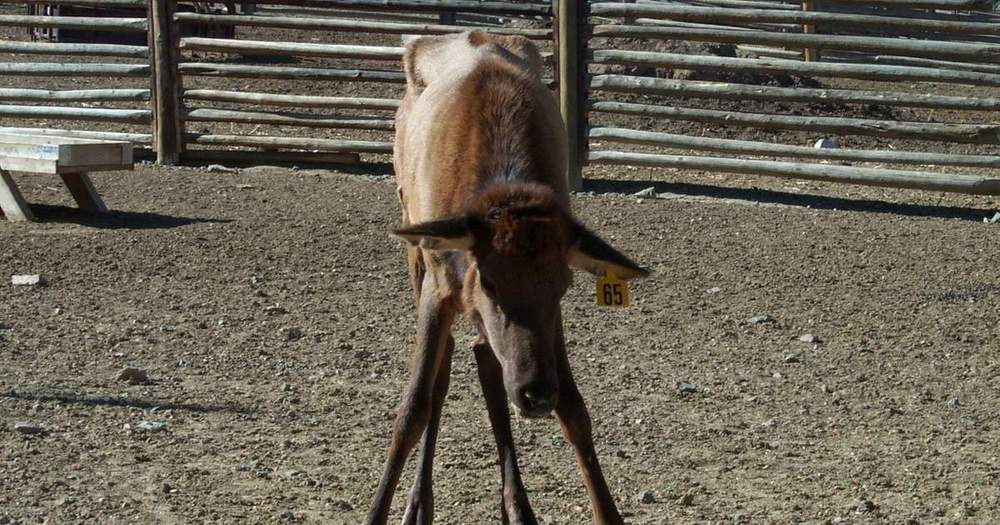
If you’ve heard of “zombie deer,” you’ve heard of the horrors of chronic wasting disease. CWD causes infected animals to stumble through the forest, sometimes drooling and becoming aggressive towards humans they once feared. They lose weight. They’re listless. The spookiest thing about it, though, isn’t its resemblance to zombie-dom—it’s the fact that it’s an incurable prion disease.
Prions are misfolded proteins that are somehow infectious (we’re still not really sure how or why) and for which we have no treatments or cures. If you were to catch one, you’d basically deteriorate over the course of several months, possibly losing the ability to speak or move, and eventually you would die. Doctors wouldn’t be able to do anything to save you.
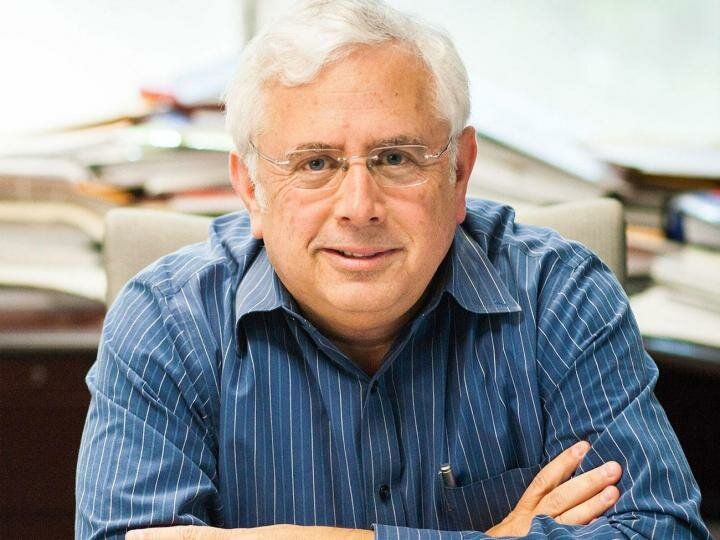
Right now, CWD appears limited to deer, moose, and elk. But University of Minnesota researchers warned local lawmakers this week that we should be taking action now to prevent the potential spread to humans. Michael Osterholm, director of the university’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Prevention, testified that “It is my best professional judgment based on my public health experience and the risk of BSE transmission to humans in the 1980s and 1990s and my extensive review and evaluation of laboratory research studies … that it is probable that human cases of CWD associated with the consumption of contaminated meat will be documented in the years ahead. It is possible that number of human cases will be substantial and will not be isolated events,” according to the Pioneer Press.