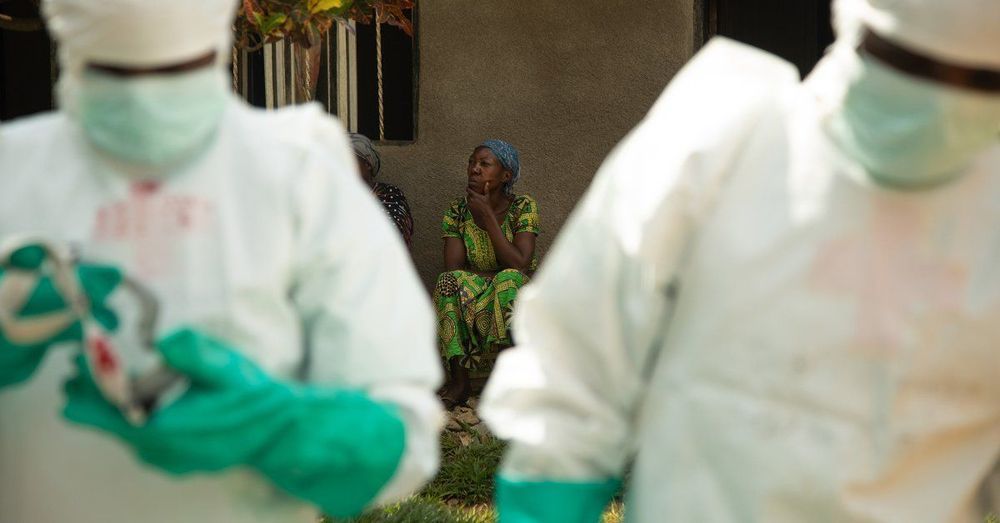
On the frontlines of the Ebola response are local Congolese workers with temporary job contracts. They are often driven into this work by economic necessity, as well as a desire to help.
Belinda Landu, a tall 28-year-old with long hair who radiates confidence, was making a meager living as a tailor in capital city Kinshasa before the outbreak. While visiting her mother in Beni last August, she spotted an advertisement for a health promoter. Today, she’s passionate about her role: decontaminating the houses of confirmed Ebola patients. “I want to stop the spread of the epidemic,” she said. “My family understand I work here to help people. If we get Ebola people will help us too.”
When she arrives at the scene of a recent diagnosis, Landu changes into a full protective outfit, including a full plastic bodysuit, mask, hairnet, gumboots, and both latex and rubber gloves, and begins the slow process of covering everything — inside and outside a house — with a chlorinated spray. Locals gather around to stare at her. They’re often terrified, she says, though she tries to be kind — speaking to them before she starts, and even stopping to play soccer with children after she changes out of her outfit.