I don’t remember what it feels like to live without pain. At 15, I began feeling aching, stabbing, and burning sensations in my lower back and down my legs. Swallowing a few Aleve didn’t help—in fact, nothing did. If I sit or stand for any period of time, or lift something heavy or fall, I pay for it, sometimes for weeks or months. I’ve slept on the kitchen linoleum, because the carpet felt too soft to stand.
For 17 years, I went to doctor after doctor, undergoing scans, physical therapy, and just about every “alternative” treatment that promised relief. Despite some amazing doctors and the expensive tests at their disposal, they could never see anything wrong, so I never got a diagnosis.
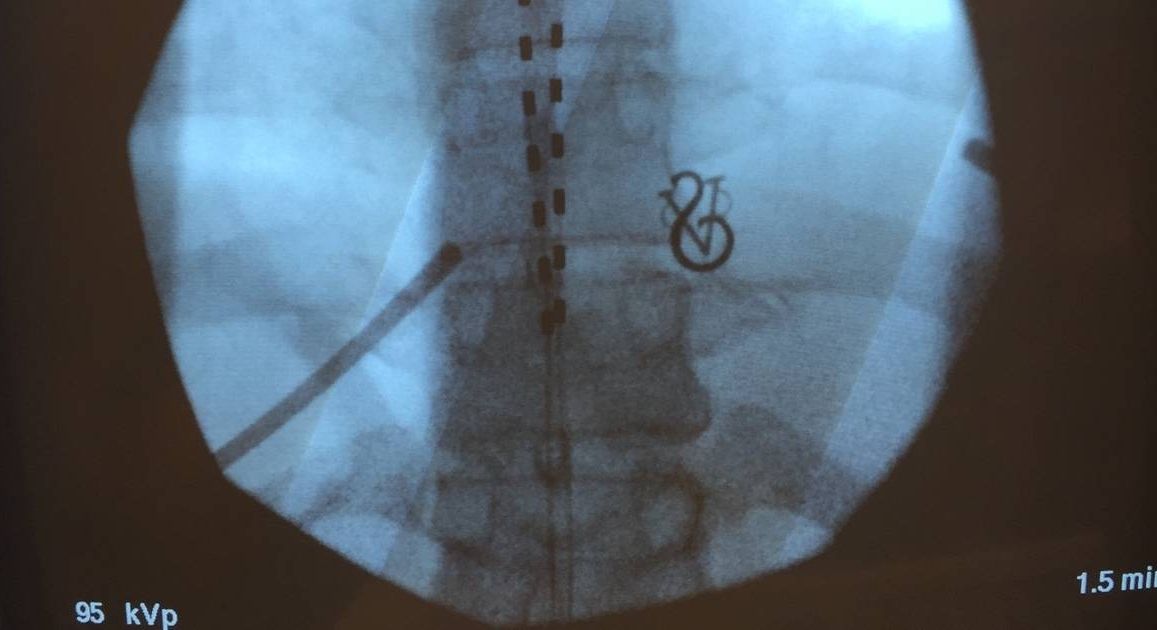
That is, until a couple of years ago, when a routine CAT scan finally caught a structural problem with my spine. Because of that, I qualified to have a spinal cord stimulator, an electronic device used to treat chronic pain, implanted into my back. Although I was scared to go under the knife, I was more than willing to become a cyborg in order to find even partial relief. And this type of therapy might also be able to help some of the 100 million Americans who suffer from chronic pain.