MaraGen Aims to Detoxify the Body from Pathogens & Harmful Substances. It Is an Alternative Medicine for Incurable Diseases.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,647

The Heterogeneity of Senescent Cells
Cellular senescence, discovered in 1961 by Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead, is a state in which cells no longer perform their functions, instead emitting harmful chemicals that turn other cells senescent. Senescence is primarily caused by telomere shortening and DNA damage, and senescent cells are known to contribute to multiple diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and dementia.
One method of removing senescent cells is caloric restriction, which is a temporary reduction of food calories. This has been shown to be one of the most effective methods to decrease and slow the onset of aging phenotypes [1].
This is related to autophagy, which is the cell’s natural method of breaking down parts of itself when it doesn’t have immediate access to food [2]. Autophagy has been shown to both promote and prevent senescence. It removes damaged macromolecules or organelles, such as mitochondria, which would otherwise cause cellular senescence. However, some of the processes that cause autophagy cause cellular senescence as well [3].


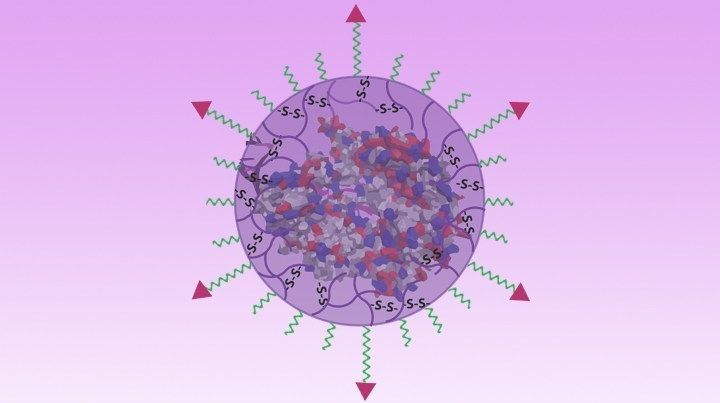
Nano-Sized Solution for Efficient and Versatile CRISPR Gene Editing
If used to make non-heritable genetic changes, CRISPR gene-editing technology holds tremendous promise for treating or curing a wide range of devastating disorders, including sickle cell disease, vision loss, and muscular dystrophy. Early efforts to deliver CRISPR-based therapies to affected tissues in a patient’s body typically have involved packing the gene-editing tools into viral vectors, which may cause unwanted immune reactions and other adverse effects.
Now, NIH-supported researchers have developed an alternative CRISPR delivery system: nanocapsules. Not only do these tiny, synthetic capsules appear to pose a lower risk of side effects, they can be precisely customized to deliver their gene-editing payloads to many different types of cells or tissues in the body, which can be extremely tough to do with a virus. Another advantage of these gene-editing nanocapsules is that they can be freeze-dried into a powder that’s easier than viral systems to transport, store, and administer at different doses.
In findings published in Nature Nanotechnology [1], researchers, led by Shaoqin Gong and Krishanu Saha, University of Wisconsin-Madison, developed the nanocapsules with specific design criteria in mind. They would need to be extremely small, about the size of a small virus, for easy entry into cells. Their surface would need to be adaptable for targeting different cell types. They also had to be highly stable in the bloodstream and yet easily degraded to release their contents once inside a cell.
Uhh, Part of the Facility Where Russia Stores Smallpox and Ebola Exploded
блядь! An explosion at Russia’s State Research Centre of Virology and Biotechnology (Vector) resulted in a fire, glass blown out throughout the building, and one worker suffering third degree burns on Monday, according to the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists. Vector is one of the only two places in the world where live smallpox virus samples are officially stored, as well as retains stocks of other deadly pathogens including the Ebola virus and anthrax spores.
According to the state-run TASS news agency, Koltsovo city head administrator Nikolai Krasnikov said that the blast occurred during scheduled repair work, blowing out glass in the building and starting a 30 square meter fire. Various reports have indicated the incident started with a gas explosion. However, Krasnikov emphasized that no biohazardous materials were stored where the explosion and blaze occurred, and that there is no threat to the general population. The Vector building in question did not suffer structural damage, Krasnikov added, while the worker is in “intensive” condition.

