% of the intestinal microbiome.

Heart & Diabetes Conference is delighted to welcome you at the “International Conference on Heart & Diabetes” scheduled on August 19–20, 2019 at Osaka, Japan based on the Theme “Innovations Of New Treatment In Diabetes & Heart Diseases”.
Heart & Diabetes Conference 2019 targets to carry out multidisciplinary research in Diabetes & Heart Diseases. Our main motto is to highlight the innovative treatments which are involved for cure of these Diseases.
August 19 (Monday) — 20 (Tuesday)