An Interview with Prof. S. Jay Olshansky
Prof. S. Jay Olshansky is a Professor of the School of Public Health at the University of Illinois at Chicago, Research Associate at the Center on Aging at the University of Chicago and at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and Chief Scientist at Lapetus Solutions, Inc. He has received multiple scientific awards, including the Irving S. Wright Award from the American Federation for Aging Research.
Prof. Olshansky is the co-author of multiple papers related to epidemiology and population, and the areas of his current research include estimates of the upper limits to human longevity, opportunities and challenges related to population aging, how morbidity changes over time, and forecasts of the size and age demographics of the population with and without medicines that address the underlying mechanisms of aging.
We had the opportunity to interview Prof. Olshansky at International Perspectives in Geroscience, a conference hosted at Weizmann Institute of Science (Israel) on September 4–5.
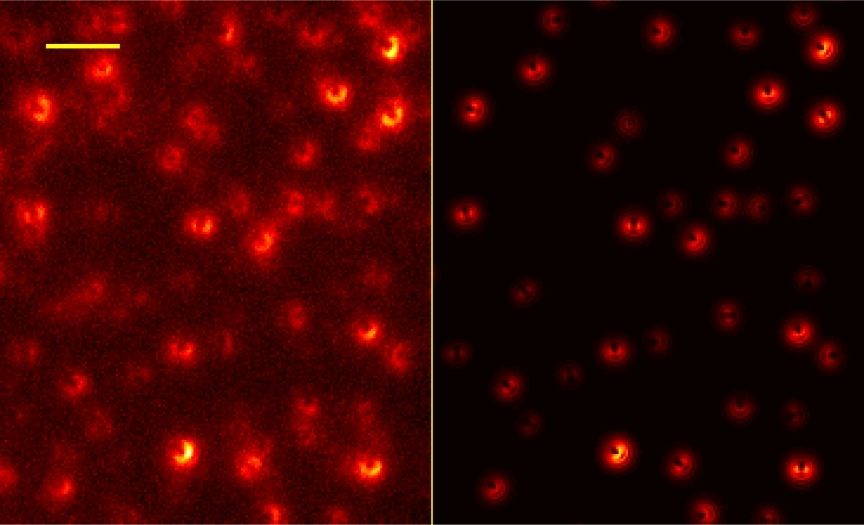
Graphene boosts microscope resolution by a factor of 10
Sub-nanometre resolution in 3D position measurements of light-emitting molecules has been achieved by physicists in Germany. Jörg Enderlein and colleagues at the University of Göttingen achieved the result by replacing metal films used in previous super-resolution techniques with single layers of graphene. Their innovation could allow researchers in a wide variety of fields to measure molecular positions to unprecedented degrees of accuracy.
Recently, the technique of single-molecule localization super-resolution microscopy (SMLM) has become an incredibly useful tool for researchers in fields ranging from fundamental physics to medical research. By analysing images of single light-emitting molecules, researchers can pinpoint the positions of their centres to within single atomic widths. However, SMLM faces one significant shortcoming: it can only locate molecules in 2D, giving no information about their positions along the out-of-plane axis.
This problem can be partially overcome through the technique of metal-induced energy transfer (MIET), which introduces a thin metal film to the setup. The idea is that the apparatus picks up changes in the molecule’s fluorescence that are caused by the molecule coupling to collective excitations of surface plasmons in the film. Since this light emission varies with distance from the film, researchers can use MIET to calculate the molecule’s distance relative to the film surface, allowing them to locate it along the third axis. Yet with current versions of the technique, the accuracy of this out-of-plane measurement is 3–5 times worse than that of lateral localization, in the plane of the film.